Draw The Structure Of An Atom
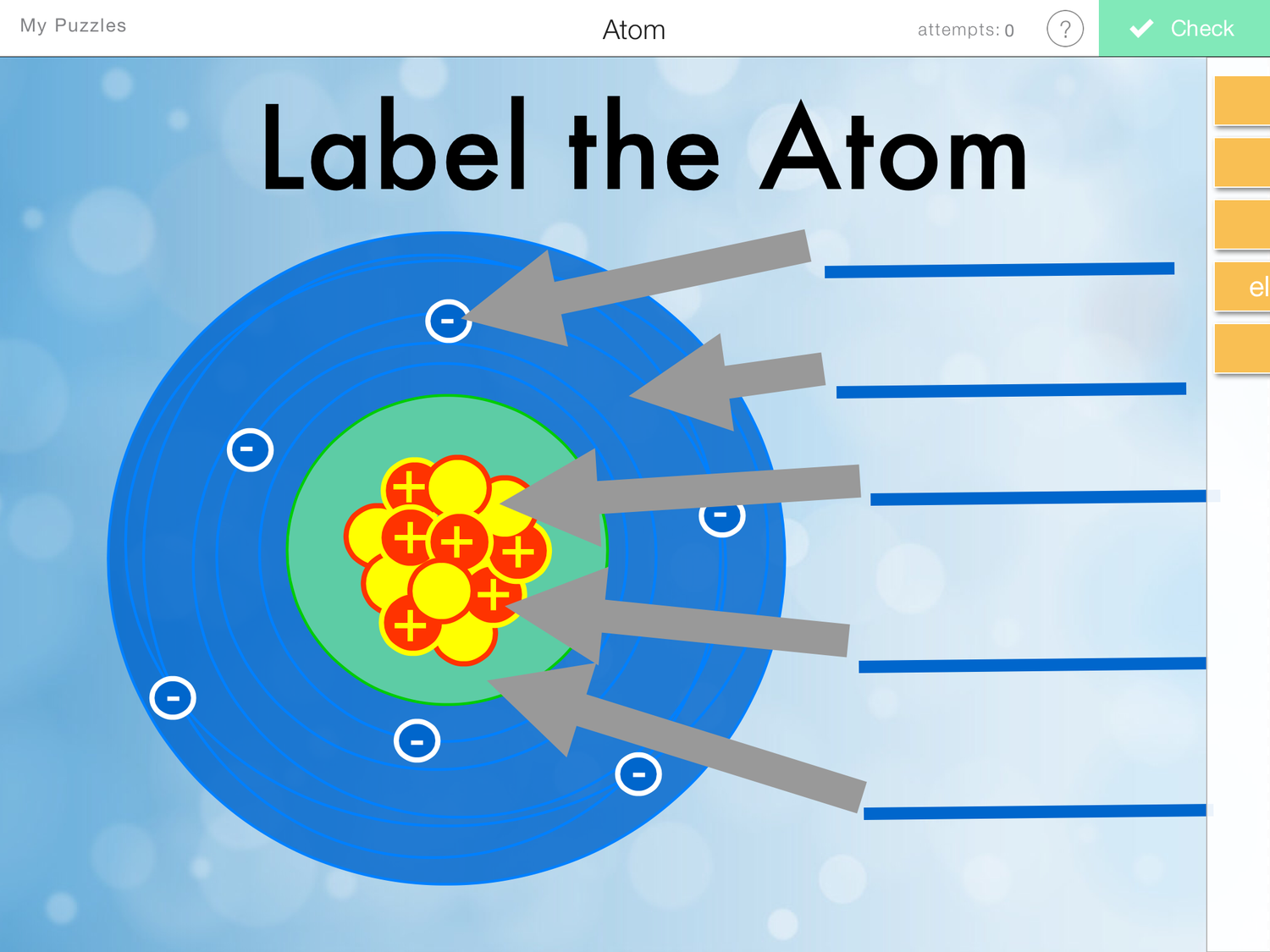
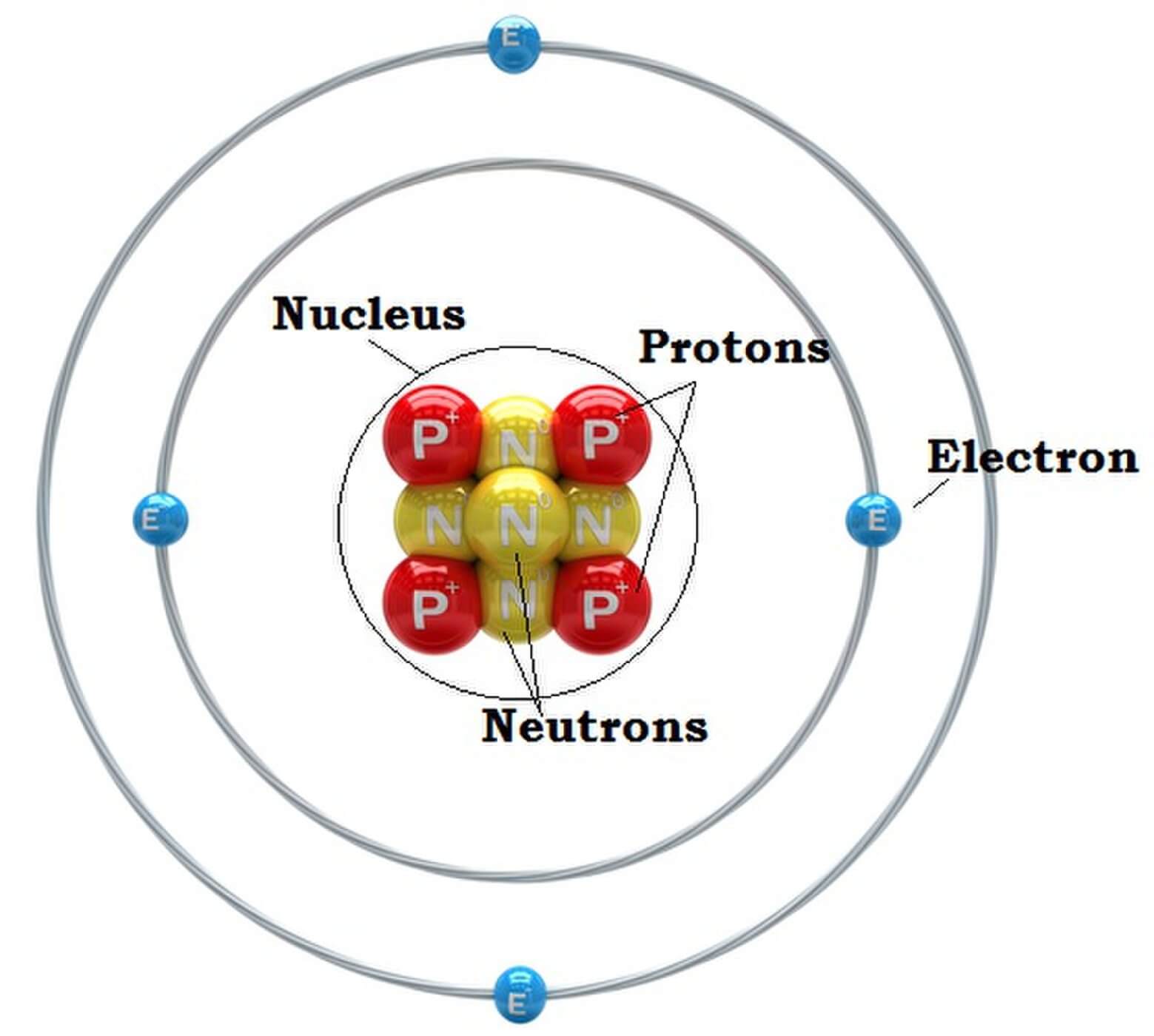
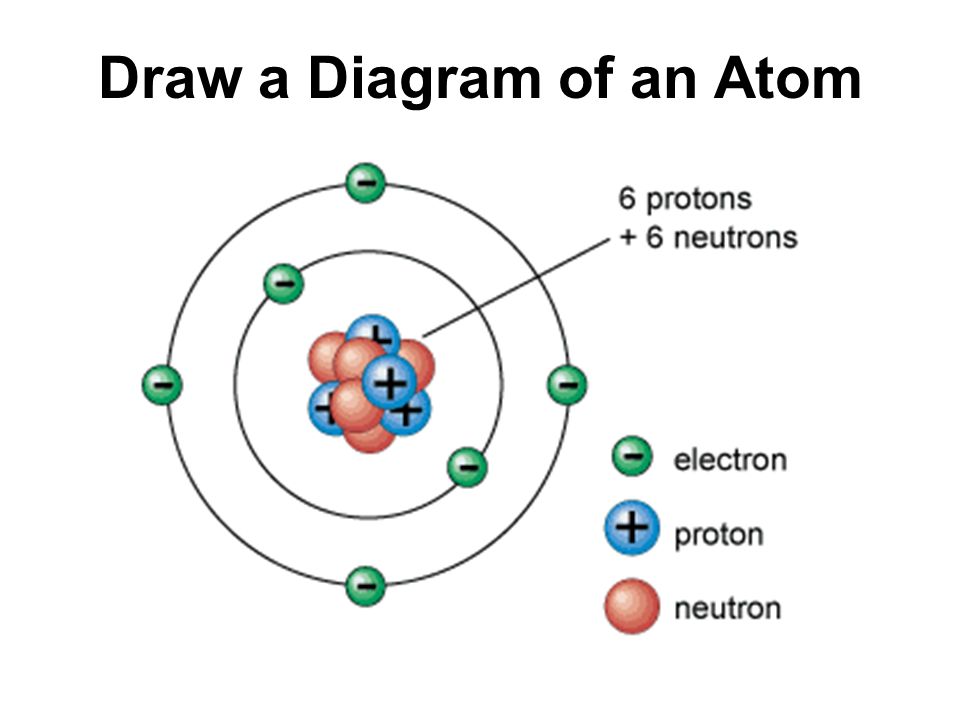
Draw The Structure Of An Atom - The specific arrangement of electrons in orbitals of an atom determines many of the chemical properties of that atom. Protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus and are together called nucleons. Other particles exist as well, such as alpha and beta particles. Figure out how many electrons the molecule must have, based on the number of valence electrons in each atom. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. Web draw tower grating (dtg) with large capacity, long distance, fast response and other advantages is rapidly becoming the current mainstream fiber optic sensors, but want to write high reflectivity fiber on the draw tower fiber is particularly difficult. Web in order to track down where a given electron lives in an atom, you need to know not only how far from the nucleus it is found (which determines its energy level, since electrons further out from the nucleus tend to have higher energy) but also the type of orbital that it can be found in. Unit 2 structure of atom. In this tutorial on atomic structure, you will learn about the different parts of the atom, along with the subatomic particles found in each region. The nucleus is positively charged since the proton is positively charged and the neutron is neutral. Most of an atom's mass is in the nucleus—… a typical atom consists of three subatomic particles: Upload a structure file or draw using a molecule editor. Web this allows us to determine which orbitals are occupied by electrons in each atom. Unit 1 welcome to physical chemistry. An atom consists of three elementary subatomic particles, i.e., protons, electrons, and. Upload a structure file or draw using a molecule editor. Web properties of atom: Web the nucleus contains the majority of an atom’s mass because protons and neutrons are much heavier than electrons, whereas electrons occupy almost all of an atom’s volume. Web atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. Add. Search by structure or substructure. Web this allows us to determine which orbitals are occupied by electrons in each atom. Then play a game to test your ideas! Add enough electrons (dots) to the outer atoms to. The structure of the atom. The structure of the atom. Web atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. Web in this video we cover the structure of atoms, what are subatomic particles, energy levels, and stable and reactive atoms.transcript and notesatomic structur. Web the atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus. The energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n, increases. In this tutorial on atomic structure, you will learn about the different parts of the atom, along with the subatomic particles found in each region. Upload a structure file or draw using a molecule editor. The nucleus is positively charged since the proton is positively charged and. Web erase the c in the center circle, and draw in your protons. Upload a structure file or draw using a molecule editor. Web step 1: Most of an atom's mass is in the nucleus—… a typical atom consists of three subatomic particles: The nucleus is positively charged since the proton is positively charged and the neutron is neutral. Web draw tower grating (dtg) with large capacity, long distance, fast response and other advantages is rapidly becoming the current mainstream fiber optic sensors, but want to write high reflectivity fiber on the draw tower fiber is particularly difficult. Search by structure or substructure. Orbital energies and atomic structure. Therefore, it is important to further study the grating formation mechanism. Web a typical atom consists of three subatomic particles: All atoms except hydrogen contain three basic subatomic particles: The following article provides you with diagrams that will help you understand the structure of an atom better. Web the atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral). Web atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. Web properties of atom: Web a layer of an atom is somewhat similar to a sheet of paper. You will also learn about the properties that can be found through the subatomic particles. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. Web a typical atom consists of three subatomic particles: Unit 1 welcome to physical chemistry. 1) electrons, 2) protons, and neutrons. Web erase the c in the center circle, and draw in your protons. Web atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. Unit 2 structure of atom. Most of an atom's mass is in the nucleus—… a typical atom consists of three subatomic particles: Search by structure or substructure. Orbital energies and atomic structure. An atom is the basic unit of matter. Web if you want (or need) to draw a model of an atom, we'll show you how! Web erase the c in the center circle, and draw in your protons. Web step 1: Other particles exist as well, such as alpha and beta particles. Figure out how many electrons the molecule must have, based on the number of valence electrons in each atom. Web a typical atom consists of three subatomic particles: Neutrons and protons are found at the center of the atom within a dense region called the nucleus. Upload a structure file or draw using a molecule editor. Since protons are the same as the. Atoms have protons and neutrons in the center, making the nucleus, while the electrons orbit the nucleus. Web in order to track down where a given electron lives in an atom, you need to know not only how far from the nucleus it is found (which determines its energy level, since electrons further out from the nucleus tend to have higher energy) but also the type of orbital that it can be found in.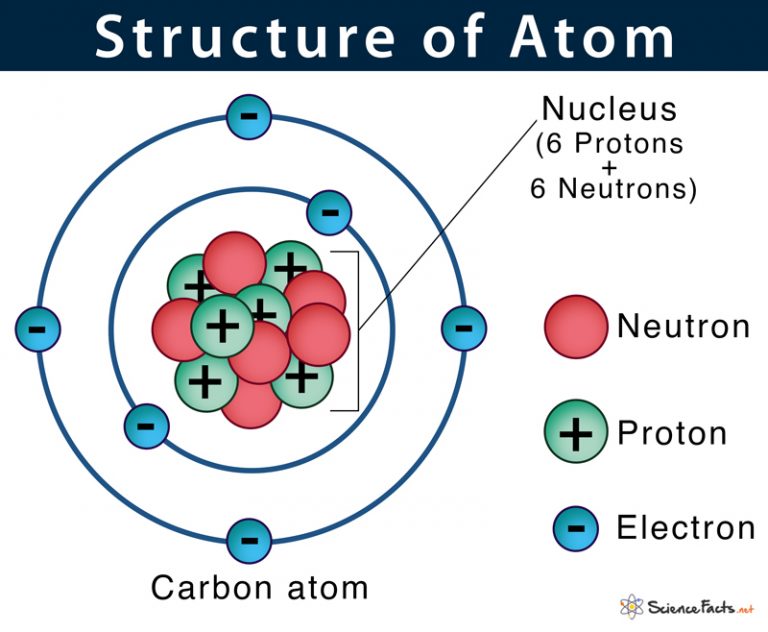
Atom Definition, Structure & Parts with Labeled Diagram
What is an Atom? Definitions & Examples Let us learn Basics News Bugz
Skills Practice AMAZING 8TH GRADE SCIENTISTS

Simple model of atom structure with electrons vector image on
Label Parts of an Atom — Learning in Hand with Tony Vincent
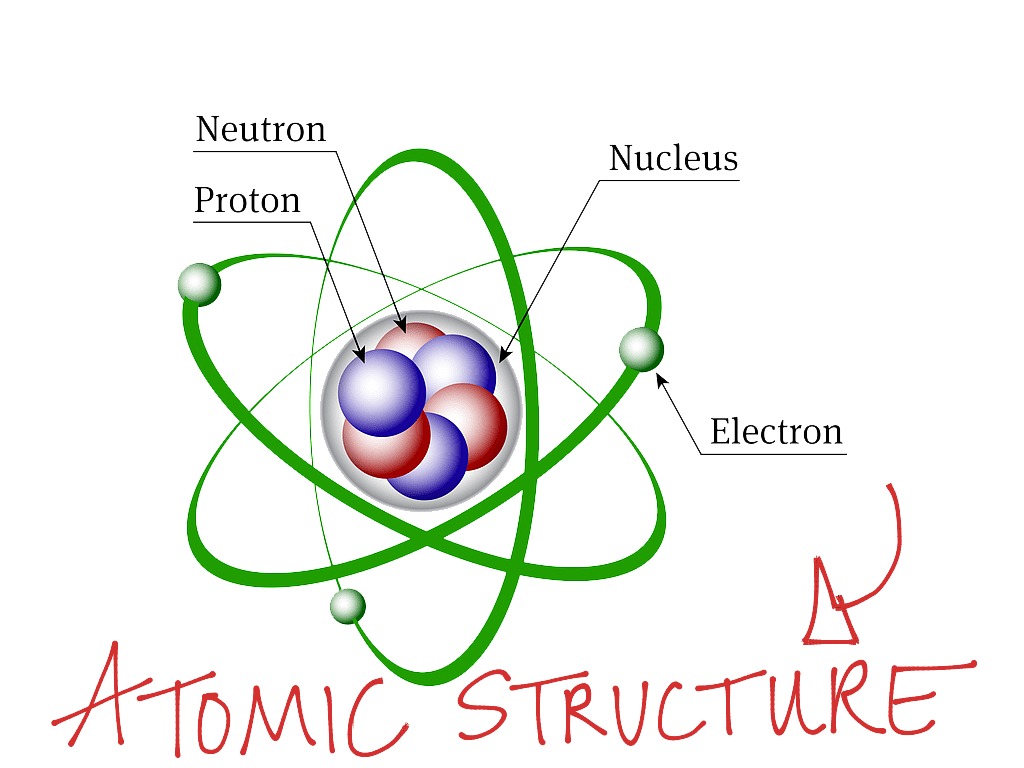
Basic Atomic Structure Science, Atoms And Elements ShowMe
/GettyImages-141483984-56a133b65f9b58b7d0bcfdb1.jpg)
Basic Model of the Atom Atomic Theory

How To Draw An Atom, Step by Step, Drawing Guide, by Dawn DragoArt

Learn the Parts of an Atom

Atomic Structure Biochemistry
Web Build An Atom Out Of Protons, Neutrons, And Electrons, And See How The Element, Charge, And Mass Change.
The Diameter Of An Atom Is On The Order Of 10 −10 M, Whereas The Diameter Of The Nucleus Is Roughly 10 −15 M—About 100,000 Times Smaller.
Web This Allows Us To Determine Which Orbitals Are Occupied By Electrons In Each Atom.
The Following Article Provides You With Diagrams That Will Help You Understand The Structure Of An Atom Better.
Related Post: