Drawing Light Rays
Drawing Light Rays - This concept is illustrated in figure 16.3 , which also shows how the angles are measured relative to the line perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray strikes it. Using the polyline lasso tool to paint light. For now i have mine set to normal so that i can see. Some general rules for drawing light. Web draw the refracted ray at 0 degrees (i.e., trace the incident ray straight through the first boundary). Then, use the mirror/lens equations to calculate (a) the location of the image and (b) its magnification. The point marked p is the focal point of the lens. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Identifying the path of a light ray that passes through a concave lens. They transfer enough energy to electrons so they can escape from the pull of the atom’s nucleus and turn the atom into an ion. How to draw ray diagram i hope you enjoy this online lecture on how to draw ray. Then, use the mirror/lens equations to calculate (a) the location of the image and (b) its magnification. Each of the following diagrams shows a ray entering a thin concave lens. Worksheet/activity file previews docx, 312.67 kb pdf, 267.9 kb pptx, 219.71 kb light. Web it explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging lens, diverging lens, concave mirrors, and convex mirrors. How to draw ray diagram i hope you enjoy this online lecture on how to draw ray. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Rays going through the focus (or coming. Web use ray tracing to get an approximate location for the image. It explains how to distinguish a real image from a virtual image and how to tell if. 25k views 11 years ago. Web drawing light rays worksheet dcjsss subject: Rays going through the focus (or coming from the focus if the object is closer to the focus) bend. Worksheet/activity file previews docx, 312.67 kb pdf, 267.9 kb pptx, 219.71 kb light lesson 1 worksheet 2 this worksheet focuses on the drawing of scientific light ray diagrams. Web a ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Light and sound age range: This concept is illustrated in figure 16.3 , which also. Light and sound age range: Once these incident rays strike the lens, refract them according to the three rules of refraction for converging. This concept is illustrated in figure 16.3 , which also shows how the angles are measured relative to the line perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray strikes it. Web use ray tracing. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Some general rules for drawing light. Each of the following diagrams shows a ray entering a thin concave lens. Web if a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror, then the behavior of the light. Web use ray tracing to get an approximate location for the image. Web how to draw refracted light rays. Second, we draw light rays from the image to the eye. For now i have mine set to normal so that i can see. At the second boundary, the normal line must be drawn (labeled n) and the angle of incidence. Worksheet/activity file previews docx, 312.67 kb pdf, 267.9 kb pptx, 219.71 kb light lesson 1 worksheet 2 this worksheet focuses on the drawing of scientific light ray diagrams. Web light reflection in plane mirror 2. It passes through the center of the lens. Once these incident rays strike the lens, refract them according to the three rules of. Complex objects. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Web a ray diagram is a diagram that traces the path that light takes in order for a person to view a point on the image of an object. They transfer enough energy to electrons so they can escape from the pull of the. Web it explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging lens, diverging lens, concave mirrors, and convex mirrors. How does a lens or mirror form an image? Broken lines from the image to mirror indicate virtual rays. This concept is illustrated in figure 16.3 , which also shows how the angles are measured relative to the line perpendicular to the. Light and sound age range: Worksheet/activity file previews docx, 312.67 kb pdf, 267.9 kb pptx, 219.71 kb light lesson 1 worksheet 2 this worksheet focuses on the drawing of scientific light ray diagrams. At the second boundary, the normal line must be drawn (labeled n) and the angle of incidence (between the incident ray and the normal) must be measured. In this tutorial i outline a very simple technique for painting straight beams of light. Before the ray enters the lens, it is parallel to the optical axis. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. The point marked p is the focal point of the lens. Web a ray diagram is a diagram that traces the path that light takes in order for a person to view a point on the image of an object. On the diagram, rays (lines with arrows) are drawn for the incident ray and the reflected ray. Web light reflection in plane mirror 2. Simulate colors simulate colors (wavelengths) of light sources, mixture of colors, color filtering, and chromatic dispersion of glasses. Observe how the image changes when you adjust the focal length of the lens, move the object, or move the screen. Broken lines from the image to mirror indicate virtual rays. Web the previous two questions are about the rules for drawing light rays for a converging lens: Low energy uv and visible light cause electron transitions. Web the rays are shown in blue, and the point(s) in yellow (real) or orange (virtual).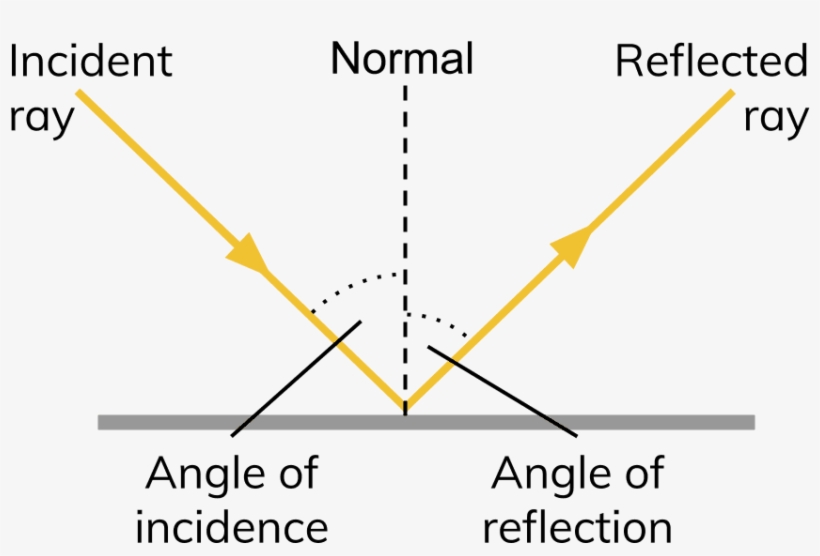
Diagram Of A Light Ray Being Reflected By Diagram Free Transparent

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
![[DIAGRAM] Practice Drawing Ray Diagrams](https://d77da31580fbc8944c00-52b01ccbcfe56047120eec75d9cb2cbd.ssl.cf6.rackcdn.com/bd276252-f823-4183-9f43-273213b7a302/rule-1---ray-parallel-to-principal-axis-will-pass-through-focus-2---teachoo.jpg)
[DIAGRAM] Practice Drawing Ray Diagrams

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
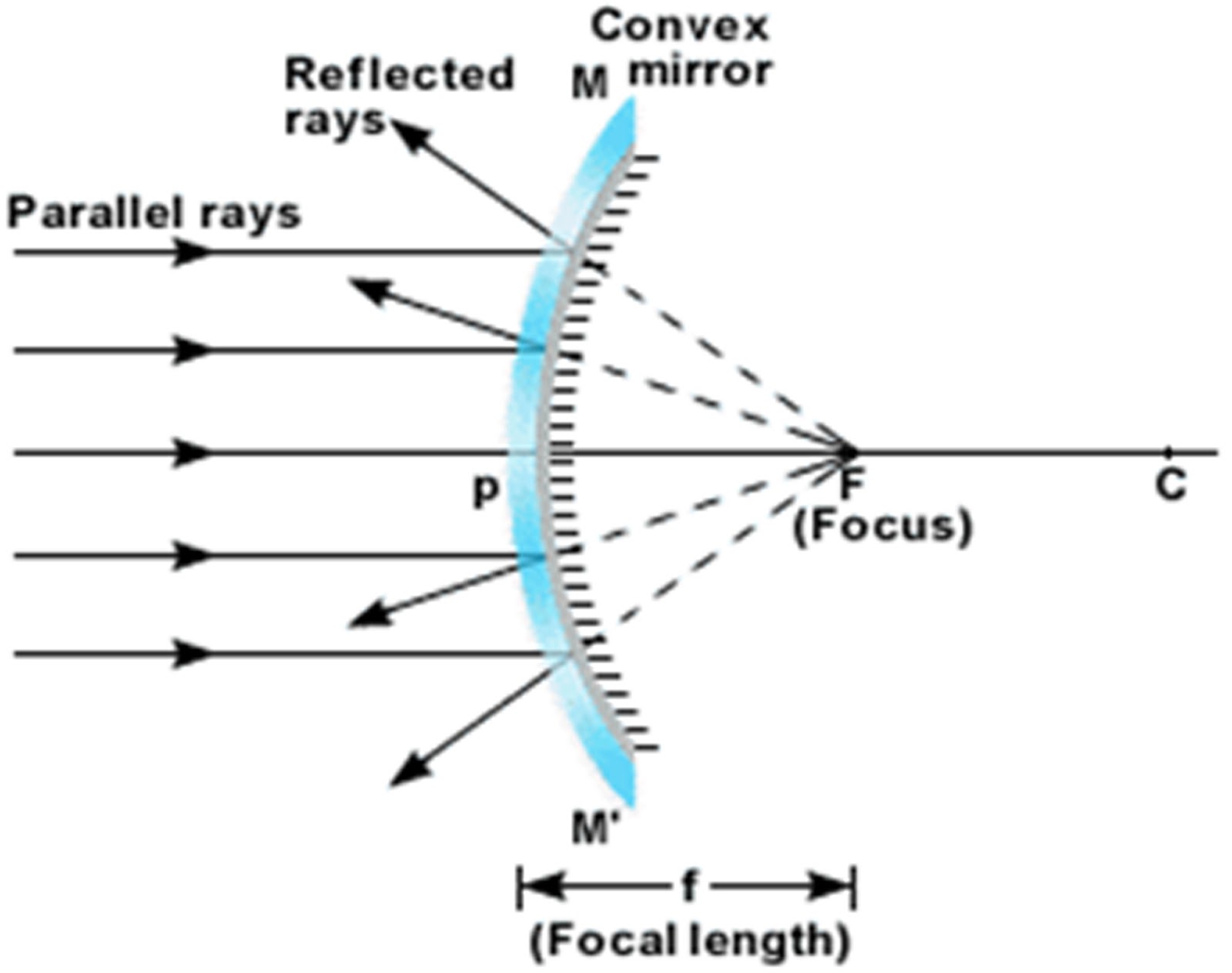
CHAPTER 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION(CBSE CLASS 10) DEX ACADEMY

How to draw light ray diagrams for reflection in plane mirrors? YouTube
[DIAGRAM] Practice Drawing Ray Diagrams

Laws of Reflection of Light MarkhasColon

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
Complex Objects Such As People Are Often Represented By Stick Figures Or Arrows.
Then, Use The Mirror/Lens Equations To Calculate (A) The Location Of The Image And (B) Its Magnification.
Web See How Light Rays Are Refracted By A Lens Or Reflected By A Mirror.
They Transfer Enough Energy To Electrons So They Can Escape From The Pull Of The Atom’s Nucleus And Turn The Atom Into An Ion.
Related Post:
![[DIAGRAM] Practice Drawing Ray Diagrams](http://www.sliderbase.com/images/referats/1483b/(16).PNG)