Activation Energy Drawing
Activation Energy Drawing - E a = activation energy. Web the activation energy shown in the diagram below is for the forward reaction (reactants → products), which is exergonic. The higher the energy hill, the slower the reaction. At the very top of the energy barrier, the reaction is at its transition state (ts), which is the point at which the bonds are in. Web the potential energy diagrams for a reaction with (a) δe < 0 and (b) δe > 0 illustrate the change in the potential energy of the system as reactants are converted to products. Web a physical or chemical process can be represented using an energy diagram, which shows how the potential energy of the initial state relates to the potential energy of the final state. The activation energy (e a) of a reaction is measured in kilojoules per mole (kj/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). When drawing a reaction profile, we should be able to label the relative energies of the reactants as compared to the products. At the very top of the energy barrier, the reaction is at its transition state (ts), which is the point at which the bonds are in. Web the activation energy is what determines the kinetics of a reaction: At the very top of the energy barrier, the reaction is at its transition state (ts), which is the point at which the bonds are in. The activated complex is an unstable, intermediate product that is formed during the reaction. Web the activation energy is what determines the kinetics of a reaction: At the very top of the energy barrier,. Web the activation energy is what determines the kinetics of a reaction: Draw and label two short horizontal lines to mark the energies of the reactants and products. Web the activation energy is what determines the kinetics of a reaction: Even exothermic reactions, such as burning a candle, require energy input. Web in the arrhenius model of reaction rates, activation. Some reactions occur readily at room temperature because the reacting particles already have the requisite activation energy at that temperature. In both cases, ea e a is positive. In this video, i go over how to properly label and explain a reaction mechanism diagram which. At the very top of the energy barrier, the reaction is at its transition state. Web 6/02 base your answers on the information and diagram below, which represent the changes in potential energy that occur during the given reaction. Web in the arrhenius model of reaction rates, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be available to reactants for a chemical reaction to occur. Web exothermic energy diagram: An enzyme or catalyst. The formula used to find the value of activation energy, e a is; Web exothermic energy diagram: Even exothermic reactions, such as burning a candle, require energy input. The higher the energy hill, the slower the reaction. (jerry crimson mann, cc 3.0) effect of enzymes and catalysts a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction. Draw and label two short horizontal lines to mark the energies of the reactants and products. Once the reaction has obtained this amount of energy, it must continue on. Draw and label a pair of axes. Web many chemical reactions have mechanisms that consist of multiple elementary steps. The energy profile can also be used to determine the overall change. The higher the energy hill, the slower the reaction. Taking log on both sides. The higher the energy hill, the slower the reaction. Graphical determination of ea example plot algebraically the activation energy can also be calculated algebraically if k is known at two different temperatures: Web in a diagram, activation energy is graphed as the height of an energy. Draw and label two short horizontal lines to mark the energies of the reactants and products. Web the activation energy shown in the diagram below is for the forward reaction (reactants → products), which is exergonic. R = gas constant = 8.34j/k/mol =8.314/1000 kj/k/mol = 2 cal/k/mol = 0.0821 lit atm/k/mol. There must be a hump in the curve to. There must be a hump in the curve to represent the energy level of the activated complex. Web in a diagram, activation energy is graphed as the height of an energy barrier between two minimum points of potential energy. When drawing a reaction profile, we should be able to label the relative energies of the reactants as compared to the. Web 6/02 base your answers on the information and diagram below, which represent the changes in potential energy that occur during the given reaction. Graphical determination of ea example plot algebraically the activation energy can also be calculated algebraically if k is known at two different temperatures: If the reaction were to proceed in the reverse direction (endergonic), the transition. Web drawing reaction profiles reaction profiles show relative energies. Web many chemical reactions have mechanisms that consist of multiple elementary steps. Label the vertical axis potential energy and the horizontal axis reaction coordinate. Web 6/02 base your answers on the information and diagram below, which represent the changes in potential energy that occur during the given reaction. The energy profile can also be used to determine the overall change in energy for the reaction. Web the potential energy diagrams for a reaction with (a) δe < 0 and (b) δe > 0 illustrate the change in the potential energy of the system as reactants are converted to products. The higher the energy hill, the slower the reaction. Web a physical or chemical process can be represented using an energy diagram, which shows how the potential energy of the initial state relates to the potential energy of the final state. At the very top of the energy barrier, the reaction is at its transition state (ts), which is the point at which the bonds are in. Web exothermic energy diagram: When drawing a reaction profile, we should be able to label the relative energies of the reactants as compared to the products. Web the activation energy is what determines the kinetics of a reaction: The higher the energy hill, the slower the reaction. Web the activation energy is what determines the kinetics of a reaction: An enzyme or catalyst lowers the activation energy. Web the activation energy (\(e_a\)), labeled \(\delta{g^{\ddagger}}\) in figure 2, is the energy difference between the reactants and the activated complex, also known as transition state.
Activation energy vector illustration example diagram Physics and

Activation Energy Definition, Formula, SI Units, Examples, Calculation
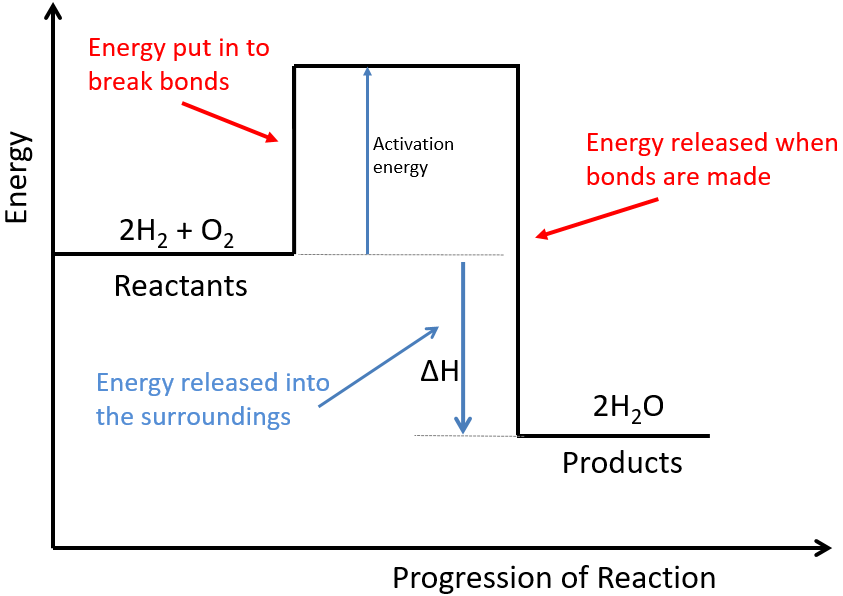
314 (Triple only) draw and explain reaction profile diagrams showing
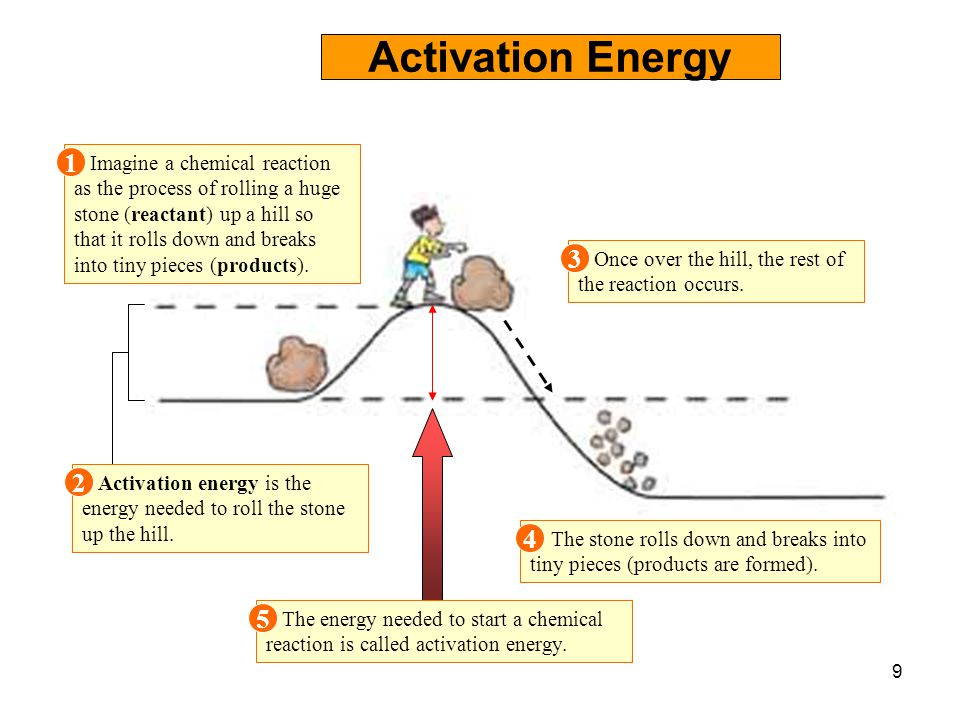
Activation Energy The Secret to Getting Started and Getting Finished
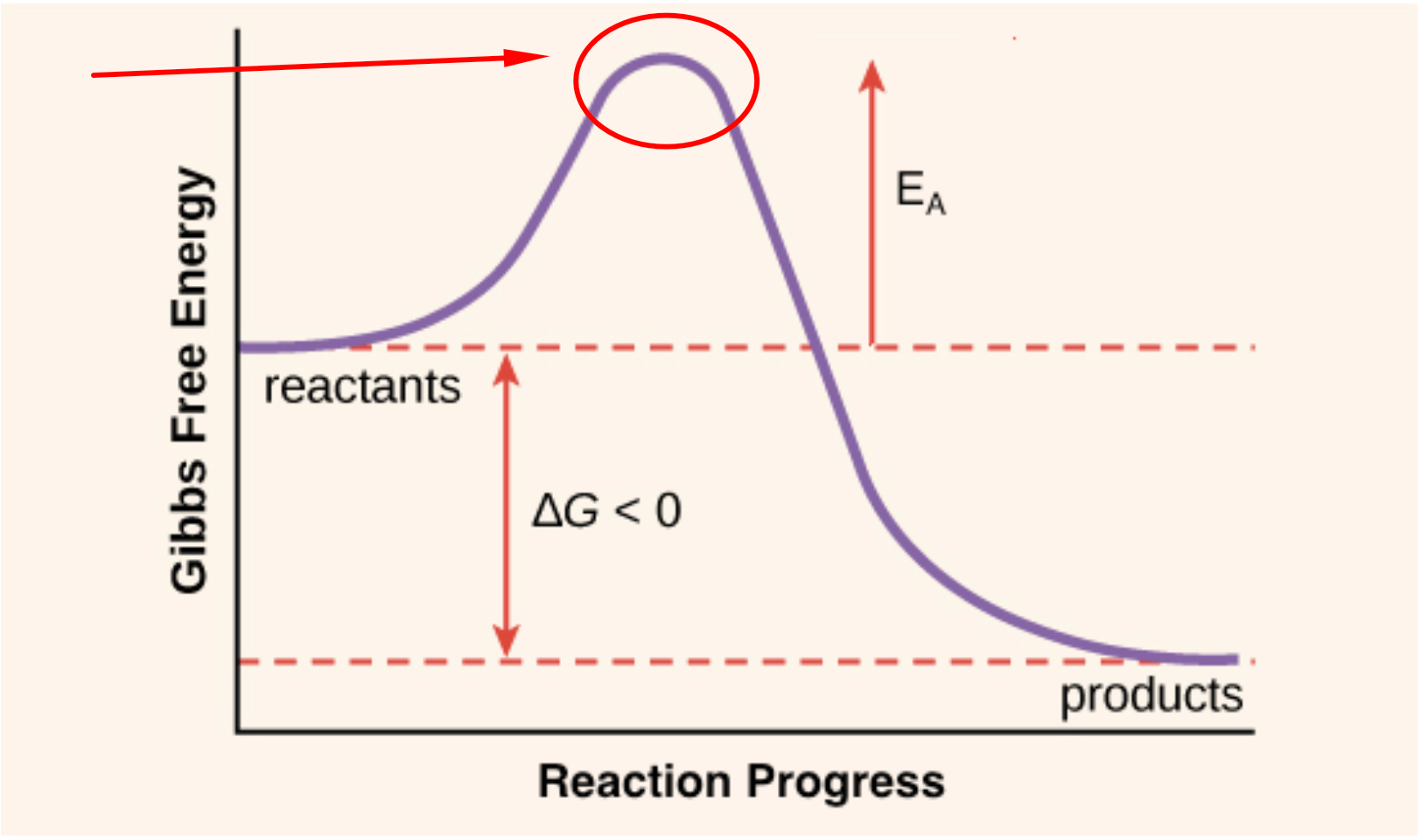
Activation Energy The Secret to Getting Started and Getting Finished

Enzymes Lower The Activation Energy Of A Reaction btccasting
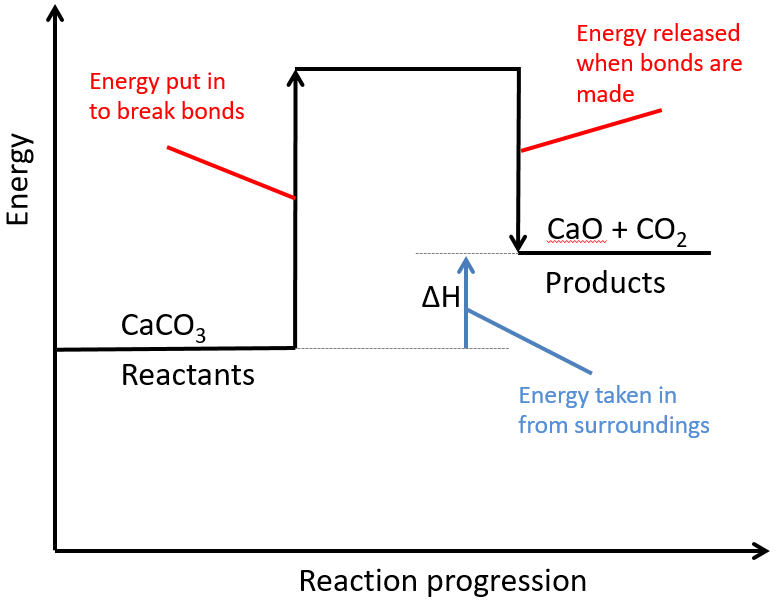
314 (Triple only) draw and explain reaction profile diagrams showing
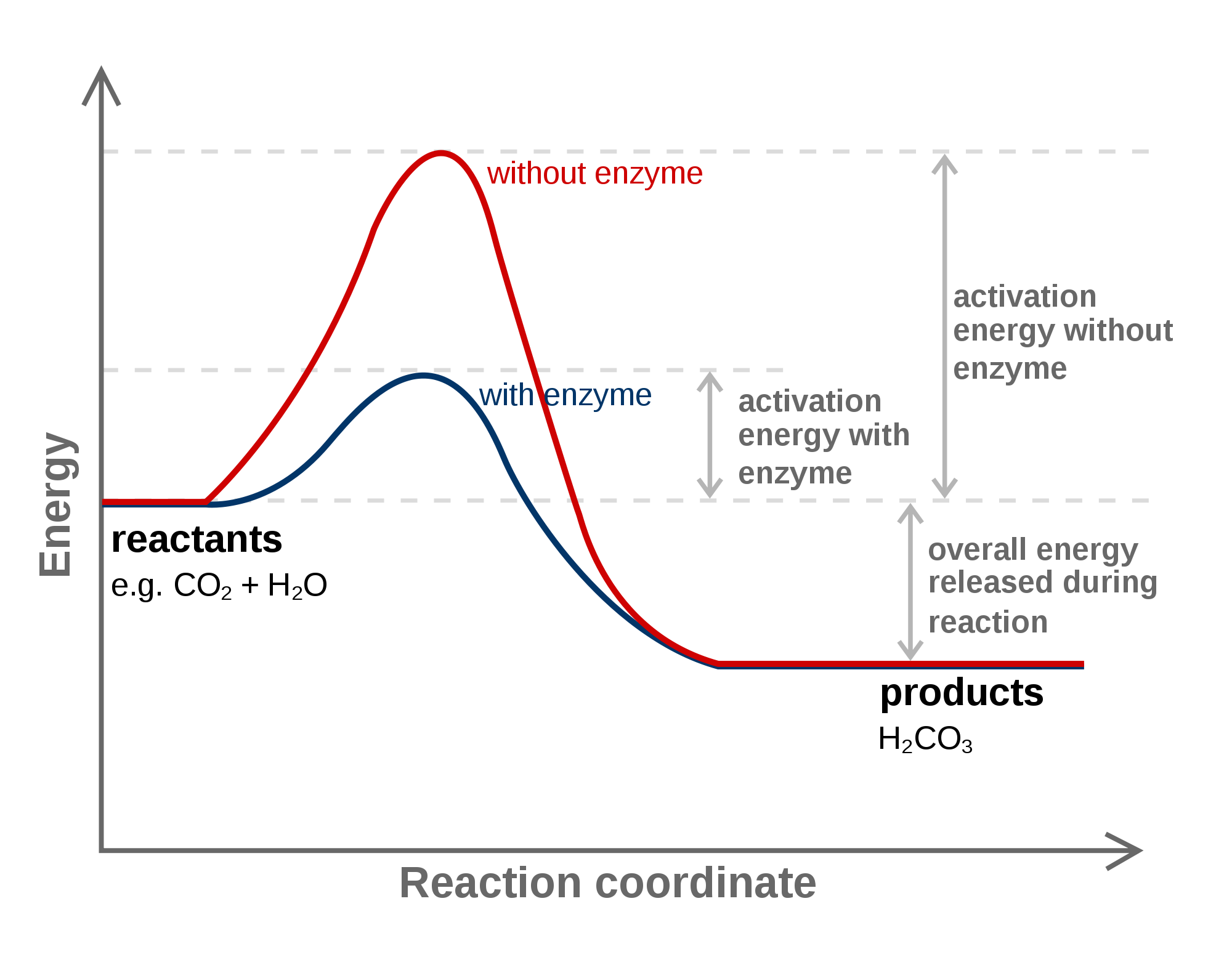
What are activation energies? Socratic

Energy Diagram — Overview & Parts Expii
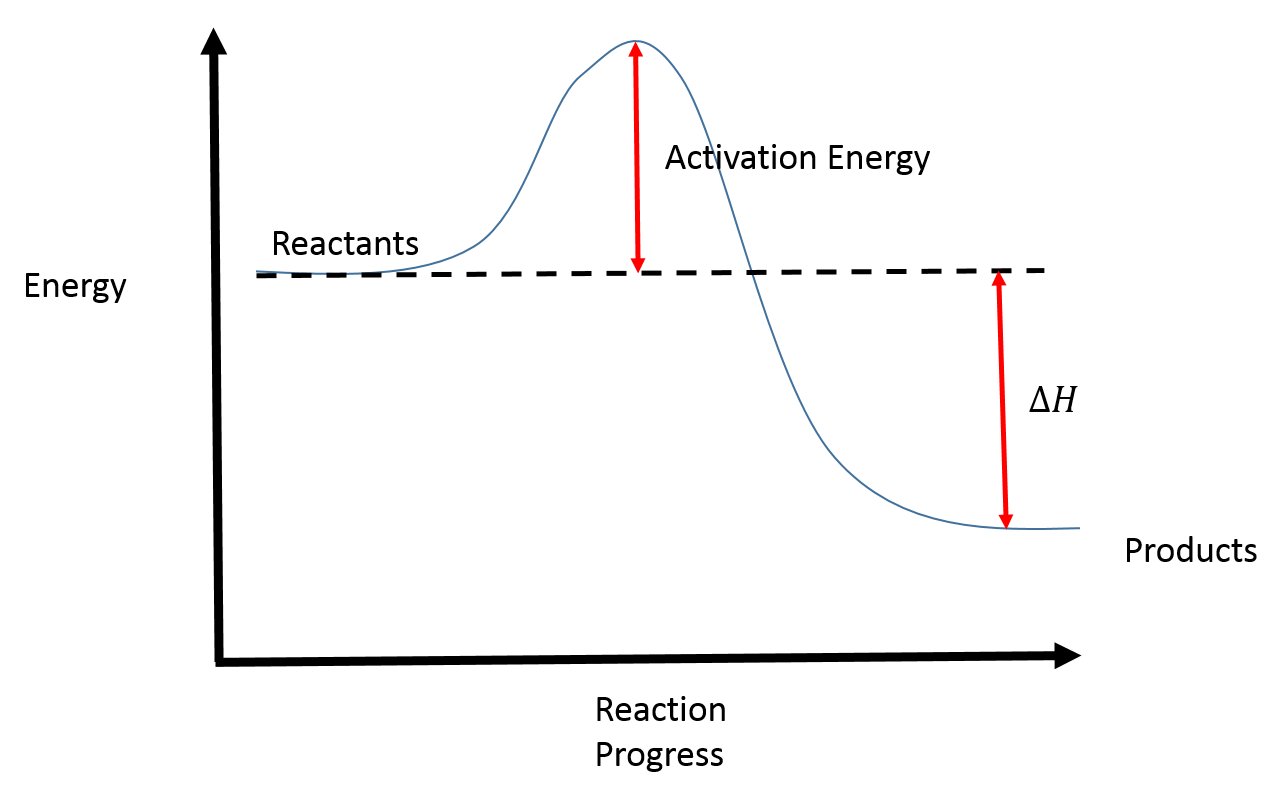
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams College Chemistry
Web In The Arrhenius Model Of Reaction Rates, Activation Energy Is The Minimum Amount Of Energy That Must Be Available To Reactants For A Chemical Reaction To Occur.
Some Reactions Occur Readily At Room Temperature Because The Reacting Particles Already Have The Requisite Activation Energy At That Temperature.
Web The Energy Difference Between Reactants And The Transition State Is Called The Activation Energy, Δg‡, And Determines How Rapidly The Reaction Occurs At A Given Temperature.
Web The Activation Energy For A Reaction Is The Minimum Energy That Colliding Particles Must Have In Order To Undergo A Reaction.
Related Post: