Draw And Label An Atp Molecule
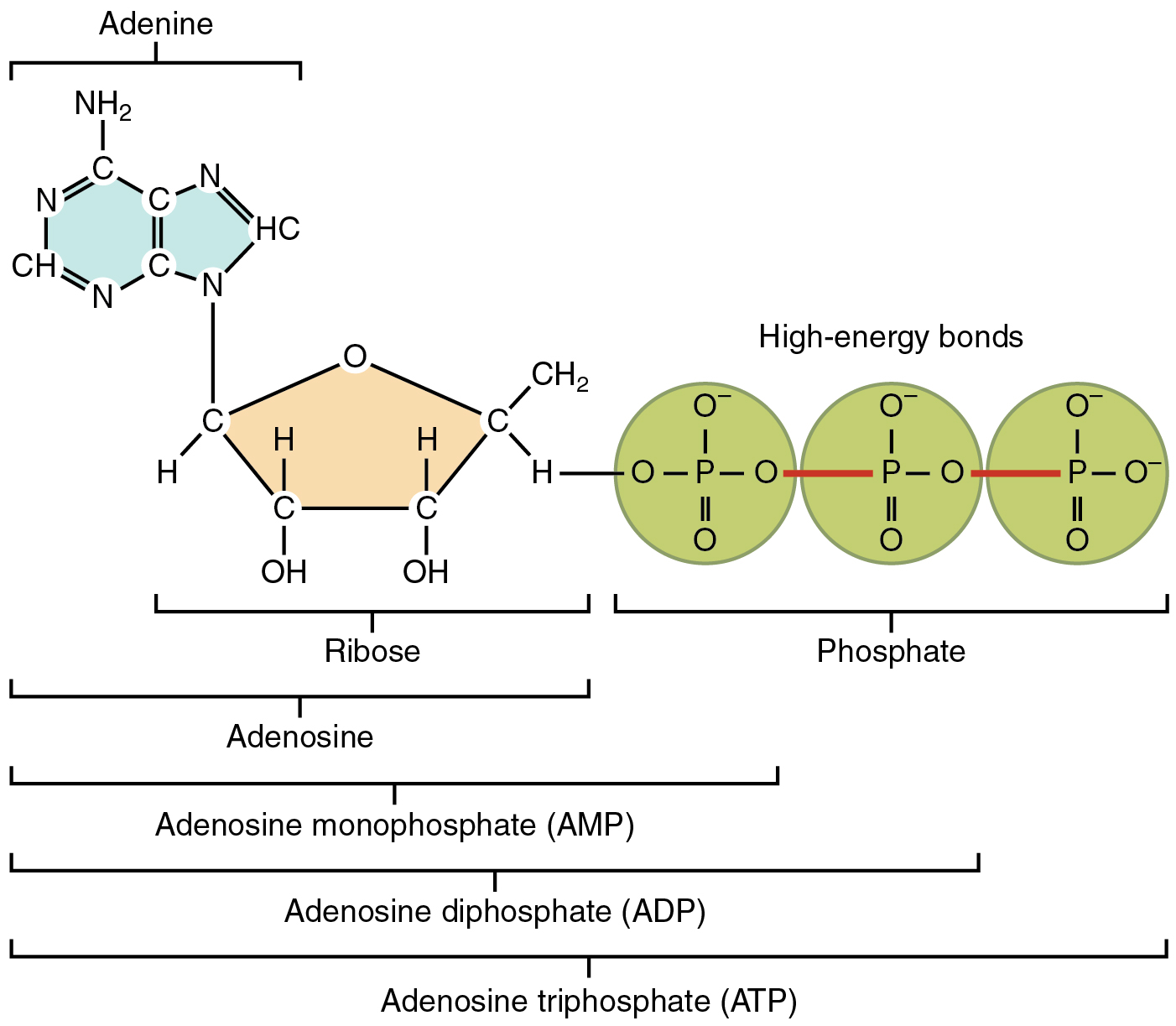
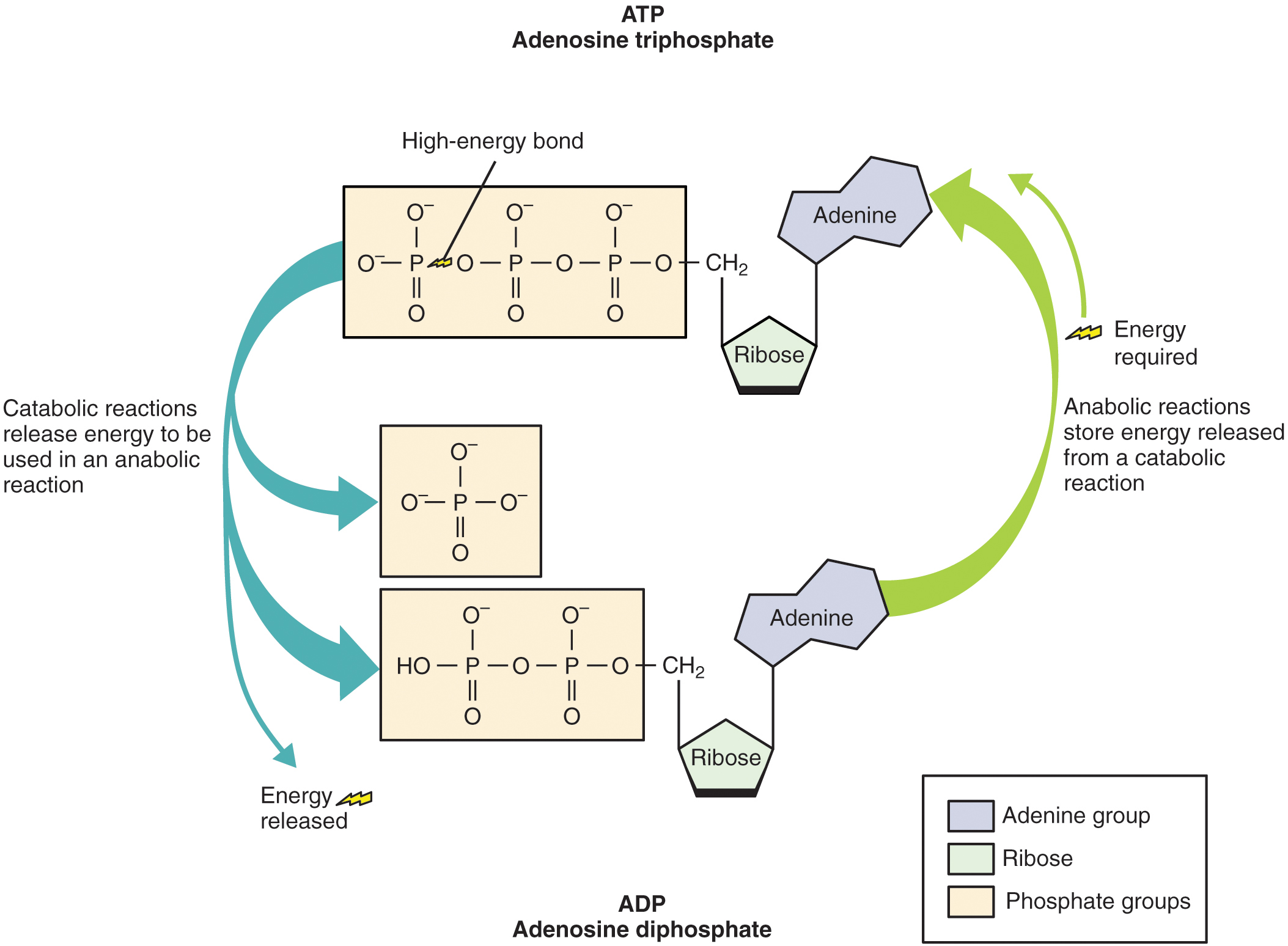
Draw And Label An Atp Molecule - Adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups. Atp is like a charged battery, while adp is like a dead battery. Use the molecule from the lesson material or find one on your own (cite the source please). Draw and label the parts of an atp molecule. This energy release powers various biological processes. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of atp. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how atp molecules release energy. Using the diagram, label the 3 parts that make up an atp molecule. It's made up of adenosine and three phosphate groups. Web image of the atp cycle. Web atp, or adenosine triphosphate, is the energy currency in biological systems. Atp is like a charged battery, while adp is like a dead battery. Energy is stored when atp is formed and released when it's broken down into adp (adenosine diphosphate) and a phosphate group. Web draw an atp molecule (label adenine, ribose, and phosphates). Web atp molecules are. Web interactive animation of the structure of atp. How is adp different from atp? It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. Use the molecule from the lesson material or find one on. Explain (or use diagrams to illustrate) how energy is released from atp molecules. This molecule is composed of three parts: Together, these chemical groups constitute an energy powerhouse. Web draw the structure of atp molecule. Web atp captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Adp what are the 3 types of cellular work that atp is used for, and what do they do: Energy is stored when atp is formed and released when it's broken down into adp (adenosine diphosphate) and a phosphate group. Atp is like a charged battery, while adp is like a dead battery. Web draw the structure of atp molecule.. Use the molecule from the lesson material or find one on your own (cite the source please). Explain (or use diagrams to illustrate) how energy is released from atp molecules. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. Include what is and is not recycled. Explain why glucose is important. It's made up of adenosine and three phosphate groups. How is adp different. Explain why glucose is important. Adenosine triphosphate (atp) is a nucleotide that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and. Include what is and is not recycled. The energy released from the hydrolysis of atp into adp + p i is used to perform cellular work. Atp. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of atp. The three phosphate groups, in order of closest to furthest from the ribose sugar, are labeled alpha, beta, and gamma. Web adenosine triphosphate, also known as atp, is a molecule that carries energy. Explain (or use diagrams to illustrate) how energy is released from atp molecules. Atp is like a charged battery, while adp is like a dead battery. Web draw an atp molecule (label adenine, ribose, and phosphates). Energy is stored when atp is formed and released when it's broken down into adp (adenosine diphosphate) and a phosphate group. Draw and label. Atp can be hydrolyzed to adp and pi by the addition of water, releasing energy. Adp what are the 3 types of cellular work that atp is used for, and what do they do: What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? Adenosine triphosphate (atp) is a nucleotide that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells,. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how atp molecules release energy. Using the diagram, label parts that make up an atp molecule. Web image of the atp cycle. Web what are the 3 parts of an atp molecule. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like draw and label an atp molecule. Web atp molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Web photosynthesis 1 draw and label an atp molecule. This problem has been solved! Web draw the structure of atp molecule. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? Energy can be stored by adding a phosphate group to an adp molecule, converting it into atp. Add has 2 phosphate atp has 3 phosphate 3. Web atp captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of atp. Draw and label an atp molecule. Explain (or use diagrams to illustrate) how energy is released from atp molecul 3.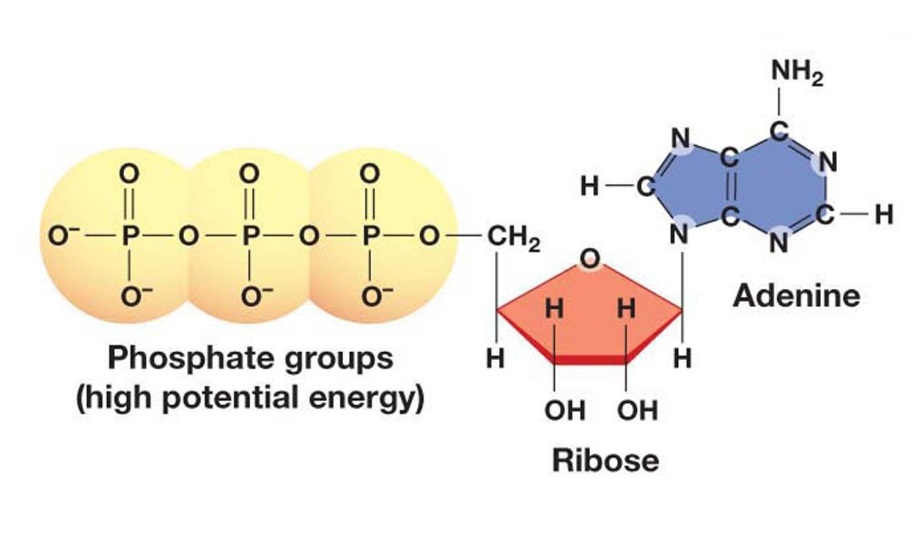
ATP and Sources of Energy.pptx on emaze
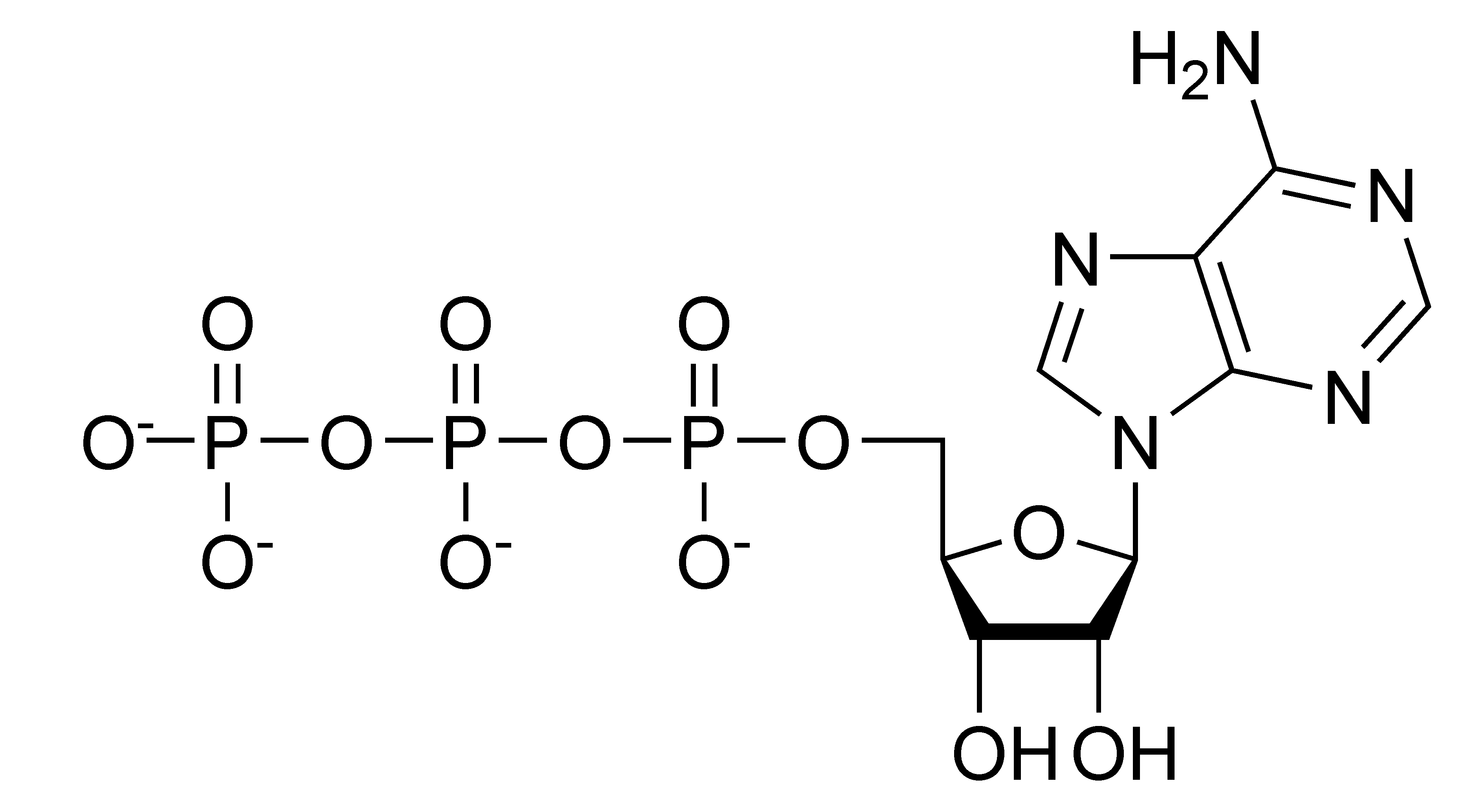
ArchivoATP chemical structure.png Wikipedia, la enciclopedia libre

35 Label Each Part Of The Atp Molecule Labels Database 2020
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule
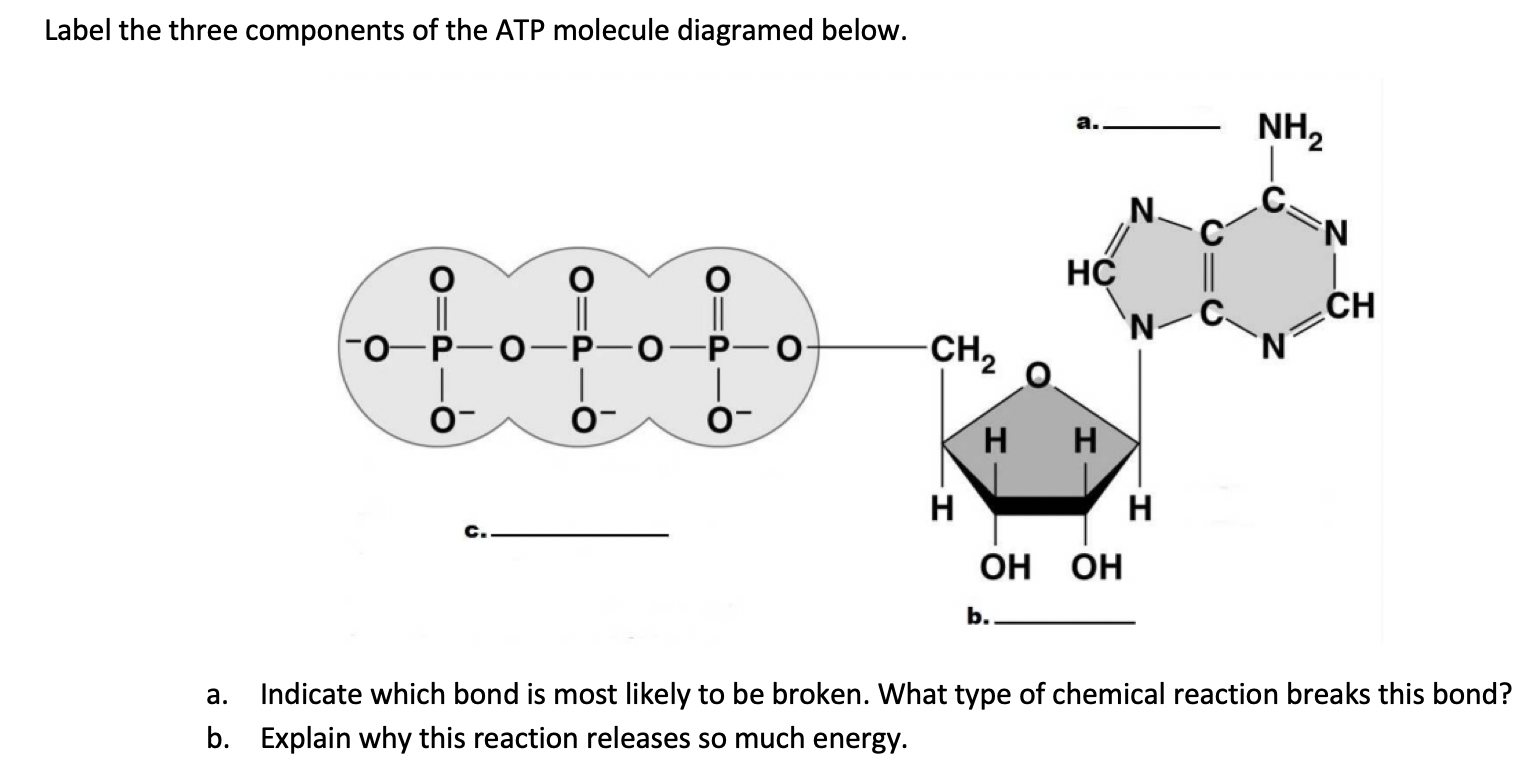
Solved Label the three components of the ATP molecule
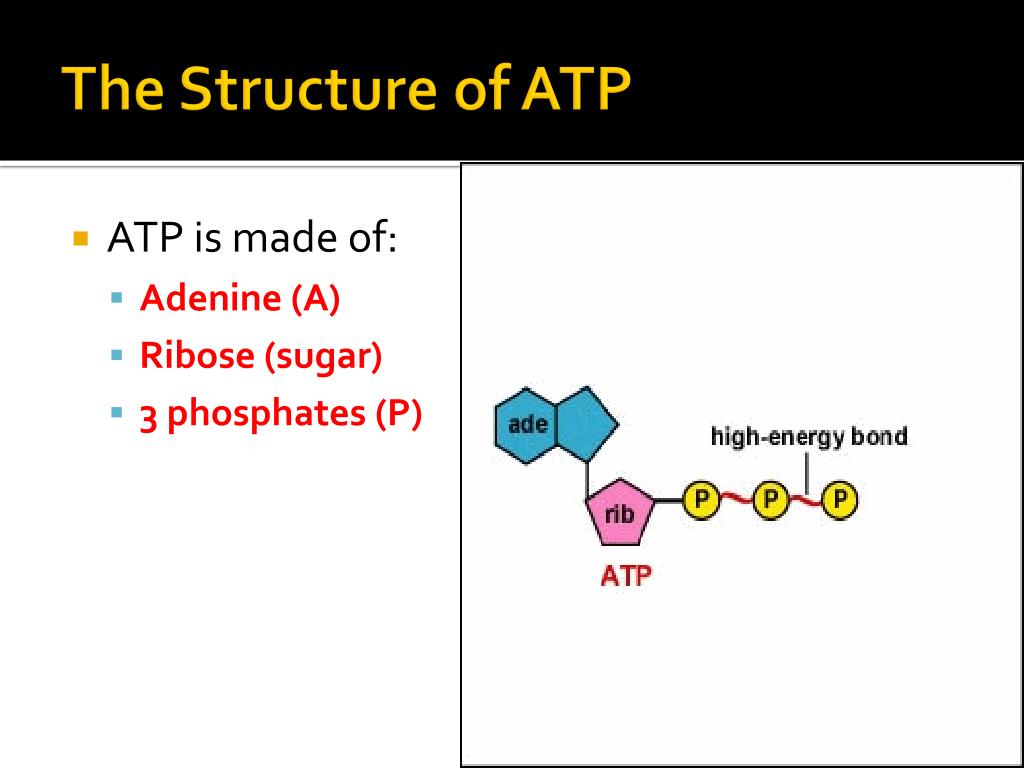
PPT ATP PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2577685

What is Adenosine Triphosphate? Definition, Function & Structure

Adp Molecule Drawing / Solved 1. Draw And Label An ATP Molecule. Using
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Definition and Synthesis
30 Draw And Label An Atp Molecule Labels Design Ideas 2020
It Is The Main Energy Currency Of The Cell, And It Is An End Product Of The Processes Of Photophosphorylation (Adding A Phosphate Group To A Molecule Using Energy From Light), Cellular Respiration, And Fermentation.
Adenine, A Ribose Sugar, And Three Serially Bonded Phosphate Groups Make Up The Nucleoside Triphosphate (Nucleoside) Structure Of Atp.
Web The Atp Molecule Consists Of A Nitrogenous Base, A Sugar, And Three Phosphate Groups.
Be Able To Identify The Adenosine Part, And 3 Phosphate Groups.
Related Post:
