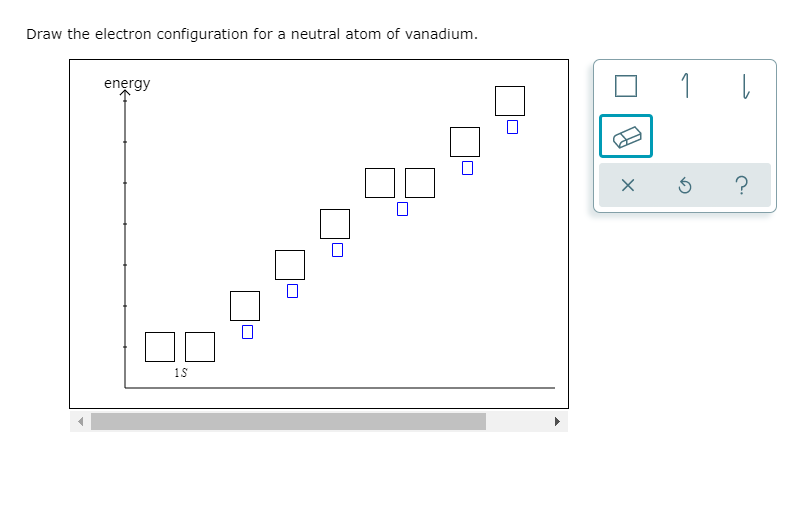
Draw The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Vanadium.
Draw The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Vanadium. - Web full electron configuration of vanadium: The first layer has 2 electrons, the second layer has 8, in the third layer there are 11 electrons and in the fourth there. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2. The neutral atom chlorine (z=17), for instance has 17 electrons. Vanadium's valence electrons, which sit in its outermost shell, are the two 4s electrons and three 3d electrons. Web electron configuration of vanadium is [ar] 3d3 4s2. Web the electronic configuration of anions is assigned by adding electrons according to aufbau principle. Web electron affinity the energy released when an electron is added to the neutral atom and a negative ion is formed. 4s2 and the term symbol is 4f3/2. First ionisation energy the minimum energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom in its. Web the full electron configuration of this element is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2 and its short, abbreviated, or simplified electron configuration is [ar]3d34s2. Web draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of vanadium. Electron configuration can be done in two ways. The distribution of the 23 electrons of vanadium is as follows: Web all of the. Alternatively, this can be abbreviated as [ar]4s²3d³, using the noble gas shorthand. Web the full electron configuration of this element is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2 and its short, abbreviated, or simplified electron configuration is [ar]3d34s2. We add electrons to fill the outermost orbital that is occupied, and then add more electrons to the next higher orbital. Web. The only exception is hydrogen, which has only protons in its nucleus but no neutrons. The first layer has 2 electrons, the second layer has 8, in the third layer there are 11 electrons and in the fourth there. Electronegativity (pauling scale) the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself, expressed on a relative scale. The atomic number. We describe an electron configuration with a symbol that contains three pieces of information ( figure 6.25 ): The electron configuration for a neutral vanadium atom is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d³. The electron configurations and orbital diagrams of these four elements are: Web we can write the electron configuration of vanadium using four different methods: The distribution of the 23 electrons of vanadium. #1 using aufbau principle #2 using periodic table #3 from its bohr model #4 from its orbital diagram let’s break down each method in detail. Although drawing out each orbital may prove to be helpful in determining unpaired electrons, it is very time consuming and often not as practical as the spdf notation, especially for atoms with much longer configurations.. The electron configuration for a neutral vanadium atom is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d³. Web the electronic configuration of anions is assigned by adding electrons according to aufbau principle. Determine the atomic number of vanadium. 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 2. Electrons revolve around the nucleus in a specific orbit. Vanadium(ii) compounds are reducing agents, and vanadium(v) compounds are oxidizing agents. Web electron configuration of vanadium is [ar] 3d3 4s2. Web unless there is a reason to show the empty higher energy orbitals, these are often omitted in an orbital diagram: The only exception is hydrogen, which has only protons in its nucleus but no neutrons. Electrons revolve around the. Determine the atomic number of vanadium. The first layer has 2 electrons, the second layer has 8, in the third layer there are 11 electrons and in the fourth there. Note, although monatomic anions are isoelectronic to a nobel gas, (chloride has the same electron configuration as argon), you write down the electrons of its valence shell. Web unless there. The only exception is hydrogen, which has only protons in its nucleus but no neutrons. 2, 8, 18, 18, 9, 2. #1 using aufbau principle #2 using periodic table #3 from its bohr model #4 from its orbital diagram let’s break down each method in detail. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn. The only exception is hydrogen, which has only protons in its nucleus but no neutrons. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Determine the atomic number of vanadium. Web draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of vanadium: Vanadium's valence electrons, which sit in its outermost shell, are the two. Experiments by various scientists have shown that the nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons. The electron configurations and orbital diagrams of these four elements are: Web electron configuration of barium (ba) [xe] 6s 2. 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 2. The neutral atom chlorine (z=17), for instance has 17 electrons. Web one is the nucleus and the other is the orbit. Electron configuration can be done in two ways. Web typically, you need at least 8 steps to determine the electron configuration, starting with finding the atomic number by looking at the list of orbitals and understanding the notation. The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral vanadium is [ ar ]. Determine the atomic number of vanadium. The only exception is hydrogen, which has only protons in its nucleus but no neutrons. Web the electron configuration for a neutral atom of vanadium (atomic number 23) can be determined by following the periodic table. Write the electron configuration for the neutral atom and then determine the number of electrons that are lost to form the cation. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 6 4d 10 5s 2 5p 6 6s 2. Web electron affinity the energy released when an electron is added to the neutral atom and a negative ion is formed. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2.Solved Draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of

Vanadium Facts

Draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of vanadi Quizlet

Vanadium Electron Configuration (V) with Orbital Diagram

Vanadium Electron Configuration (V) with Orbital Diagram

Orbital Diagram For Vanadium (V) Vanadium Electron Configuration

Vanadium Facts, Symbol, Discovery, Properties, Uses

3d render of atom structure of vanadium isolated over white background

Vanadium Electron Configuration (V) with Orbital Diagram
/Vanadium-58b602345f9b5860464c4ae3.jpg)
Atoms Diagrams Electron Configurations of Elements
We Describe An Electron Configuration With A Symbol That Contains Three Pieces Of Information ( Figure 6.25 ):
You'll Get A Detailed Solution From A Subject Matter Expert That Helps You Learn Core Concepts.
First Ionisation Energy The Minimum Energy Required To Remove An Electron From A Neutral Atom In Its.
1S 2 2S 2 2P 6 3S 2 3P 6 3D 10 4S 2 4P 6 4D 10 5S 2 5P 6 5D 1 6S 2.
Related Post: