Dog Drawer Test
Dog Drawer Test - Web on an orthopedic examination, muscle mass asymmetry, joint effusion, tissue warmth, painful flexion and extension of the stifle joint and decreased joint range of motion point towards knee involvement can be observed. Web an agitated dog with plenty of quadriceps muscle tone can make detection of the drawer sign a challenge. Web in this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the distal femur while posterior pressure is applied to the proximal tibia. The other hand flexes & extends the hock. This motion is just like pulling a drawer open. Web the cranial cruciate ligament helps the stifle (knee) function as a hinge joint. Priya streram bvsc 165 subscribers subscribe 9k views 2 years ago one of the difficult orthopedic test to learn when you are just. However, it does help up further confirm joint instability when ‘drawer’ motion is observed. Web pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. A positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm cclr. Sedation or general anesthesia may be necessary ( 1 , 3 ). This test isolates the ccl and eliminates joint compression. Web the other test is the cranial drawer test. With the posh dog knee brace, we can correct a dog knee injury (or. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing palpable instability. Immature dogs are often misdiagnosed with crclr because they have greater than expected cranial drawer sign due to normal puppy laxity. Dr jones shows you the drawer sign, the tibial compression test and meniscal click. Ccl injury is diagnosed through a physical exam and a cranial drawer test, which functions to elicit instability of the joint. If the tibia moves. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing palpable instability. Web on an orthopedic examination, muscle mass asymmetry, joint effusion, tissue warmth, painful flexion and extension of the stifle joint and decreased joint range of motion point towards knee involvement can be observed. Evaluation of the cranial thrust of the tibia via the tibial compression test. Web how to tell if your dog has injured or torn his anterior cruciate ligament. In a mature dog, a healthy, intact cranial cruciate ligament will not permit cranial tibial translation with the stifle held in extension or in flexion.3 in an immature dog, puppy laxity may permit a few millimeters of cranial and caudal tibial translation, but. Ccl injury. Evaluation of the cranial thrust of the tibia via the tibial compression test is another useful way of assessing stifle stability. The beauty of the tibial compression test is that it mimics the loading that causes cranial tibial thrust when the dog walks. Some dogs are more relaxed in the standing position than when restrained in lateral recumbency. Web drawer. This test is a bit more passive (and less painful) than the tibial compression test since it does not mimic a natural movement of the joint. Web once the ligament tears to a certain degree the tibia can be manually manipulated to show instability in what is called the “cranial drawer test” in which the tibia can be moved forward. Web the correct performance of either test is a learned skill, mastered only after much experience and practice on healthy dogs as well as those with partial or complete crclrs. Web pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. If the tibia moves forward, known as a positive drawer because. If the tibia moves forward, known as a positive drawer because of the way the bone moves similar to a drawer being opened, the ligament is ruptured. Have your dog lie on their side while you perform this test. This test is a bit more passive (and less painful) than the tibial compression test since it does not mimic a. Web on an orthopedic examination, muscle mass asymmetry, joint effusion, tissue warmth, painful flexion and extension of the stifle joint and decreased joint range of motion point towards knee involvement can be observed. Have your dog lie on their side while you perform this test. In a mature dog, a healthy, intact cranial cruciate ligament will not permit cranial tibial. Web pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Have your dog lie on their side while you perform this test. Web the cranial cruciate ligament helps the stifle (knee) function as a hinge joint. Web veterinarians often need to perform the drawer test because a torn cranial cruciate ligament. Web an agitated dog with plenty of quadriceps muscle tone can make detection of the drawer sign a challenge. Sedation or general anesthesia may be necessary ( 1 , 3 ). If the tibia moves forward, known as a positive drawer because of the way the bone moves similar to a drawer being opened, the ligament is ruptured. Web this is a positive drawer sign, as there is a forward movement now where the tibia is shifting forward. Web drawer test and cranial tibial thrust test on a 85 lb dog with a torn acl. Have your dog lie on their side while you perform this test. Web this video demonstrates how to perform the cranial drawer and tibial compression (tibial thrust) tests. Evaluation of the cranial thrust of the tibia via the tibial compression test is another useful way of assessing stifle stability. Web the cranial cruciate ligament helps the stifle (knee) function as a hinge joint. Web the cranial drawer test should be done with the leg in flexion and extension, to test both parts of the crcl. Ccl injury is diagnosed through a physical exam and a cranial drawer test, which functions to elicit instability of the joint. However, it does help up further confirm joint instability when ‘drawer’ motion is observed. Web in this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the distal femur while posterior pressure is applied to the proximal tibia. In a mature dog, a healthy, intact cranial cruciate ligament will not permit cranial tibial translation with the stifle held in extension or in flexion.3 in an immature dog, puppy laxity may permit a few millimeters of cranial and caudal tibial translation, but. Web the index finger of one hand is placed over the tibial crest. The other hand flexes & extends the hock.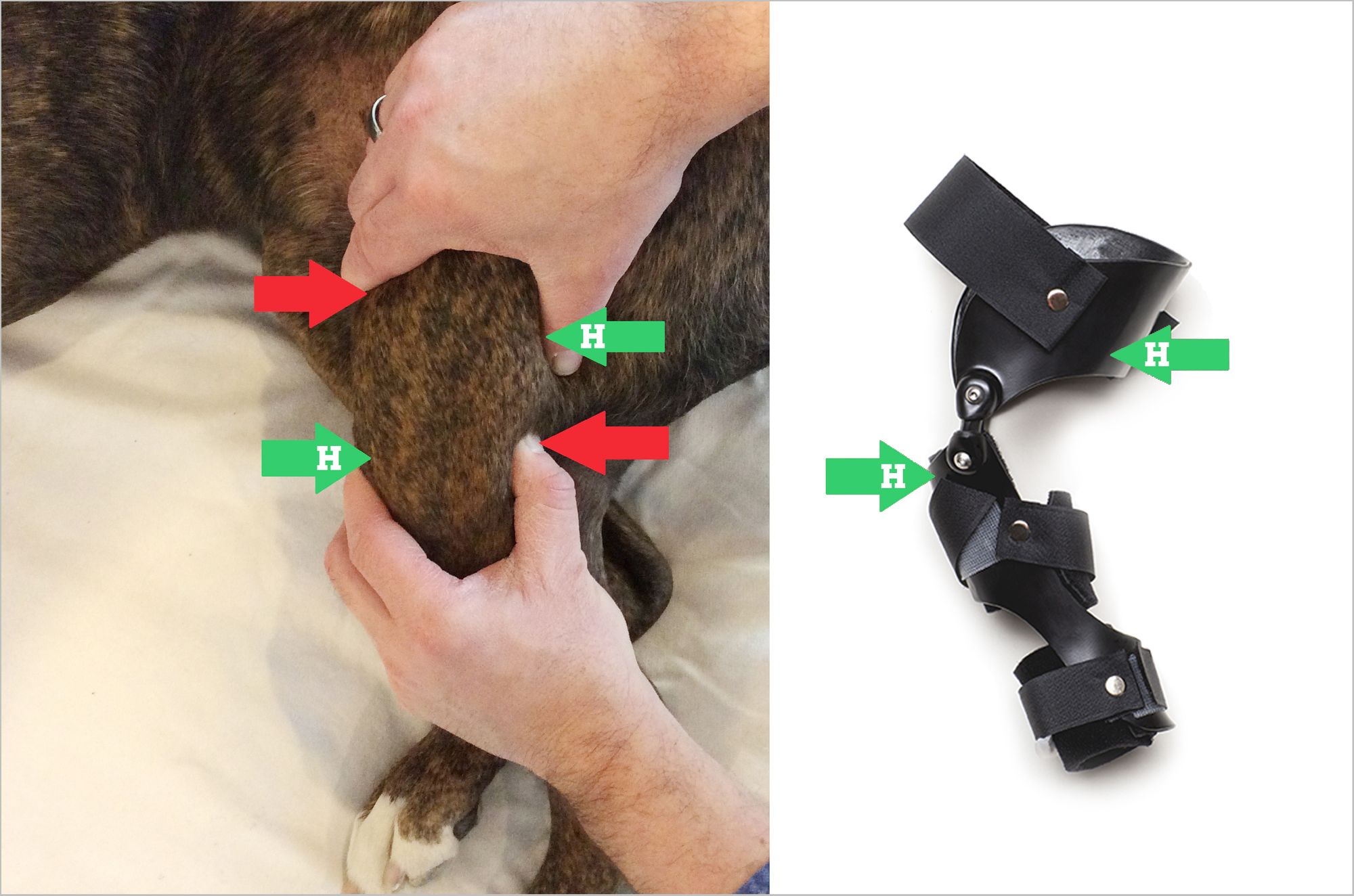
Torn ACL in Dogs How Braces Help

Posterolateral Drawer Test YouTube

Anterior drawer test YouTube

Examination And Examination Of The Anterior Cruciate

ACL Drawer Sign and Tibial Compression Test for Torn ACL in Dog YouTube

Drawer Test Bruin Blog

Anterior Drawer Test Different Elements of Anterior Drawer Test

Drawer Test Bruin Blog
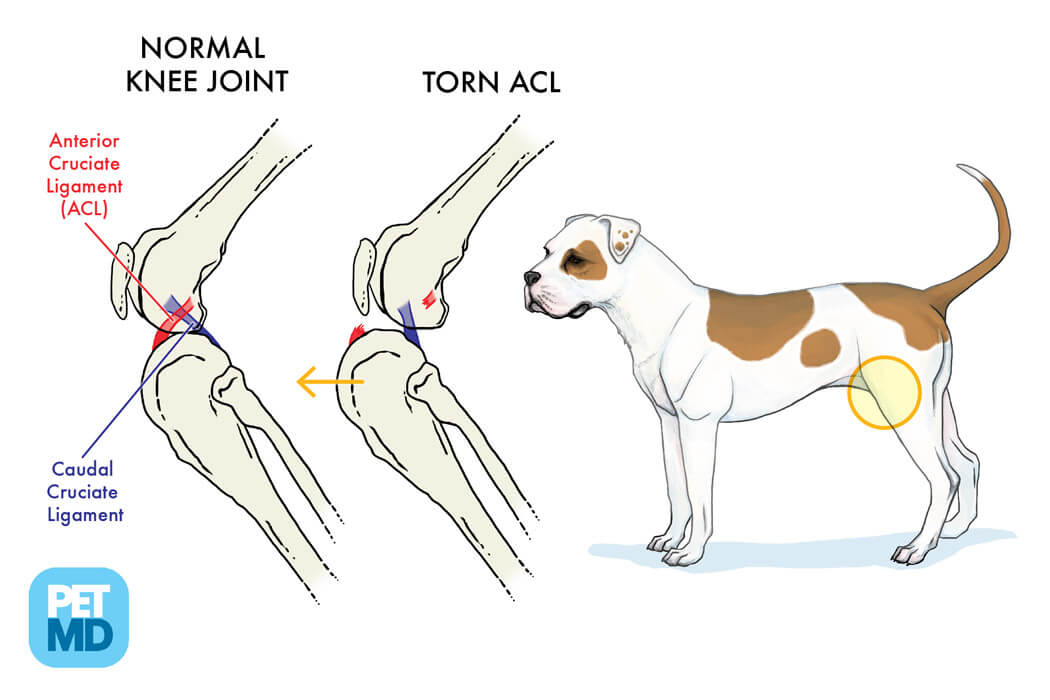
ACL and CCL diagram provided by PetMD

Cruciate Disease The Cranial Drawer Test YouTube
Priya Streram Bvsc 165 Subscribers Subscribe 9K Views 2 Years Ago One Of The Difficult Orthopedic Test To Learn When You Are Just.
Web To Test For Cranial Tibial Translation, Perform The Cranial Drawer Test (Figure 6).
The Drawer Test Involves The Veterinarian Or Physical Therapist Placing Their Hands Around The Dog’s Stifle Joint, Using A Gliding Motion Used To Test The “Tightness” Of The Ligament.
Web Pain Upon Forced Full Extension Of The Stifle Is A Simple Test That Is Suggestive Of Early Crcld.
Related Post: