Cerebral Cortex Drawing
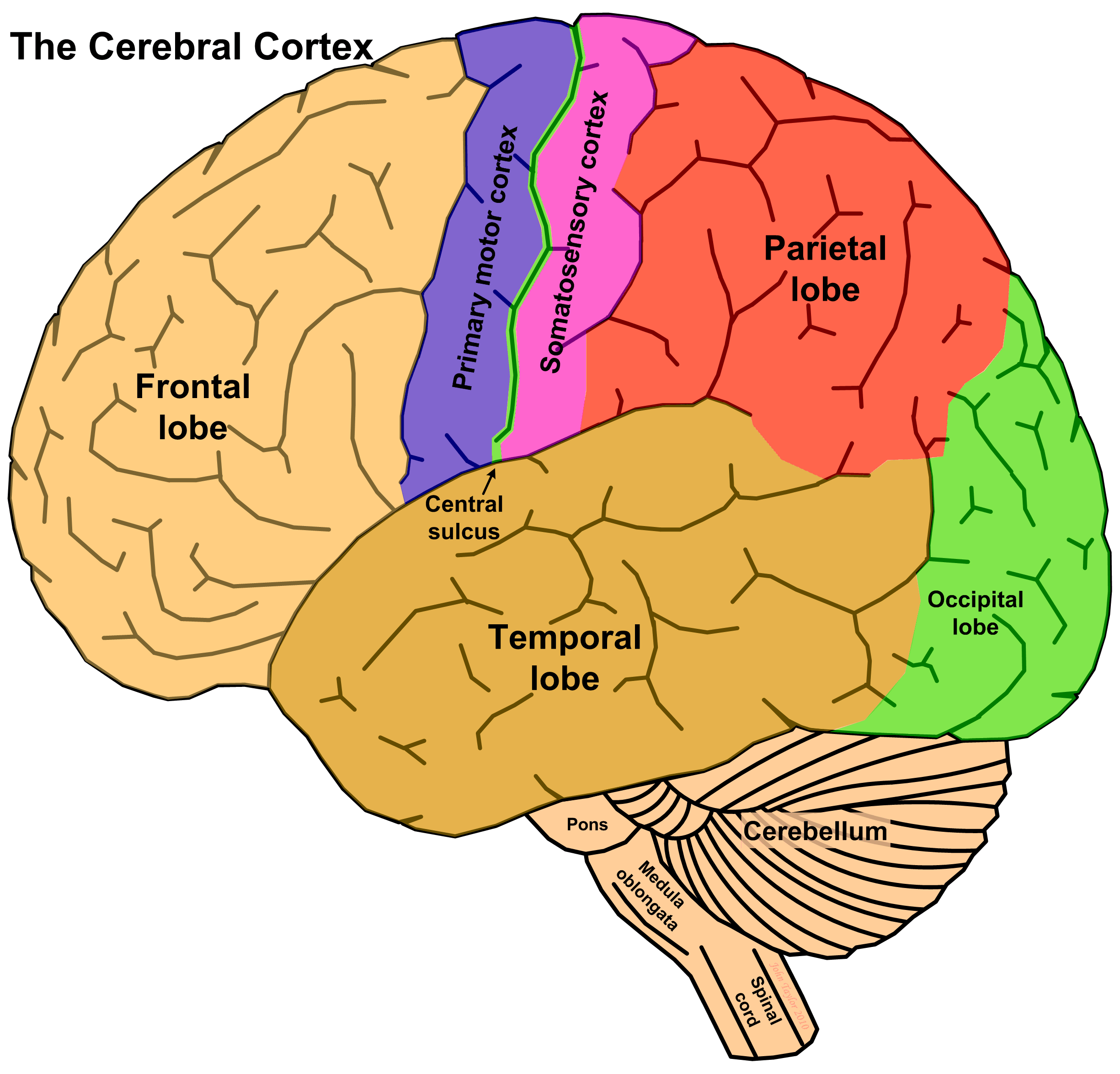
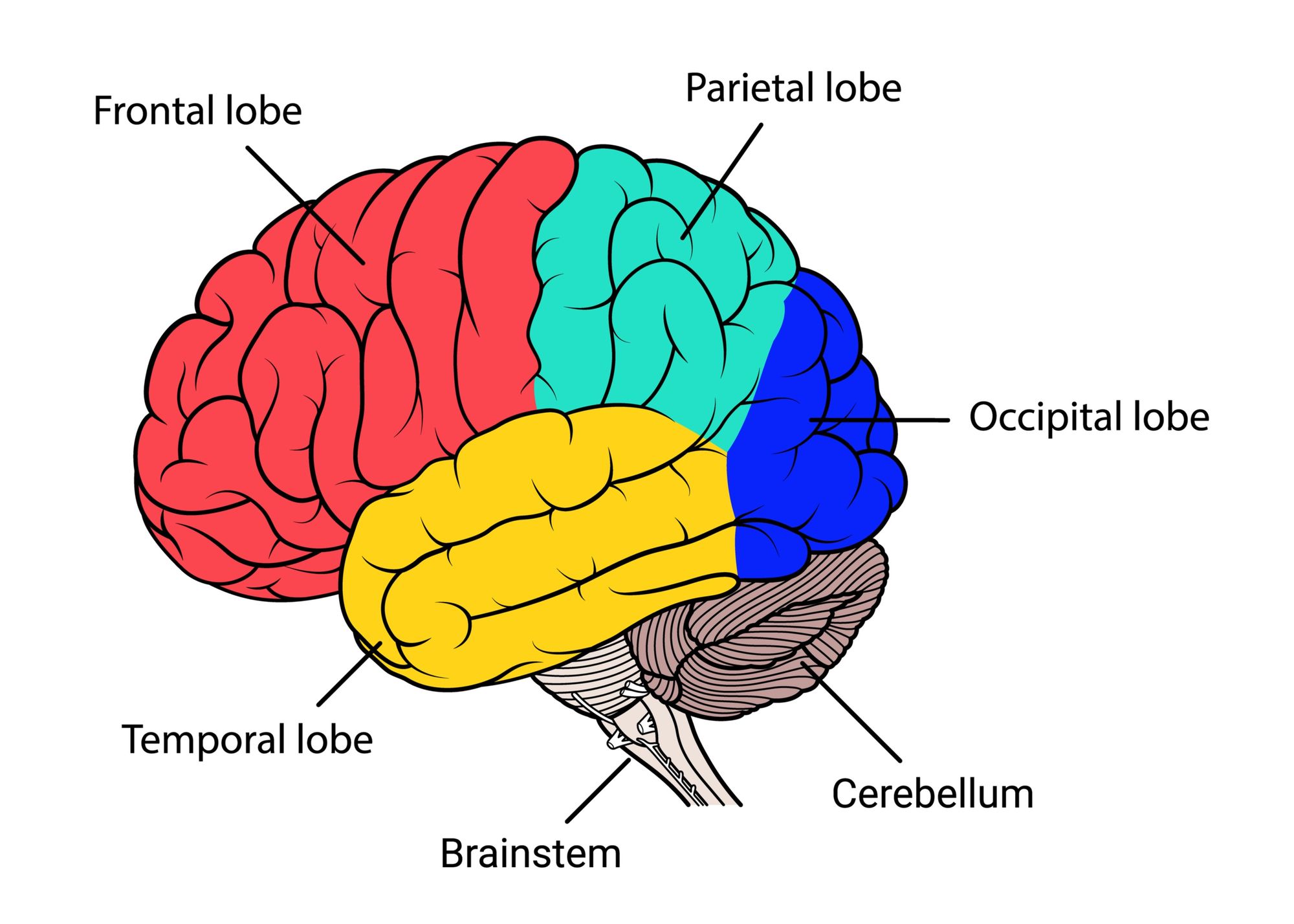
Cerebral Cortex Drawing - External granular layer of cerebrum structure #4. Sensory functions interpreted by the cerebral cortex include hearing, touch, and vision. Two imaginary lines are drawn on the cerebral hemisphere. Frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital. Structure functions clinical relevance in psychology, the cerebral cortex is defined as the outermost layer of the brain, composed of folded gray matter, playing a. Web the occipital lobe mainly processes vision and the temporal lobe, audition. Web the area seen from the superolateral view of the cerebrum is known as the cerebral cortex. Due to its large surface area, the cerebral cortex accounts for 50% of the brain’s total weight. This outermost layer of the brain integrates information. Down the front of the parietal lobe runs a thin strip of somatosensory cortex, which is the term for touch in medical science. Anatomical divisions the cerebral cortex is divided in cortical areas based on anatomical location, function and protein expression. Your cortex is divided into four lobes: “cells in the retina of the eye” (1904), one of. It is composed of a series of tortuous folds known as the gyri (singular: Web schematic drawing of six cortical lobes: Anatomical divisions the cerebral cortex is divided in cortical areas based on anatomical location, function and protein expression. External molecular layer of cerebrum #3. Due to its large surface area, the cerebral cortex accounts for 50% of the brain’s total weight. Web learn about its structure, including ridges (gyri), small grooves (sulci), and large grooves (fissures). Polymorphic layer of cerebral. It’s two millimeters (mm) to four mm (0.08 inches to 0.16 inches) thick. This layer is thrown into complex folds, with elevations called gyri and grooves known as sulci. The folds on the surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres are comprised of ridges of tissue, called gyri, separated by shallow grooves, called sulci (marieb 2016/p435/c1/para 3) Web cerebrum the cerebrum (front. Web the area seen from the superolateral view of the cerebrum is known as the cerebral cortex. Web in summary, the cerebral cortex is divided into four lobes that are responsible for processing and interpreting input from various sources and maintaining cognitive function. Web the functional study of the cerebral cortex is illustrated by the penfield motor homunculus and brodmann. Frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital. Your cortex is divided into four lobes: For descriptive purposes each cerebral hemisphere can. It is composed of a series of tortuous folds known as the gyri (singular: Internal pyramidal layer or ganglionic layer of cerebral cortex #7. Two imaginary lines are drawn on the cerebral hemisphere. It’s two millimeters (mm) to four mm (0.08 inches to 0.16 inches) thick. Your cortex is divided into four lobes: External granular layer of cerebrum structure #4. Structure functions clinical relevance in psychology, the cerebral cortex is defined as the outermost layer of the brain, composed of folded gray matter, playing. Polymorphic layer of cerebral cortex #8. “cells in the retina of the eye” (1904), one of. Cognitive functions include thinking, perceiving, and understanding language. External granular layer of cerebrum structure #4. It is composed of a series of tortuous folds known as the gyri (singular: It’s two millimeters (mm) to four mm (0.08 inches to 0.16 inches) thick. The cerebral cortex is 2 to 4 millimeters thick, contains billions of neurons, and has folds that nearly triple its surface area (marieb 2016/p435/c2/para3). Web schematic drawing of the human brain, indicating the location of cerebral cortex from a sagittal view. It is about 2 to 4. Sensory functions interpreted by the cerebral cortex include hearing, touch, and vision. So the rear of the cerebrum deals with the three main human senses: Occupying the upper part of the cranial cavity, the cerebral cortex has 4 lobes and is divided into 2 hemispheres that are joined centrally by the corpus callosum. Internal pyramidal layer or ganglionic layer of. It is composed of a series of tortuous folds known as the gyri (singular: This layer is thrown into complex folds, with elevations called gyri and grooves known as sulci. Internal pyramidal layer or ganglionic layer of cerebral cortex #7. So the rear of the cerebrum deals with the three main human senses: Polymorphic layer of cerebral cortex #8. Polymorphic layer of cerebral cortex #8. Between these gyri are grooves or indentations called sulci (singular: It is necessary to keep in mind that these data are old and probably incomplete or erroneous. The brain, along with the spinal cord, is the main organ of the central nervous system. This layer is thrown into complex folds, with elevations called gyri and grooves known as sulci. This chapter considers the overall organization of cortex from the gross topographic down to the cellular neurophysiology of the cortex. It’s two millimeters (mm) to four mm (0.08 inches to 0.16 inches) thick. External pyramidal layer of cerebral cortex #5. Web schematic drawing of the human brain, indicating the location of cerebral cortex from a sagittal view. So the rear of the cerebrum deals with the three main human senses: External molecular layer of cerebrum #3. Web october 16, 2023 reviewed by saul mcleod, phd on this page: Thick, and makes up 40% of the brain's mass. Web the cerebral cortex is the largest and most developed part of the human brain and central nervous system (cns). Your cortex is divided into four lobes: Web the cerebral cortex represents the highest level of function of the human brain.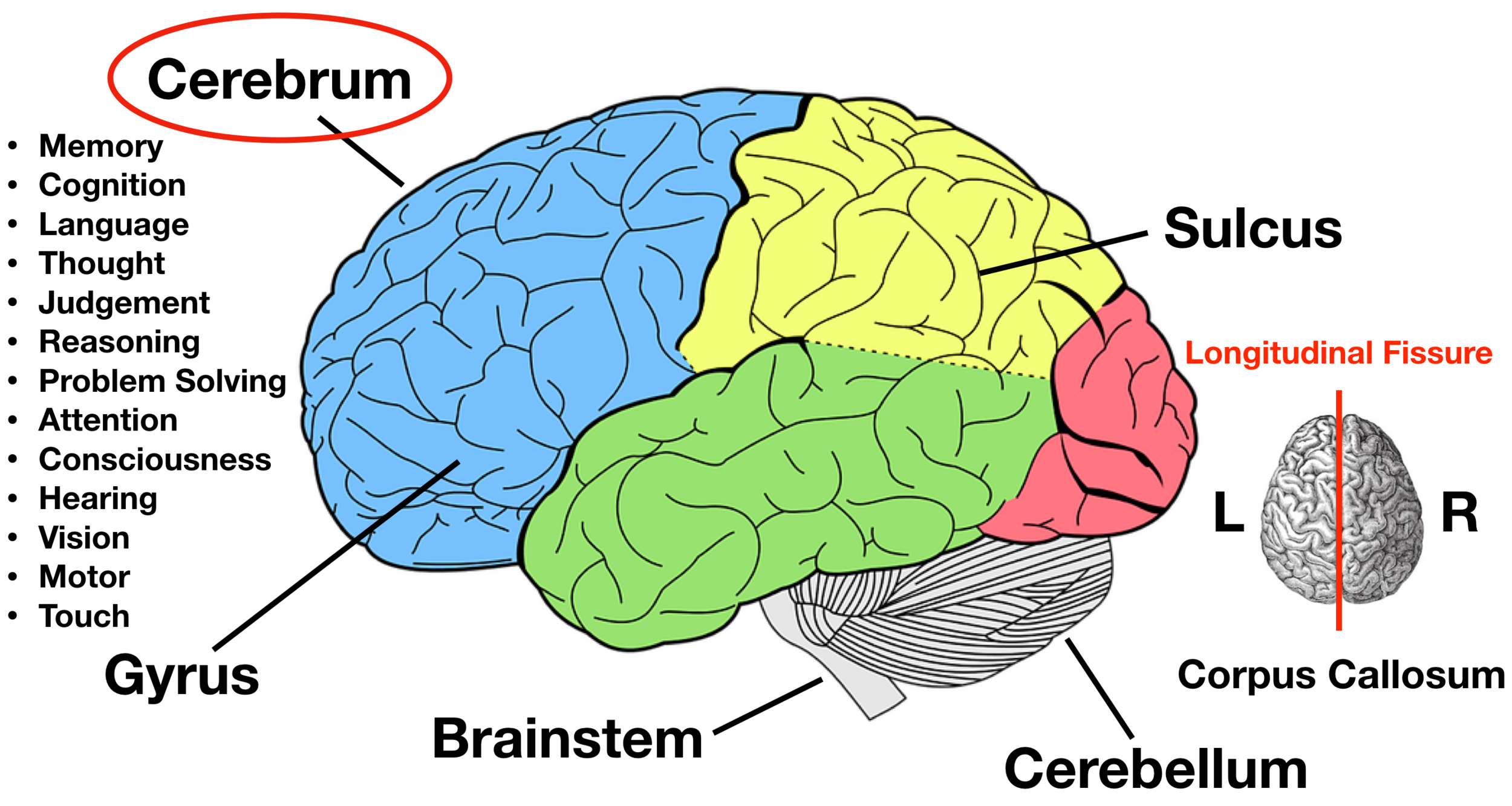
Lobes of the Brain Cerebral Cortex Anatomy, Function, Labeled Diagram
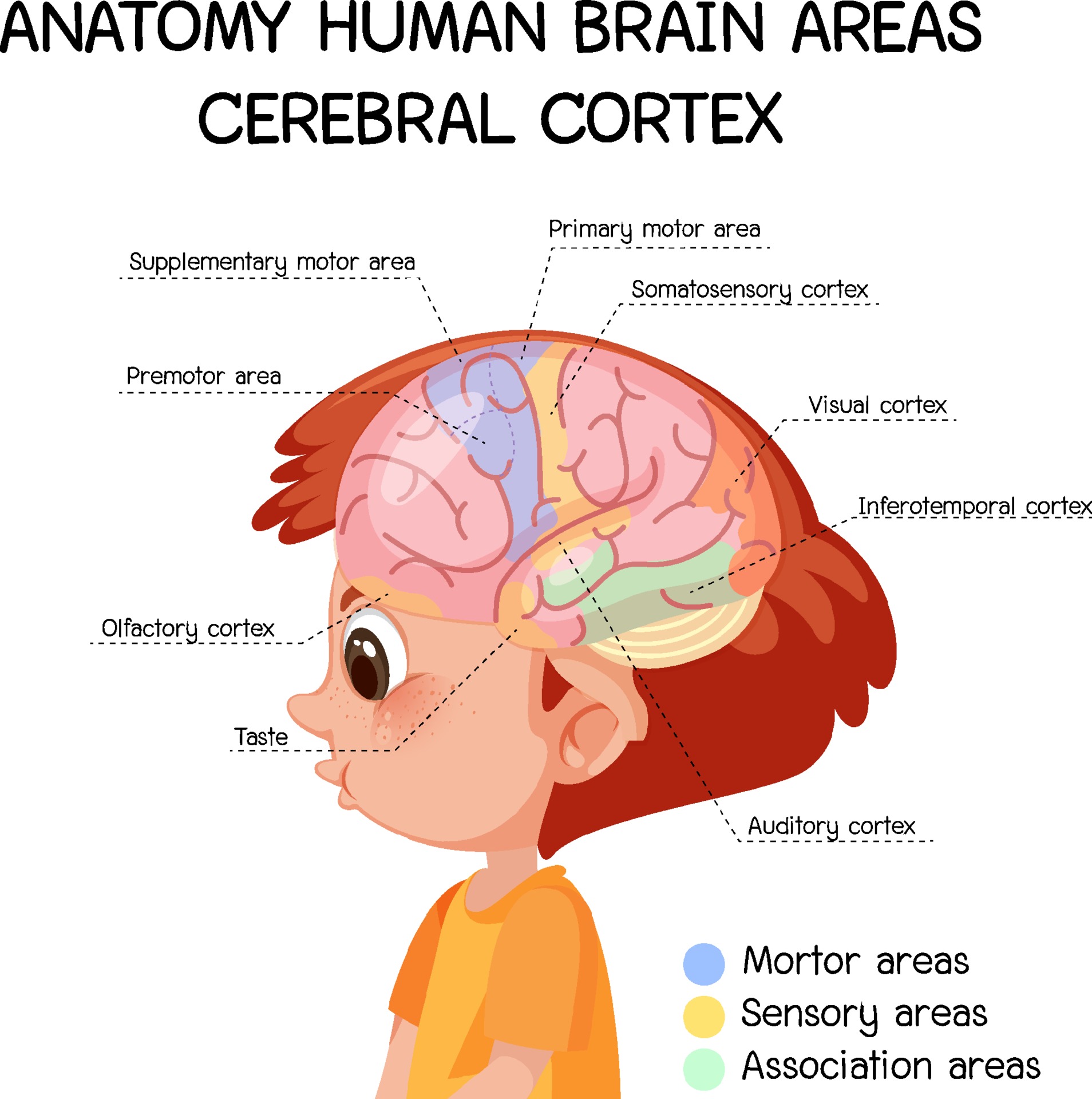
Anatomy human brain areas cerebral cortex with label 1988532 Vector Art

Cerebral Cortex Rishi Kathrotia AP Psych 2A

Parts Of The Brain Cerebral Cortex Human Anatomy
The Brain Concept with Synaesthesia The Syn Moment

Hand drawn cerebral cortex Vector Free Download
PostStroke Dizziness How Vestibular Therapy Can Help
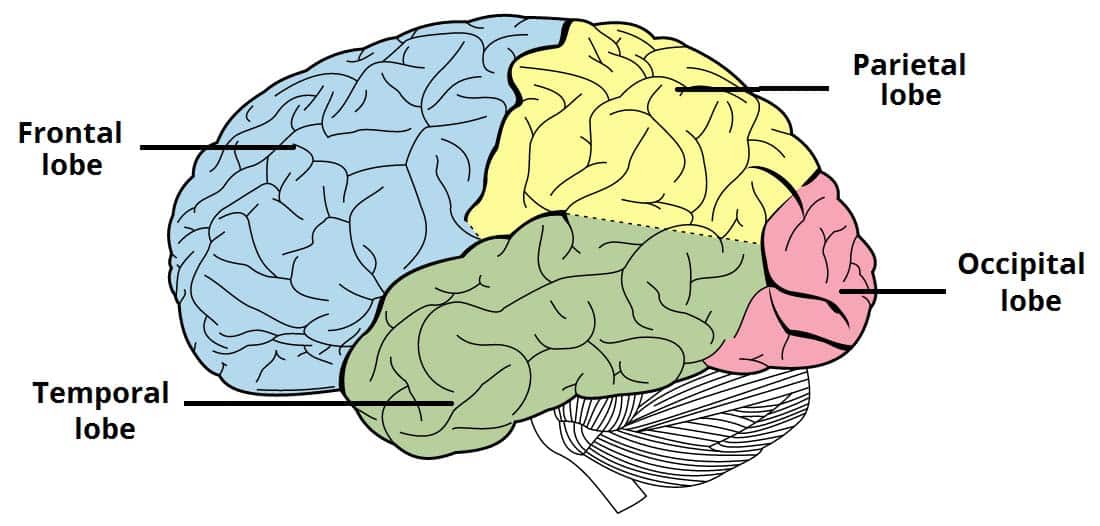
Elevated Portions Of The Cerebral Cortex Are Called mapasebab

How to Draw a Brain 14 Steps wikiHow

Lateral view of the cerebral cortex showing the principal gyri and
Web The Area Seen From The Superolateral View Of The Cerebrum Is Known As The Cerebral Cortex.
“Cells In The Retina Of The Eye” (1904), One Of.
Web Your Cerebral Cortex Consists Of Six Layers Of Nerve Cells That Contain Between 14 Billion And 16 Billion Nerve Cells.
Web Schematic Drawing Of Six Cortical Lobes:
Related Post: