Draw The Base Thymine From Dna
Draw The Base Thymine From Dna - Web a nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: Web the rules of base pairing explain the phenomenon that whatever the amount of adenine (a) in the dna of an organism, the amount of thymine (t) is the same (called chargaff's rule ). The human genome contains 6 billion base pairs across 46 chromosomes, making it a compact and efficient information storage system. The sugars and phosphates form a backbone, along which the base pairs are strung. The two strands of the duplex are antiparallel and plectonemically coiled. Adenine and thymine are bound to one another via two hydrogen bonds while guanine and cytosine are bound to one another via three hydrogen bonds. C and t bases, which have just one ring, are called pyrimidines, while a and g bases, which have two rings, are called purines. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. Adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g), and cytosine (c). Web there are four different nucleotides that make up a dna molecule, each differing only in the type of nitrogenous base. • do not include lone pairs in your answer. In rna, it is usually replaced by uracil, but transfer rna (trna) contains trace amounts of thymine. Antiparallel (a), plectonemically coiled (b, c, d) dna strands. Web bases include the pyrimidine bases (cytosine, thymine in dna, and uracil in rna, one ring). Along with cytosine, it is one of the two. Principle in which the nitrogenous bases of the dna molecules bond with one another: Similarly, whatever the amount of guanine (g), the amount of. C and t bases, which have just one ring, are called pyrimidines, while a and g bases, which have two rings, are called purines. In rna, thymine is replaced by the nucleobase uracil. Antiparallel (a), plectonemically. Similarly, whatever the amount of guanine (g), the amount of. These include adenine (a), thymine (t), cytosine (c), and guanine (g), often indicated by their first letters only. The arrows in a are pointed 3’ to 5’, but they illustrate the antiparallel nature of the duplex. There are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. Adenine pairs with thymine, and. The nucleotides arrayed in a 5' to 3' orientation on one strand align with. Web the rules of base pairing explain the phenomenon that whatever the amount of adenine (a) in the dna of an organism, the amount of thymine (t) is the same (called chargaff's rule ). The human genome contains 6 billion base pairs across 46 chromosomes, making. Principle in which the nitrogenous bases of the dna molecules bond with one another: The arrows in a are pointed 3’ to 5’, but they illustrate the antiparallel nature of the duplex. Web in the case of the nucleotides in dna, the sugar is deoxyribose attached to a single phosphate group (hence the name deoxyribonucleic acid), and the base may. Web bases include the pyrimidine bases (cytosine, thymine in dna, and uracil in rna, one ring). C and t bases, which have just one ring, are called pyrimidines, while a and g bases, which have two rings, are called purines. Adenine and thymine are bound to one another via two hydrogen bonds while guanine and cytosine are bound to one. The nucleotides arrayed in a 5' to 3' orientation on one strand align with. Adenine and thymine are bound to one another via two hydrogen bonds while guanine and cytosine are bound to one another via three hydrogen bonds. Principle in which the nitrogenous bases of the dna molecules bond with one another: These include adenine (a), thymine (t), cytosine. They will not be considered in the grading. Adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g), and cytosine (c). The arrows in a are pointed 3’ to 5’, but they illustrate the antiparallel nature of the duplex. • do not include lone pairs in your answer. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases: Adenine and thymine are bound to one another via two hydrogen bonds while guanine and cytosine are bound to one another via three hydrogen bonds. You do not have to consider stereochemistry • you do not have to explicitly draw h atoms. Rna nucleotides may also contain adenine, guanine and cytosine bases, but instead of thymine they have another base.. Adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g), and cytosine (c). Know more about these dna bases in. In rna, thymine is replaced by the nucleobase uracil. Web the rules of base pairing explain the phenomenon that whatever the amount of adenine (a) in the dna of an organism, the amount of thymine (t) is the same (called chargaff's rule ). Adenine. Web there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases: The arrows in a are pointed 3’ to 5’, but they illustrate the antiparallel nature of the duplex. The bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the dna ladder. In rna, it is usually replaced by uracil, but transfer rna (trna) contains trace amounts of thymine. Web chemistry questions and answers. Updated on january 12, 2020 thymine is one of the nitrogenous bases used to build nucleic acids. They will not be considered in the grading. Web diagram showing how adenine and thymine base pair while guanine and cytosine base pair. April 28, 2017 thymine definition thymine is one of the four nitrogenous nucleobases that form the basic building blocks of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). Web the building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: Rna nucleotides may also contain adenine, guanine and cytosine bases, but instead of thymine they have another base. Web the dna of all the living beings is composed of just four bases i.e. Adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g), and cytosine (c). Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. Principle in which the nitrogenous bases of the dna molecules bond with one another: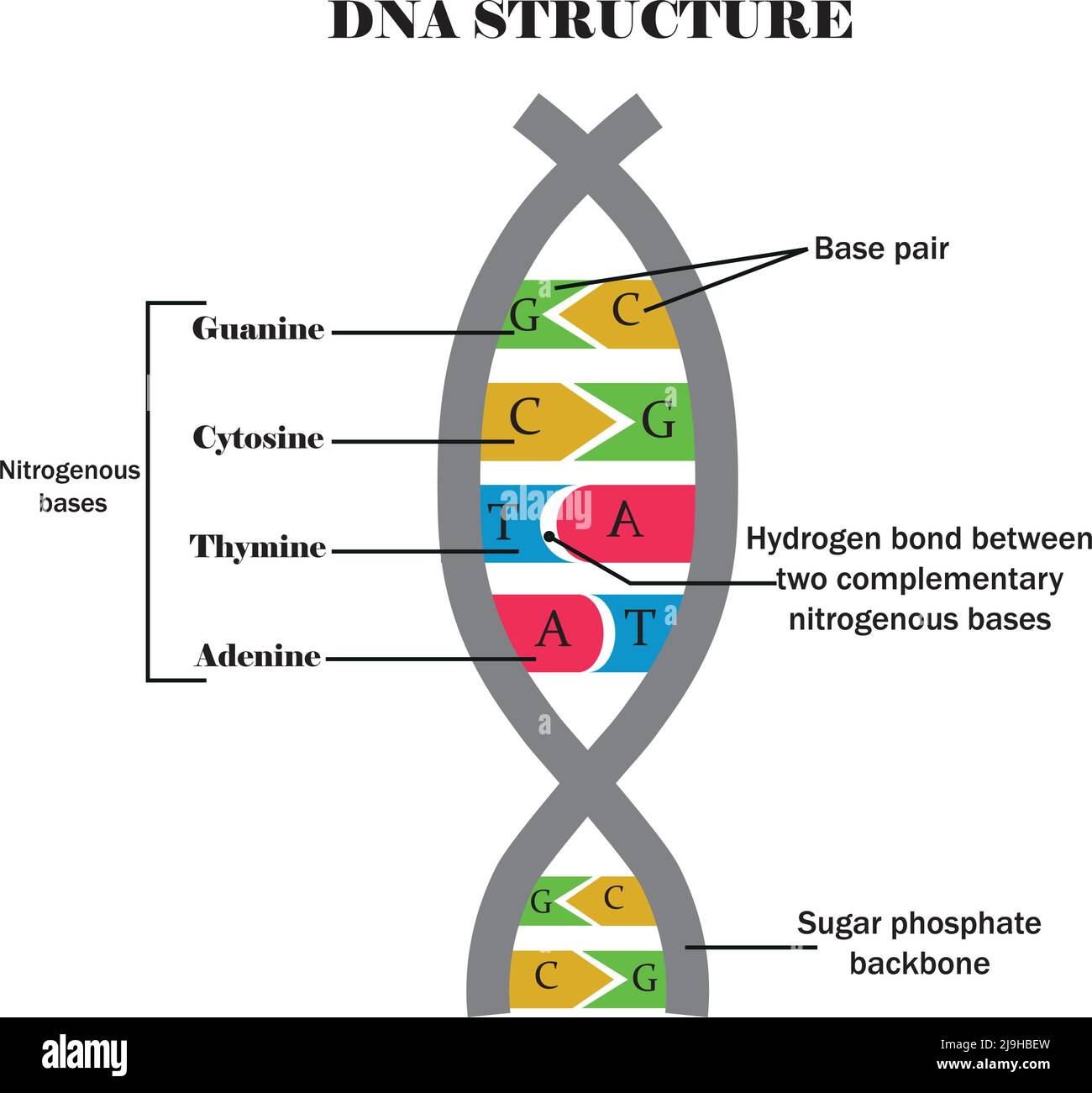
DNA structure.DNA with its components cytosine,guanine,adenine
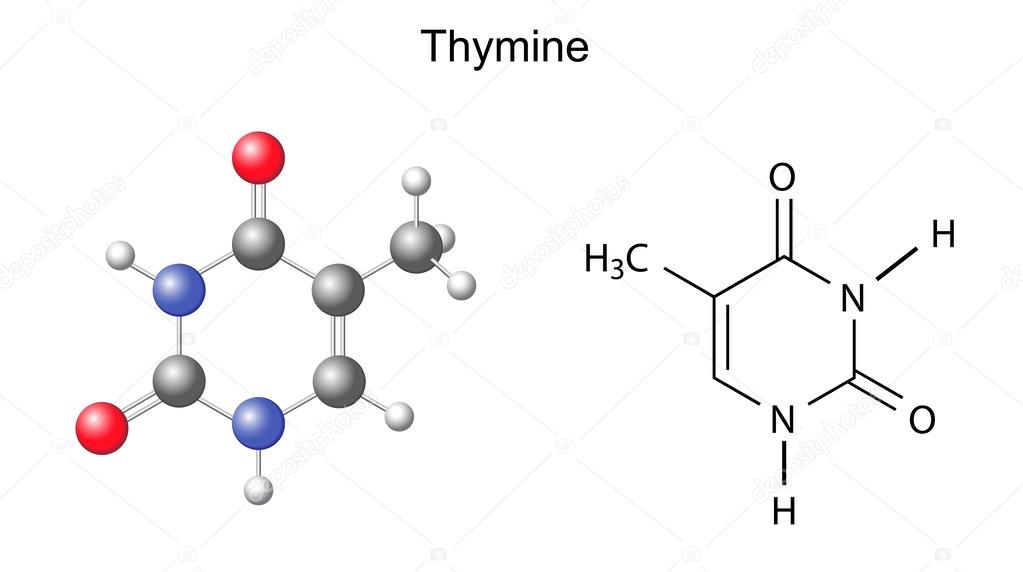
Chemical structural formula and model of thymine (DNA and RNA nitrogen

Structure Of DNA Function, Summary, Diagram & Model
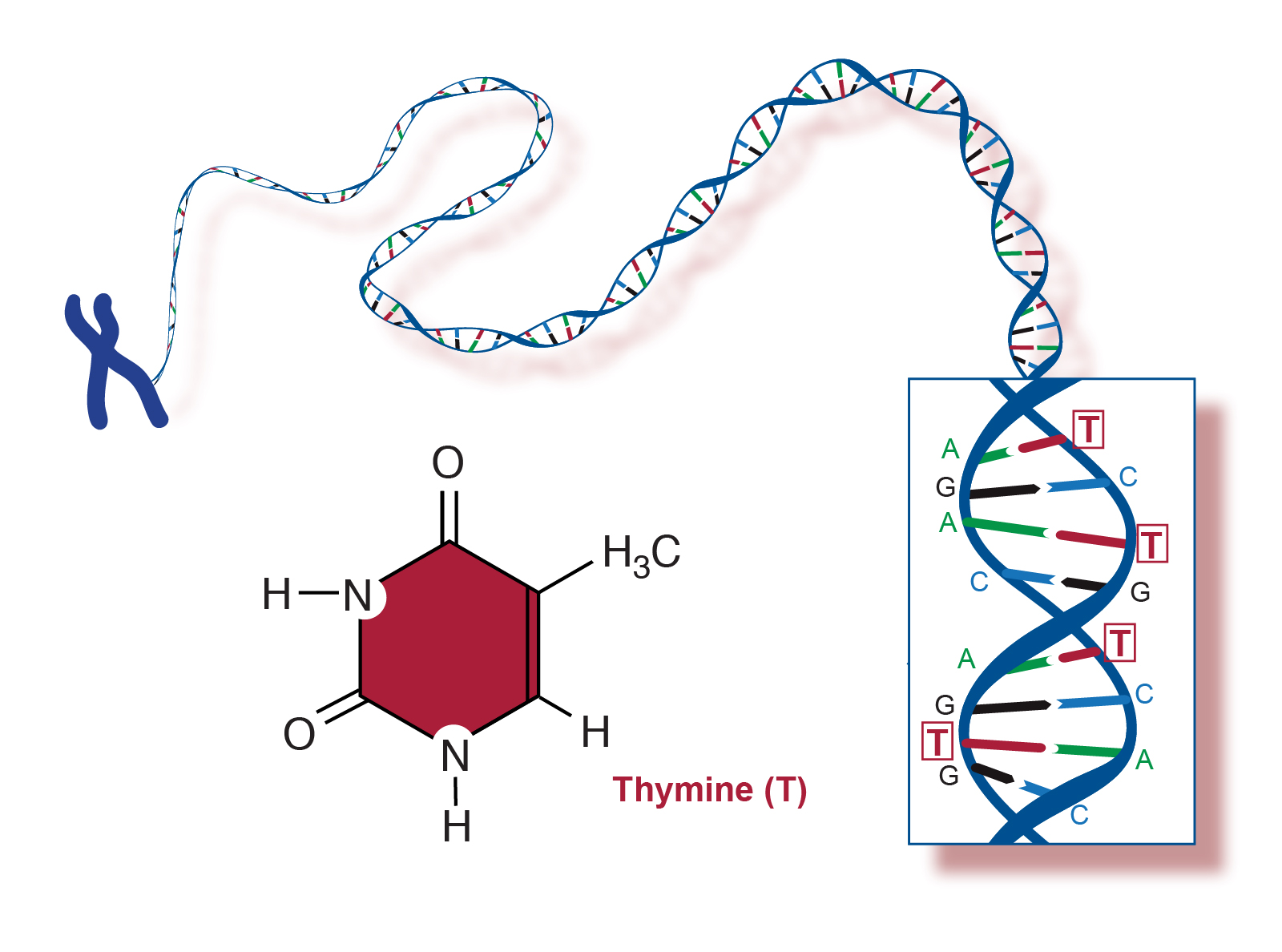
Best Describes the Structure of a Thymine Nucleotide

The Structure of DNA by Ron Vale
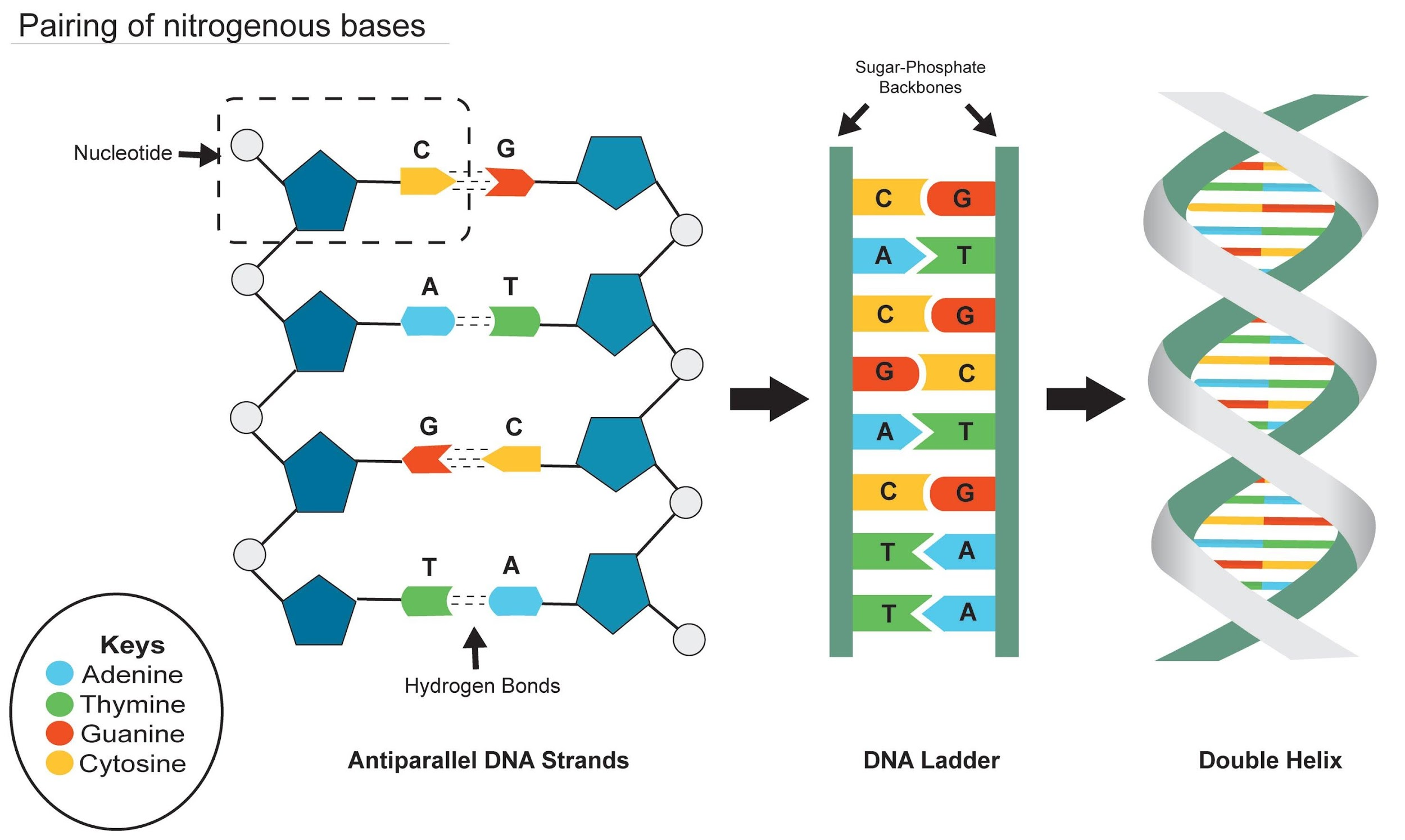
Adenine of DNA is equimolar with(a) Uridine(b) Thymine(c) Guanine(d
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/thymine-in-dna-3e96b05000f94f03992a95d05dee60bc.jpg)
Thymine Definition, Facts, and Functions
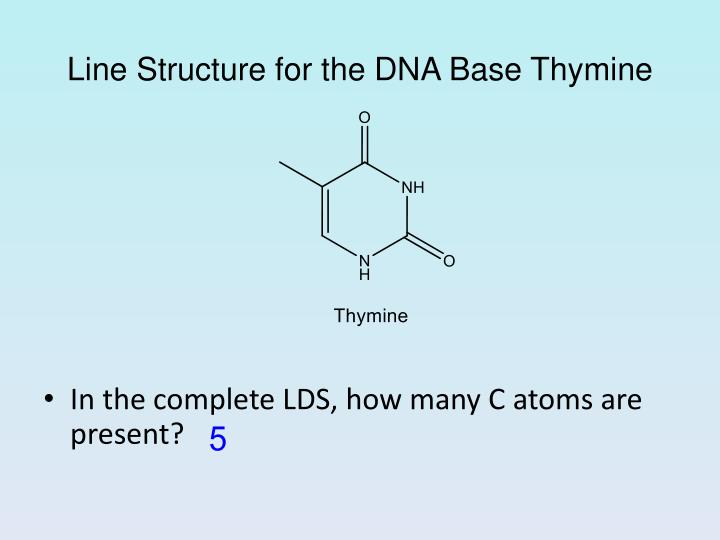
PPT Draw the complete LDS for this compound. How many bonds are in
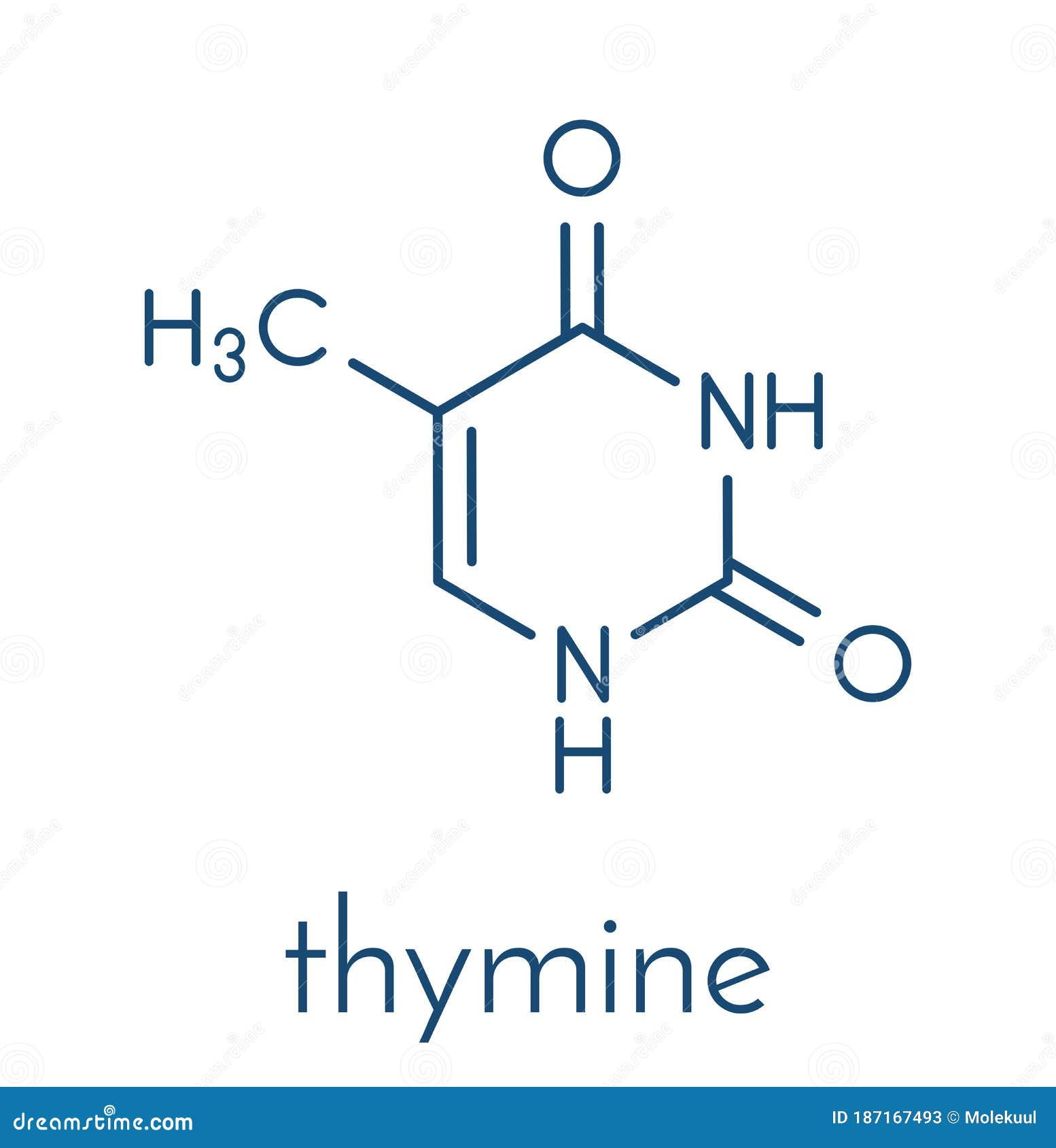
Thymine T Nucleobase Molecule. Present in DNA. Skeletal Formula. Stock

(Left) DNA strand of base pairs (top left) with
December 15, 2023 Definition 00:00 00:42 Thymine (T) Is One Of The Four Nucleotide Bases In Dna, With The Other Three Being Adenine (A), Cytosine (C) And Guanine (G).
Dna, Along With Rna (Ribonucleic Acid), Regulates Hereditary Characteristics In All Living Cells.
The Two Strands Of The Duplex Are Antiparallel And Plectonemically Coiled.
There Are Four Types Of Nitrogenous Bases In Dna.
Related Post: