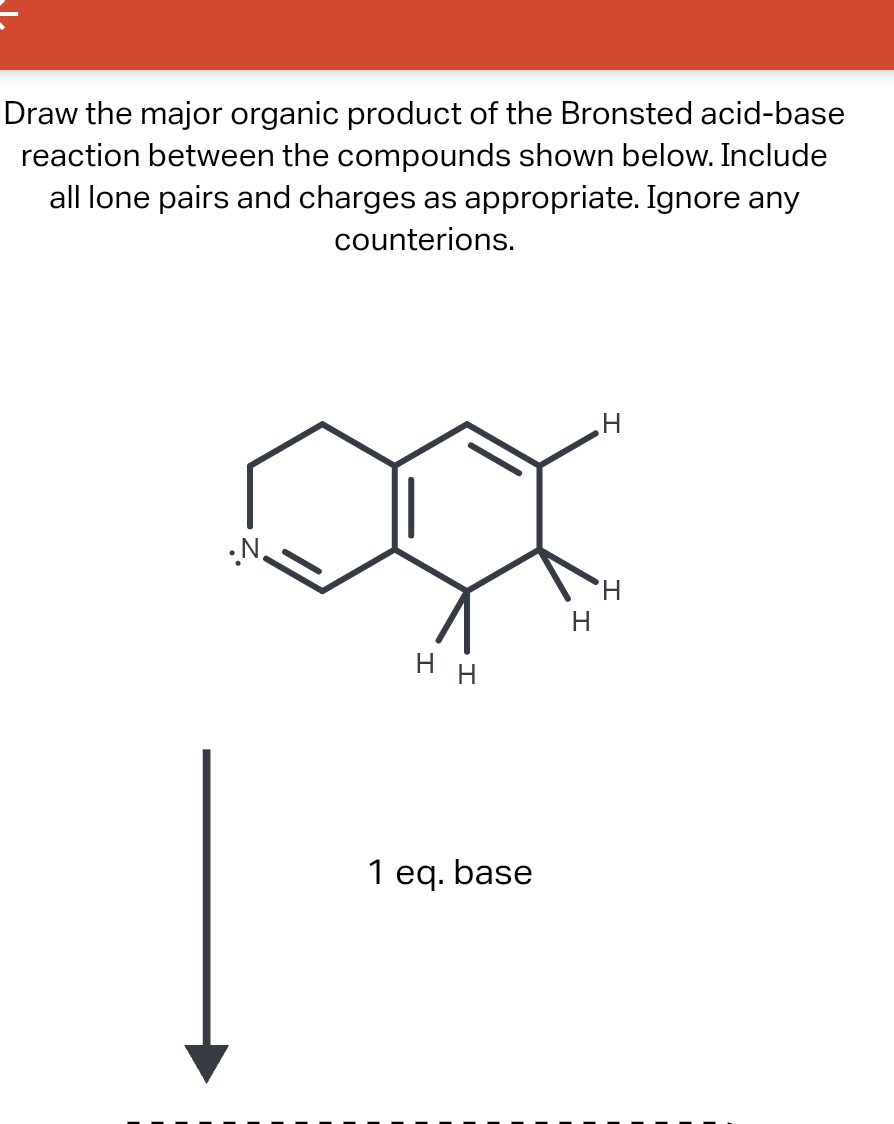
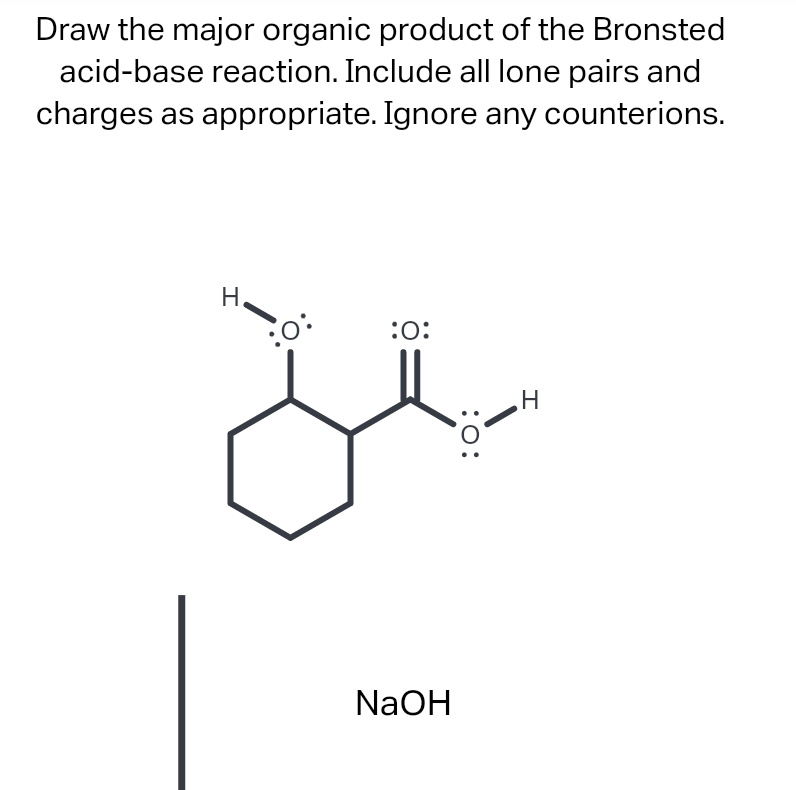
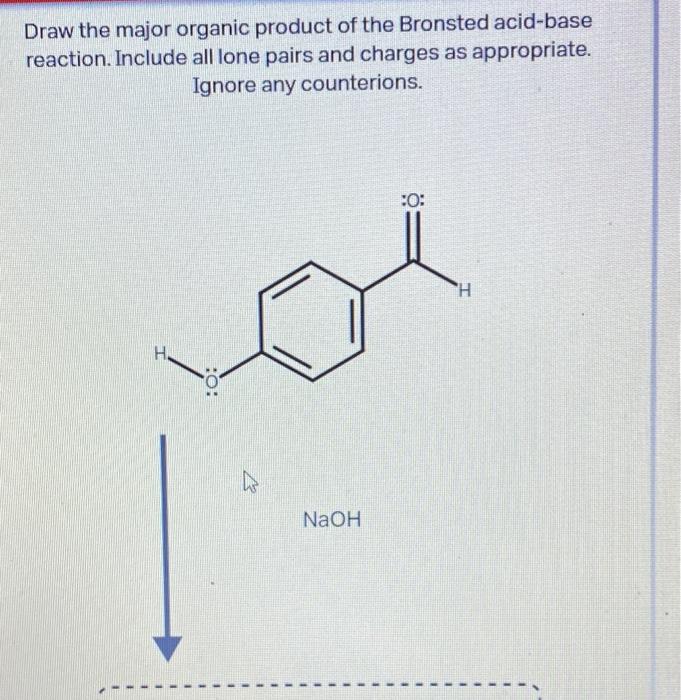
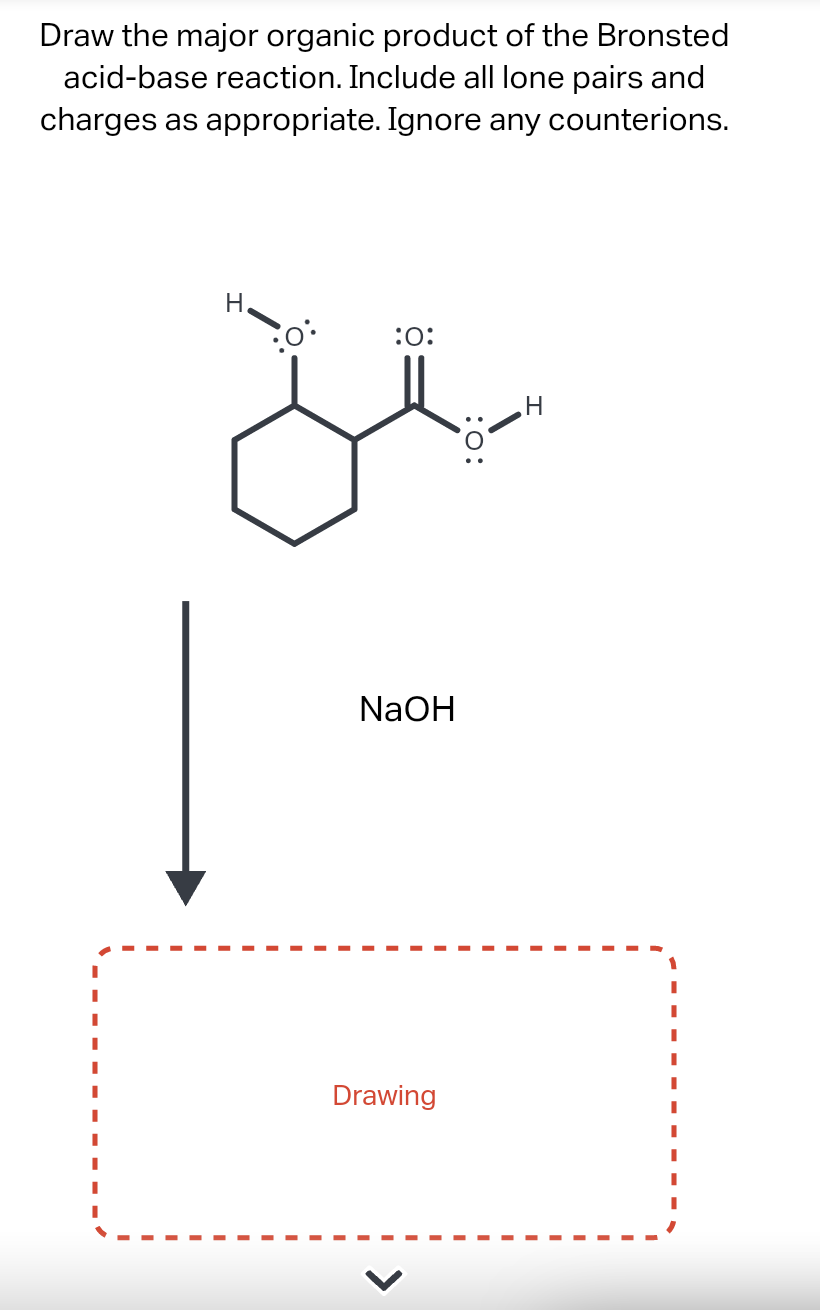
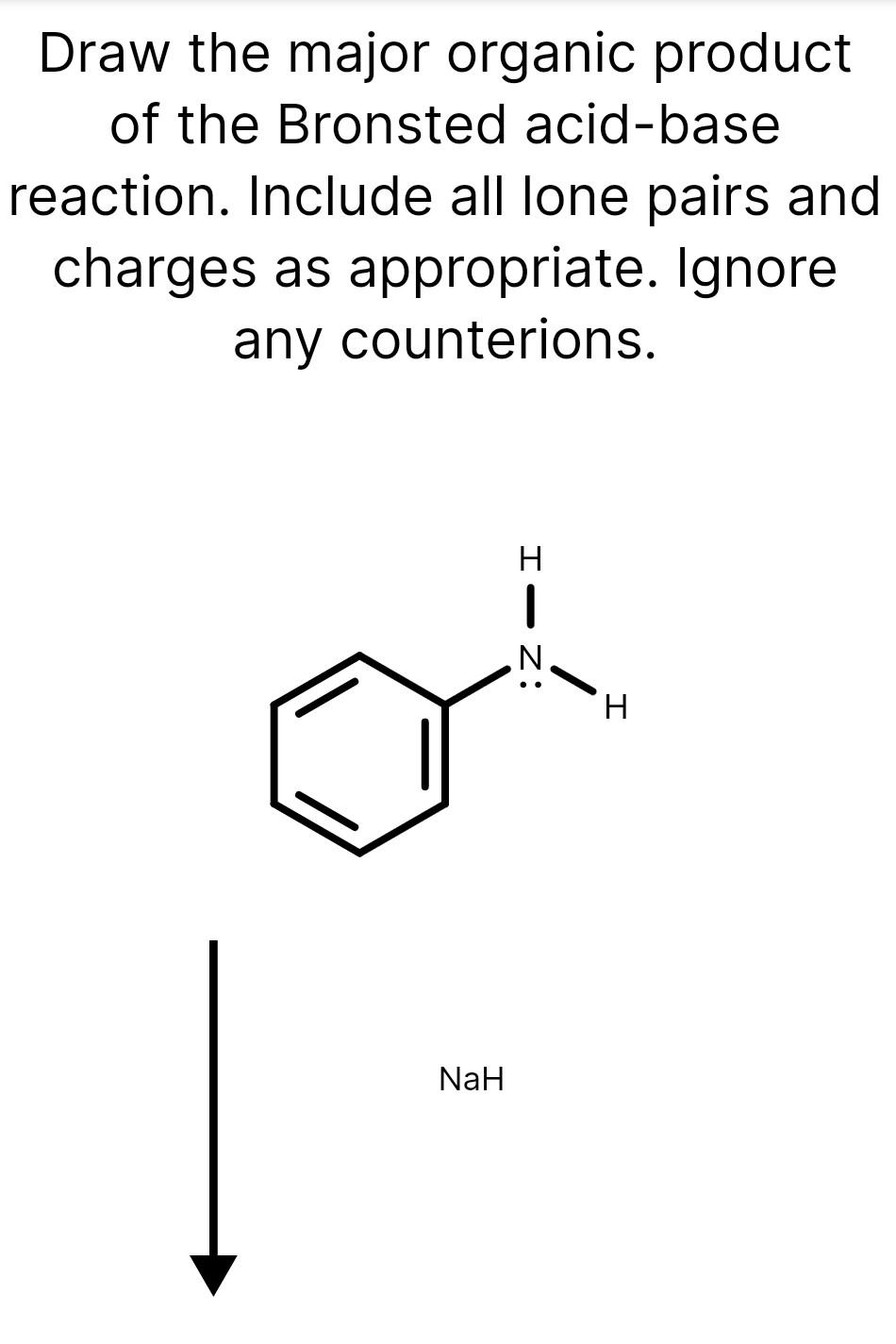
Draw The Major Organic Product Of The Bronsted Acid-Base Reaction
Draw The Major Organic Product Of The Bronsted Acid-Base Reaction - Naoh select to fdit draw the organic product of. The product is water (the conjugate acid of hydroxide) and chloride ion (the conjugate base of hcl). Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. You do not have to consider stereochemistry. Draw the reaction between the compounds. In the reverse of this reaction, acetate ion is the base and methylammonium ion (protonated methylamine) is the acid. The product would be alcohol. What makes a compound acidic (likely to donate a proton) or basic (likely to accept a proton)? A proton is transferred from hcl, the acid, to hydroxide, the base. This problem has been solved! What makes a compound acidic (likely to donate a proton) or basic (likely to accept a proton)? You have undoubtedly seen this. Lone pairs have been left out. Web chemistry questions and answers. B) rank the conjugate base in the order you would predict, from most to least stable. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Questions tips & thanks want to join the conversation? Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Lone pairs have been left out. The product is water (the conjugate acid of hydroxide) and chloride ion (the conjugate base of hcl). Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Include all ione pairs and charges as appropriate. Web bookshelves organic chemistry map: A conjugate acid is the particle produced when a base accepts a proton. Base drawing h organic chemistry 9th edition isbn: That's a mixture of two acids. What makes a compound acidic (likely to donate a proton) or basic (likely to accept a proton)? They will not be considered in the grading. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Naoh select to draw using the arrows provided in the image, predict the product of this reaction. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Naoh select to fdit draw the organic product of. A) for each compound show its conjugate base. Draw the reaction between the compounds. So in other words, it's going to lose a hydrogen. Web chemistry questions and answers. This problem has been solved! The product would be alcohol. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Base drawing h organic chemistry 9th edition isbn: You have undoubtedly seen this. What makes a compound acidic (likely to donate a proton) or basic (likely to accept a proton)? So in other words, it's going to lose a hydrogen. You have undoubtedly seen this. In the reverse of this reaction, acetate ion is the base and methylammonium ion (protonated methylamine) is the acid. Base drawing h organic chemistry 9th edition isbn: Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. In the reverse of this reaction, acetate ion is the base and methylammonium ion (protonated methylamine) is the acid. Do not include lone pairs in your answer; Lone pairs have been left out. The product would be alcohol. A proton is transferred from hcl, the acid, to hydroxide, the base. You have undoubtedly seen this. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Web bookshelves organic chemistry map: Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Naoh select to draw using the arrows provided in the image, predict the product of this reaction. For example, when hydrogen fluoride dissolves in water and ionizes, protons are transferred from hydrogen fluoride molecules to water molecules, yielding hydronium ions and fluoride ions: So let's, really quickly, review what this. B) rank the conjugate base in the order you would predict, from most to least stable. There is a transfer of the proteins from benzoic acid to hydrocarbonate. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. 2) curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. In the reverse of this reaction, acetate ion is the base and methylammonium ion (protonated methylamine) is the acid. So remember here that an acid is going to be a hydrogen donor. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Lone pairs have been left out. The product is water (the conjugate acid of hydroxide) and chloride ion (the conjugate base of hcl). A conjugate acid is the particle produced when a base accepts a proton. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate.Solved Draw the major organic product of the Bronsted
Solved Draw the major organic product of the Bronsted
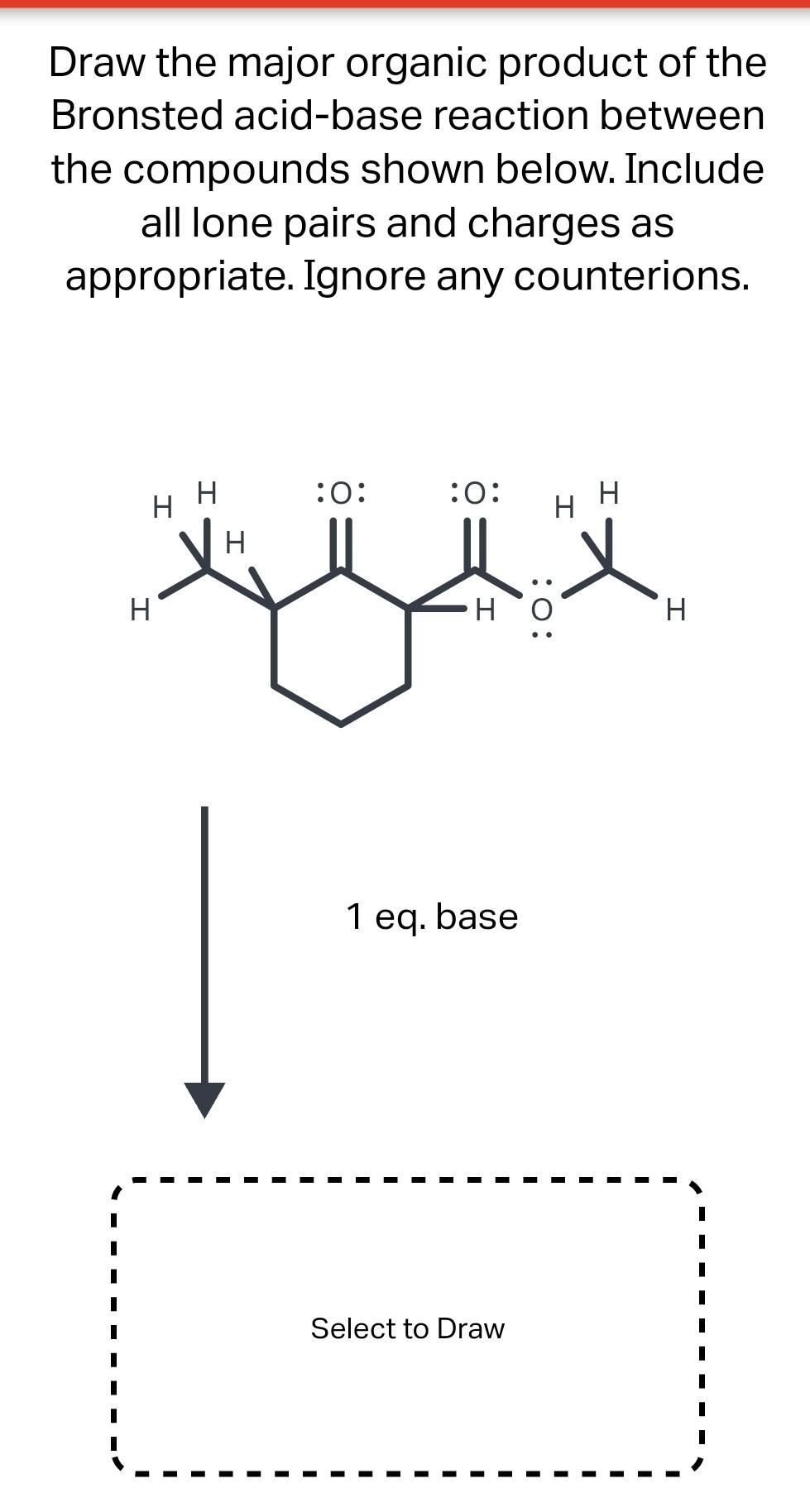
Solved Draw the major organic product of the Bronsted
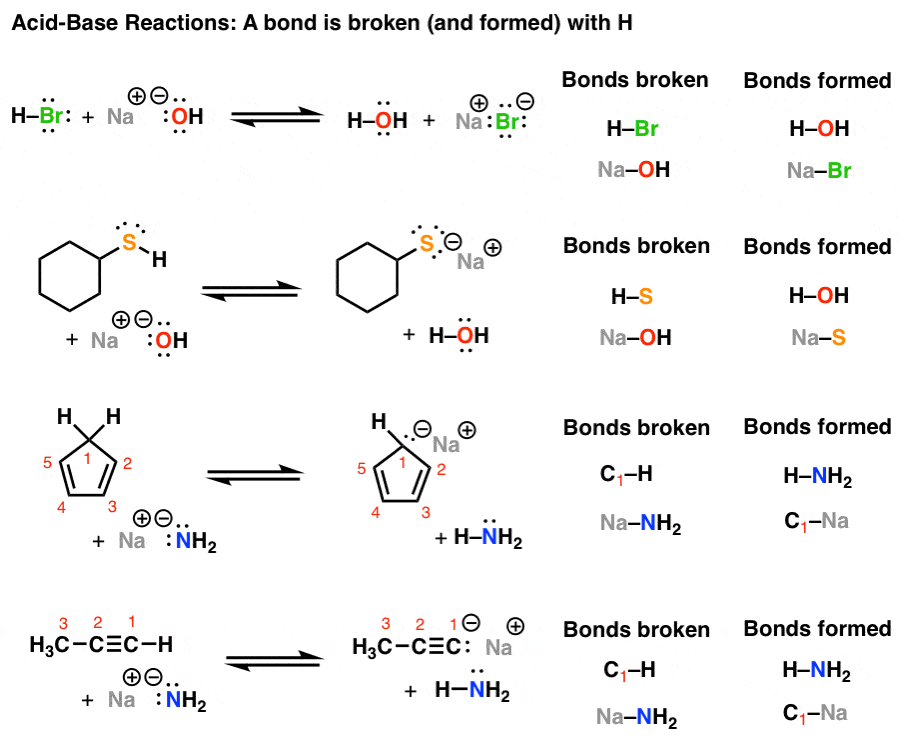
Introduction to AcidBase Reactions Master Organic Chemistry
Solved Draw the major organic product of the Bronsted
Draw the major organic product of the Bronsted acidbase reaction
[Solved] Draw the major organic product of the Bronsted acidbase
Solved Draw the major organic product of the Bronsted
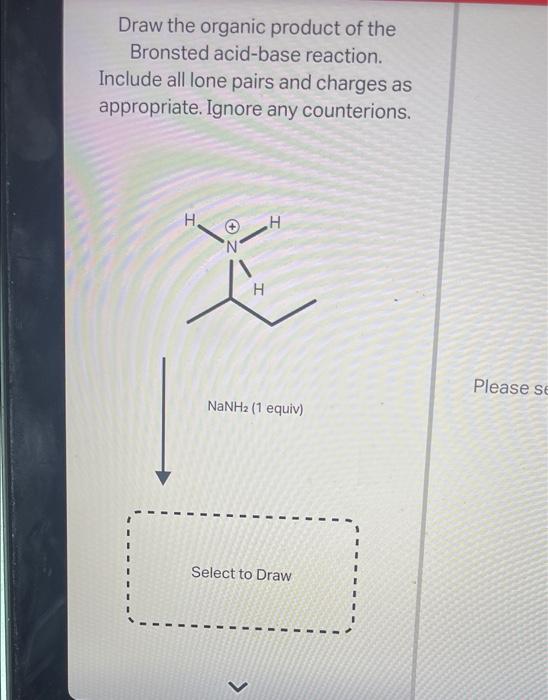
Solved Draw the organic product of the Bronsted acidbase
Solved Draw the organic product of the Bronsted acidbase
Draw The Reaction Between The Compounds.
Web Organic Chemistry I (Cortes) 11:
They Will Not Be Considered In The Grading.
Include All Lone Pairs And Charges As Appropriate.
Related Post: