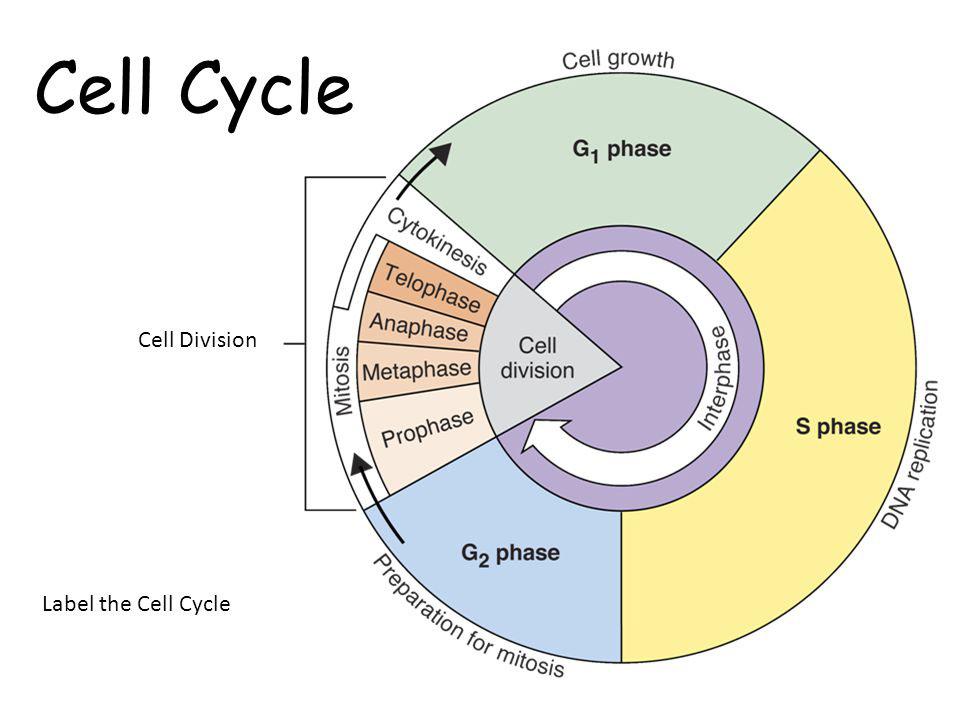
Draw And Label The Cell Cycle
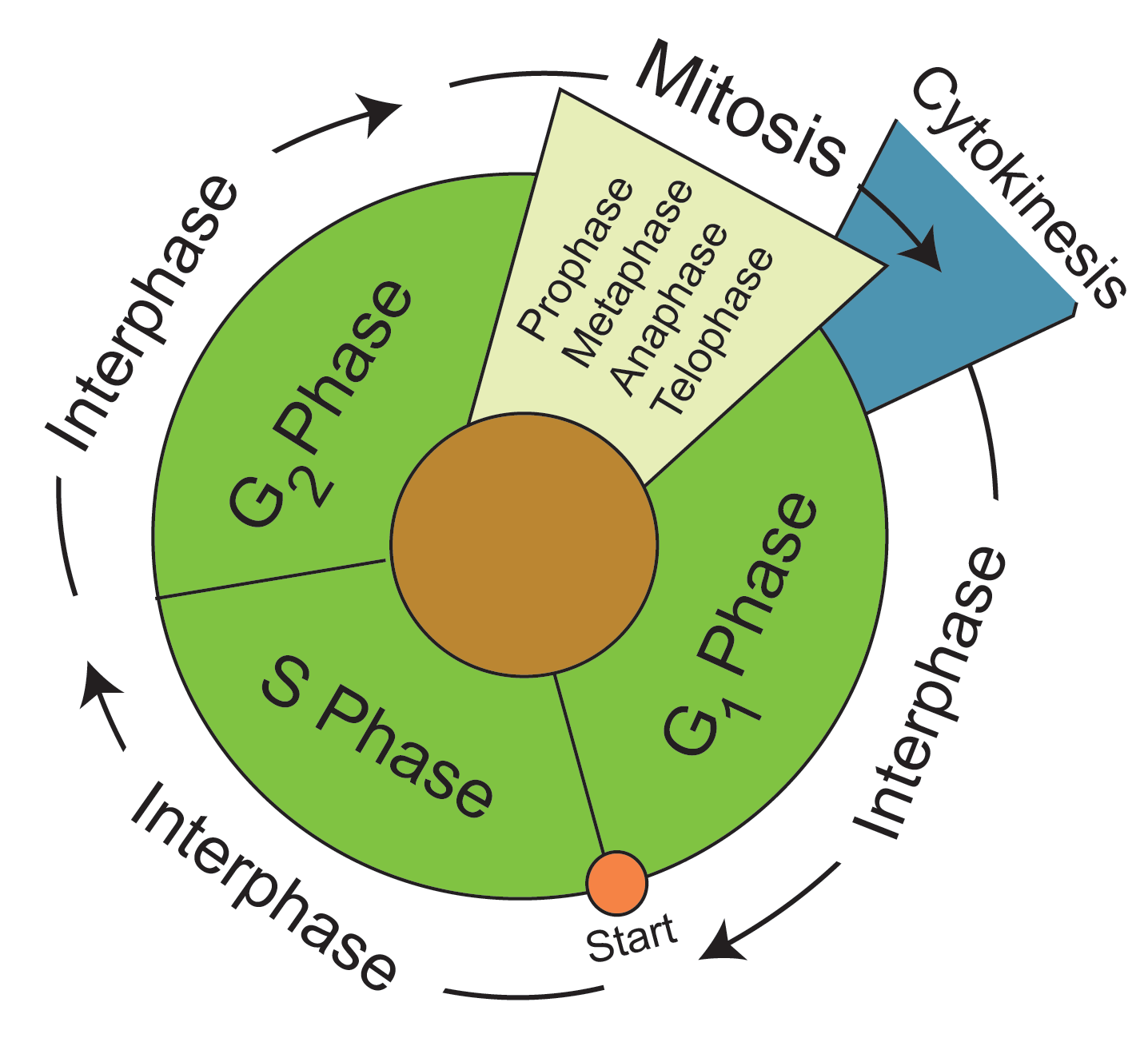
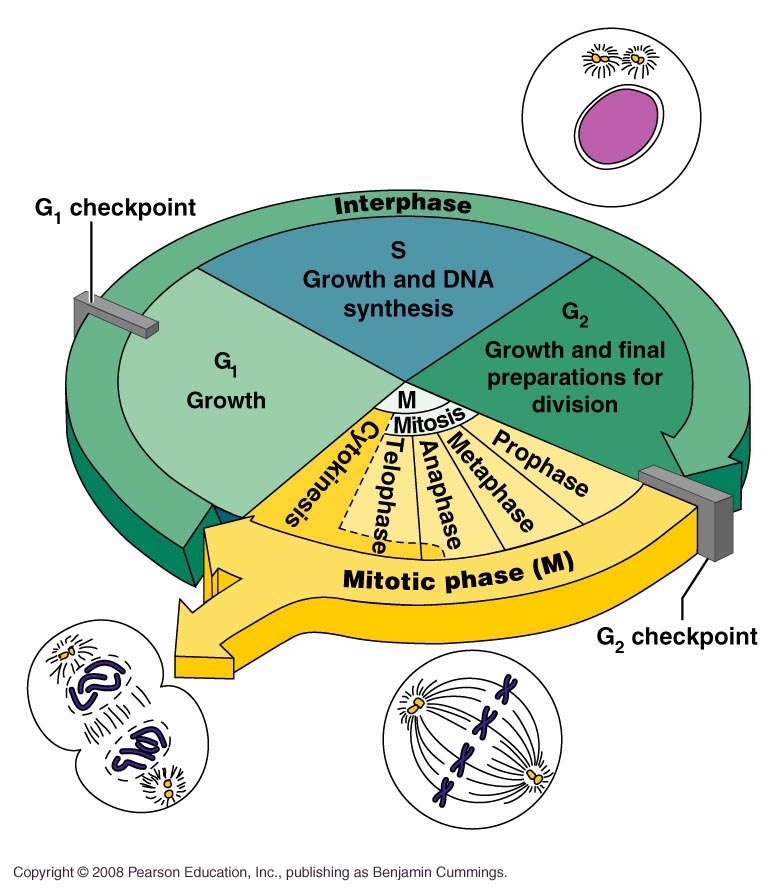
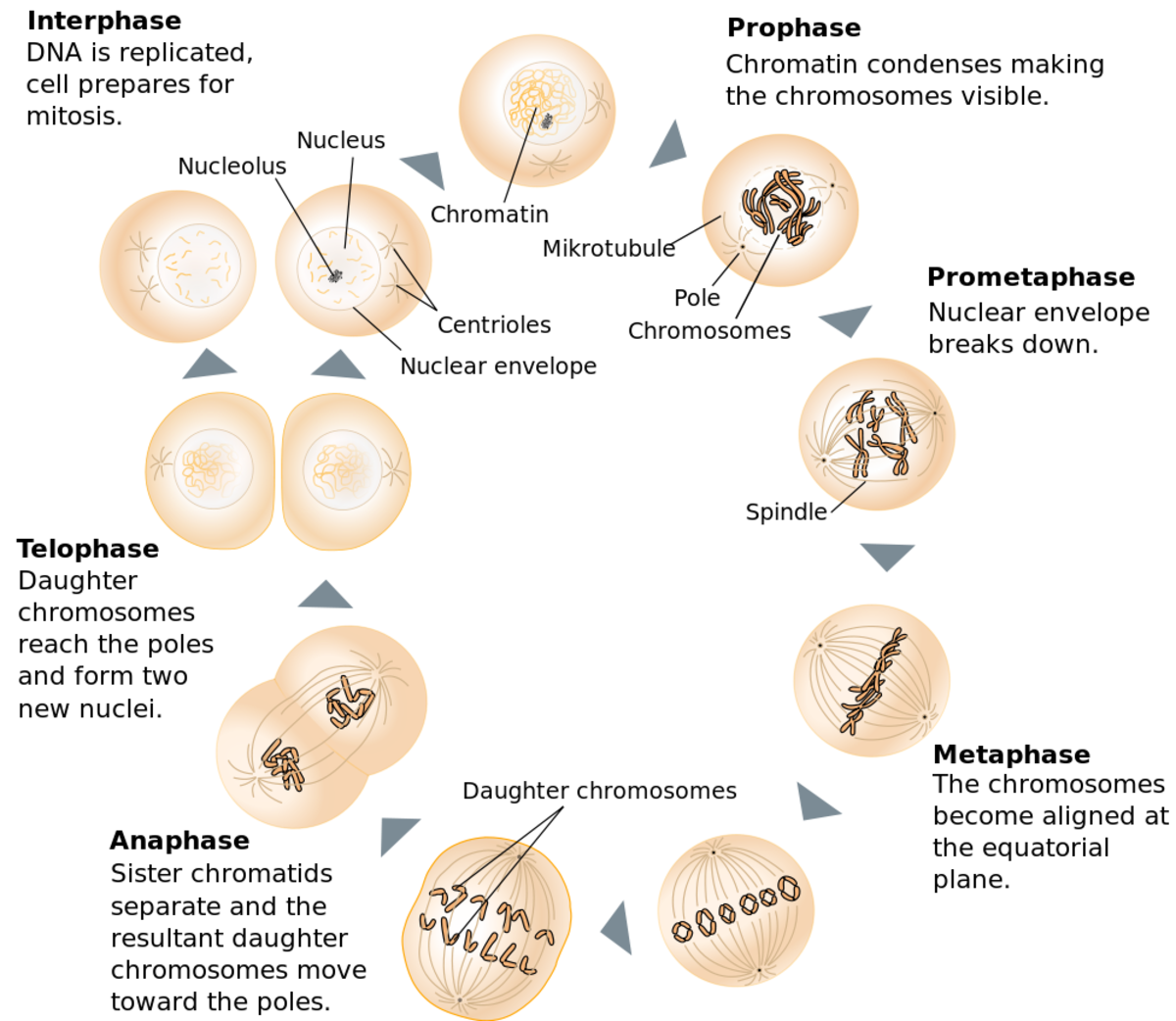
Draw And Label The Cell Cycle - _____ during what phase does cytokinesis begin? Labeling diagrams examine the images below. From g0, the cell can undergo terminal differentiation. The stages between one mitosis and. The g 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. What moves the chromatids during mitosis? Web cell cycle or cell division refers to the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its maturity and subsequent division. G 1 (gap1) phase 2. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. The main phases are shown: In the context of the cell cycle, mitosis is the part of the division process in which the dna of the cell's nucleus is split into two equal sets of chromosomes. Web what you’ll learn to do: Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. The. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. When a sperm and an egg join in fertilization, the two haploid sets of chromosomes form a. G 1 (gap1) phase 2. Web the duration of these cell cycle phases varies considerably in different kinds of cells. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth. Other types of cells, however, can divide much more rapidly. When a sperm and an egg join in fertilization, the two haploid sets of chromosomes form a. What moves the chromatids during mitosis? The g 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Identify the stages of the cell cycle, by picture and by description of major milestones. Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Web the cell cycle. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and nuclear and cytoplasmic division that ultimately produces. As completely as possible, list the key events that occur in each stage of mitosis. It is characterised by a change in the chromosome from the condensed mitotic. Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. _____ how many daughter cells are created from mitosis and cytokinesis? These processes define the two major phases of the cell. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. In the context of the cell cycle, mitosis is the part of the division process in which the dna of the cell's nucleus is split into two equal sets of chromosomes. From g0, the cell can undergo terminal. The stages g1, s, and g2 make up interphase, which accounts for the span between cell divisions. Web the 46 chromosomes of a human cell are organized into 23 pairs, and the two members of each pair are said to be homologues of one another (with the slight exception of the x and y chromosomes; Web the following points highlight. Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Web what you’ll learn to do: Web the following points highlight the four major phases of the cell cycle. Mitosis is a type of cell division in which one cell (the mother) divides to produce two new cells (the daughters) that are genetically identical to itself. Web the cell. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. Identify and draw a cell in each of the four stages of mitosis in the onion slide. _____ what anchors the spindle? Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a. The g 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. It is sometimes referred to as the “cell division cycle” for that reason. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and nuclear. Identify the stages of the cell cycle, by picture and by description of major milestones. Mitosis bead simulations in this exercise you will make models of chromosomes to study the meiosis chromosome replication and comparing mitosis and process of mitosis. In humans, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs. The g 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. _____ how many daughter cells are created from mitosis and cytokinesis? Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and nuclear and cytoplasmic division that ultimately produces two identical (clone. The role of mitosis in the cell cycle is to replicate the genetic material in an existing cell—known as the “parent cell”—and distribute that genetic material to two new cells, known as “daughter cells.” _____ if a human cell has 46 chromosomes, how many. _____ during what phase does cytokinesis begin? It is characterised by a change in the chromosome from the condensed mitotic. After completing the cycle it either starts the process again from g1 or exits through g0. G 2 (gap 2) phase 4. Mitosis is a type of cell division in which one cell (the mother) divides to produce two new cells (the daughters) that are genetically identical to itself. These processes define the two major phases of the cell cycle. Other types of cells, however, can divide much more rapidly. Identify and draw a cell in each of the four stages of mitosis in the onion slide.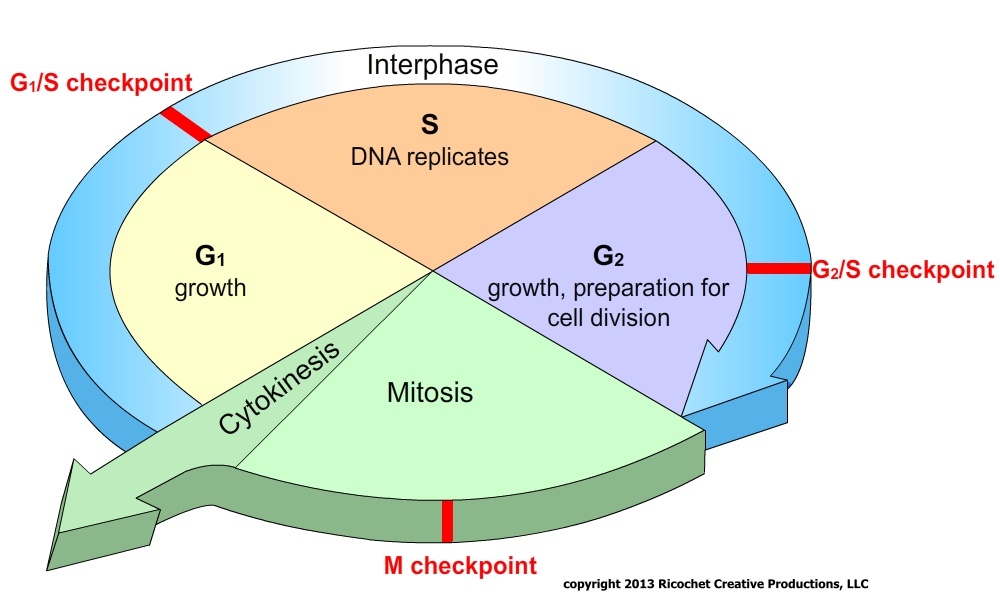
Mrs.Cruz's Biology Class Chapter 5 Cell Growth and Division

The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology

Cell Division An Intro AmoebaMike
Cell Cycle Phases , Diagram , Types and Comparison
CSIR LIFE SCIENCE PREPARATION Fundamental Processes Overview of the
Cell Division Mitosis and Meiosis Owlcation

Cell cycle labelling. Schematic representation of the cell cycle and
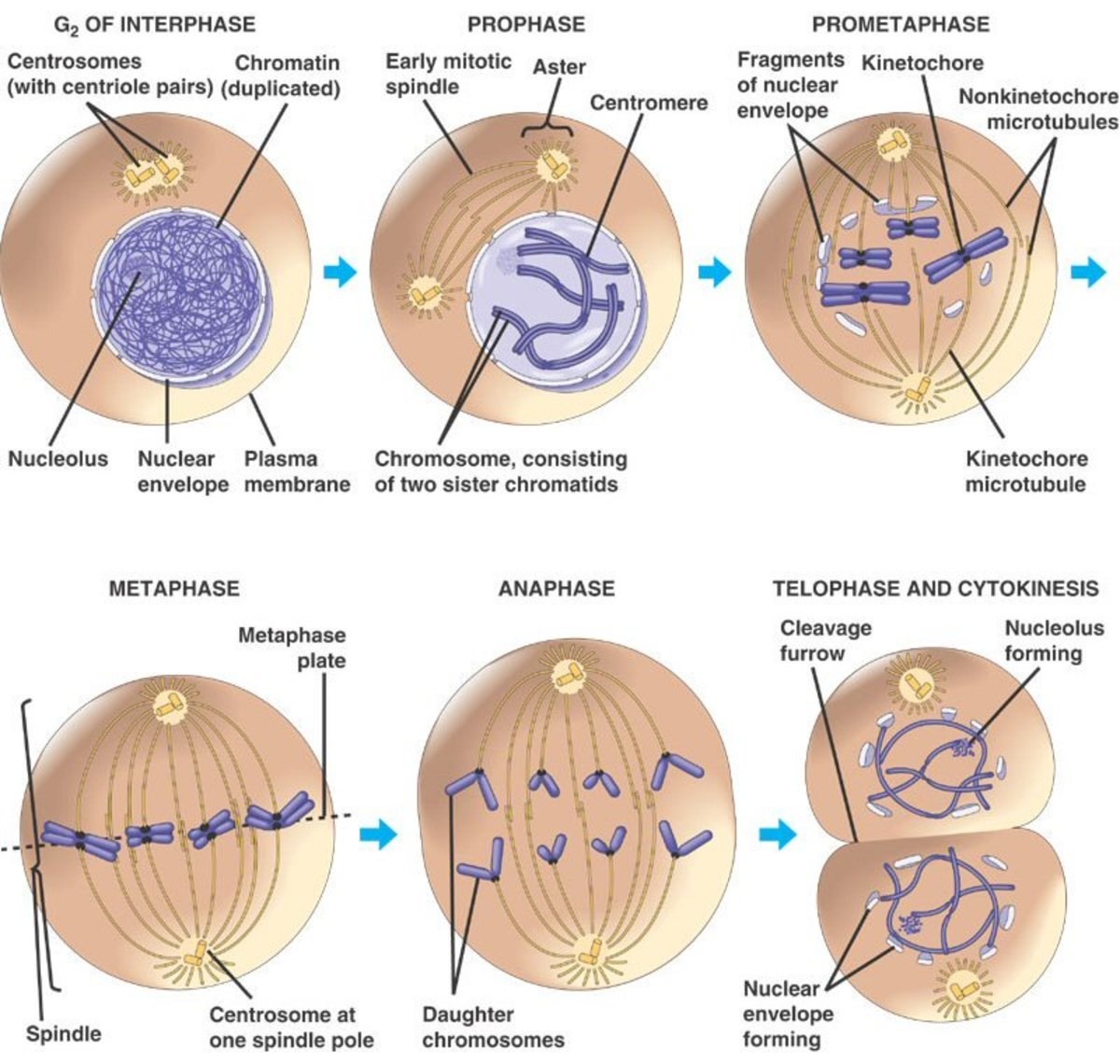
Stages of the Cell Cycle Mitosis (Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase
Phases of Cell cycle Online Biology Notes

Cell Cycle Phase Definition, Fours phases of Cell cycle Division
The Most Basic Function Of The Cell Cycle Is To Duplicate Accurately The Vast Amount Of Dna In The Chromosomes And Then Segregate The Copies Precisely Into Two Genetically Identical Daughter Cells.
Web Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Describe The Overall Purposes Of Cell Division And The Cell Cycle., Draw The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle, Labeling The Different Phases And Describing What Occurs In Each., Describe The Structure Of Eukaryotic Chromosomes, Drawing A Labeled Picture Of A Chromosome After S Phase And More.
The Stages G1, S, And G2 Make Up Interphase, Which Accounts For The Span Between Cell Divisions.
Web Cell Cycle Or Cell Division Refers To The Series Of Events That Take Place In A Cell Leading To Its Maturity And Subsequent Division.
Related Post: