Drawing Of Convection
Drawing Of Convection - Web convection is the transfer of thermal energy by particles moving through a fluid. Show how the super hot core of the earth is like the candle heating the mantle above it until the hot mantle rises towards the surface of the earth. Web a convection cell is an area within a fluid where warm material is rising in the center and cold material is sinking at the edges. This is the most common and relatable household example of convection. Web in this video, we examine how energy travels from one place to another on earth's surface, in the atmosphere, and in space. Web convection currents are flowing fluid that is moving because there is a temperature or density difference within the material. Web convection is heat transfer by the macroscopic movement of mass. Convection cells in earth's atmosphere are responsible for the blowing of wind, and can be found in a variety of other natural and manmade phenomena. Convection can produce horizontal flow that can cause (or is related to) plate motions. Hot air rises, transferring heat upward. Hot air rises, transferring heat upward. These cells occur at small scales within a pot of boiling. It involves a bulk transfer of portions of the fluid. Web convection is the process of heat transfer in fluids by the actual motion of matter. The thermal convection in this model is similar to the convection that is inferred for the earth's. Because particles within a solid are fixed in place, convection currents are seen only in gases and liquids. The cycle repeats and a pattern of motion forms. Web convection, process by which heat is transferred by movement of a heated fluid such as air or water. Convection can be natural or forced and generally transfers thermal energy faster than conduction.. Web a convection cell is a system in which a fluid is warmed, loses density and is forced into a region of greater density. Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of a heated material. Relate this picture to the convection cells observed in the pie pan. This process heats from the earth’s core, mantle, and internal radioactive. Moving particles transfer thermal energy through a fluid by forming convection currents. Convection can produce horizontal flow that can cause (or is related to) plate motions. Primary means of transferring heat in solids. Web mantle convection is like earth’s engine. Web faqs activities what is the definition of convection in science? Web faqs activities what is the definition of convection in science? In the atmosphere, on a hot summer day, the surface of the earth is heated by energy from the sun. This is the most common and relatable household example of convection. The definition of convection in science is the transfer of heat through liquids or gases. Web on the. Web convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy ). This is the most common and relatable household example of convection. In the atmosphere, on a hot summer day, the surface of the earth is heated. It may be natural or forced. Convection occurs when hot air. The definition of convection in science is the transfer of heat through liquids or gases. Heat is always transferred from higher t to lower t. How is heat transferred through convection? It may be natural or forced. Web the circulation of rising and sinking air is called convection. Web convection is the transfer of internal energy into or out of an object by the physical movement of a surrounding fluid that transfers the internal energy along with its mass. Web a convection cell is an area within a fluid where warm. Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of a heated material. Web in this video, we examine how energy travels from one place to another on earth's surface, in the atmosphere, and in space. It happens in liquids and gases. Although the heat is initially transferred between the object and the fluid by conduction, the bulk transfer of. Hot air rises, transferring heat upward. Heating water on a stove is a good example. Convection can be natural or forced and generally transfers thermal energy faster than conduction. Web convection is heat transfer via the movement of a fluid, such as air or water. It shapes the earth’s surface features and plays a crucial role in geological processes such. Web faqs activities what is the definition of convection in science? The cycle repeats and a pattern of motion forms. Mantle convection is a fundamental driver of tectonic plate movements. Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of a heated material. Web detailed explanation of the convection examples. Web convection, process by which heat is transferred by movement of a heated fluid such as air or water. Although the heat is initially transferred between the object and the fluid by conduction, the bulk transfer of energy comes from the motion of the fluid. How is heat transferred through convection? It may be natural or forced. The water at the top of the pot becomes hot because water near the heat source rises. Web convection is heat transfer via the movement of a fluid, such as air or water. Hot air rises, transferring heat upward. Natural convection results from the tendency of most fluids to expand when heated—i.e., to become less dense and to rise as a. It involves a bulk transfer of portions of the fluid. This process heats from the earth’s core, mantle, and internal radioactive decay, which moves towards the surface of the earth. Web the circulation of rising and sinking air is called convection.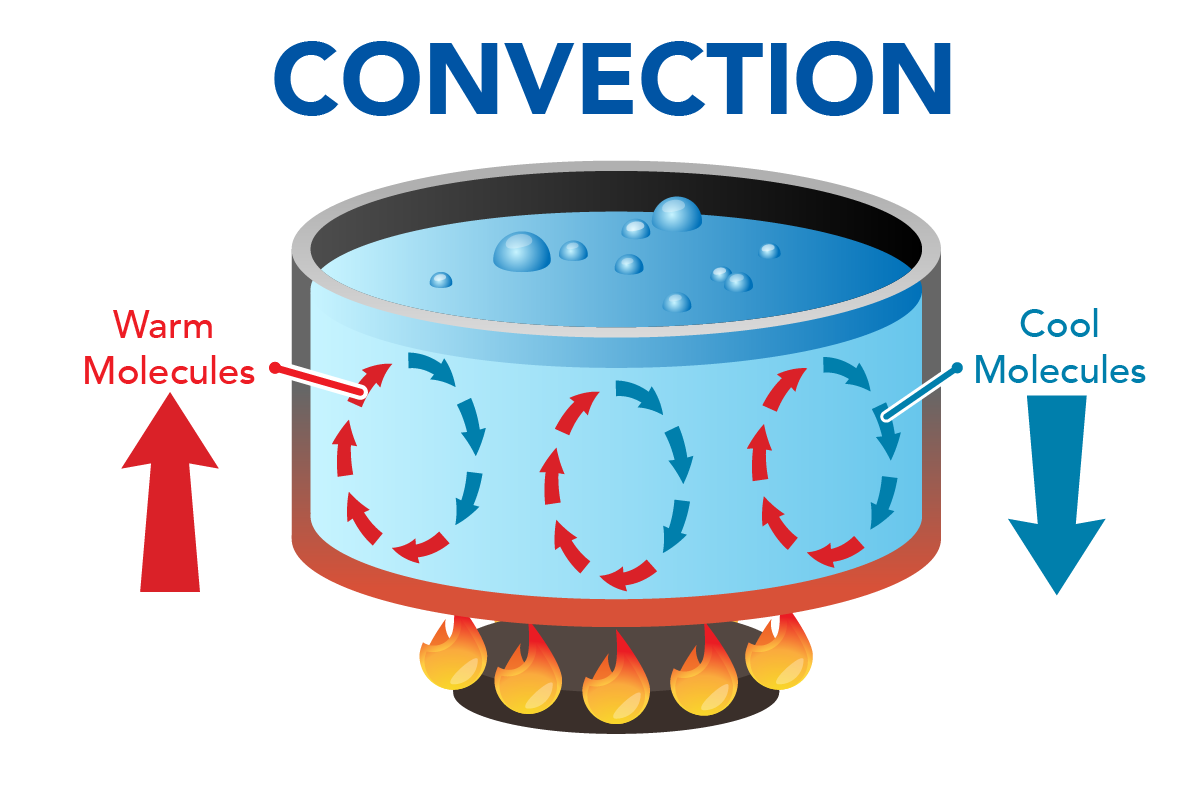
Introduction to Heat Transfer Let's Talk Science

Examples Of Convection In The Atmosphere CONVEKTION CDR
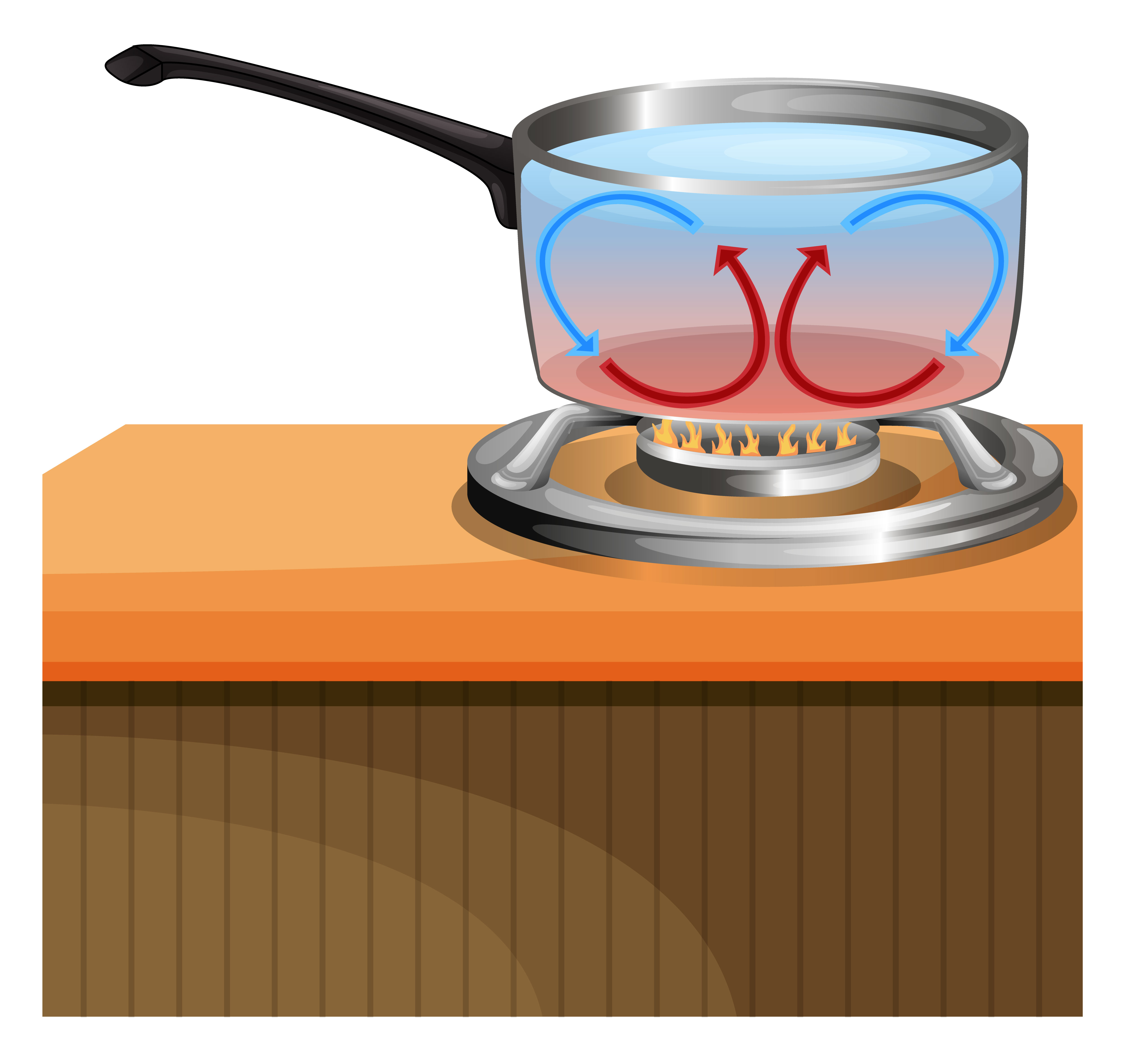

Convection Currents 448214 Vector Art at Vecteezy

How Do Convection Currents Work Inside The Earth CONVEKTION CDE

Convection
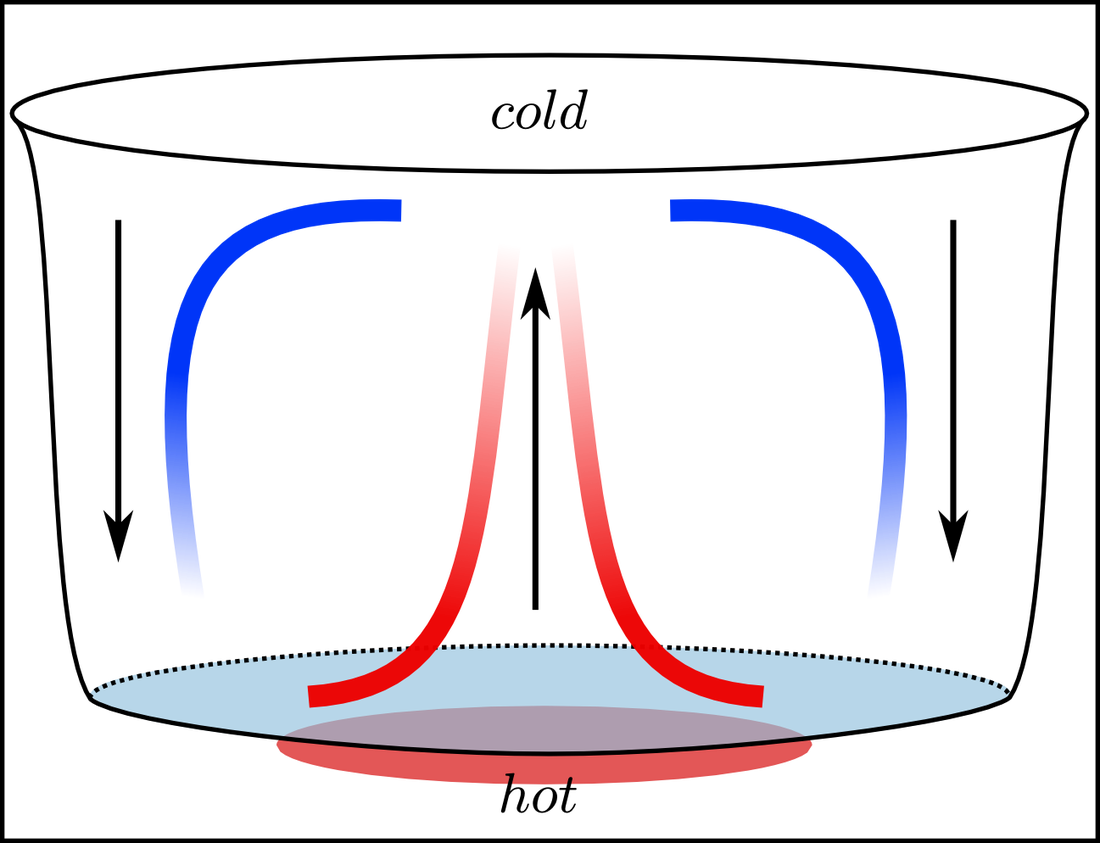
Convection in the Sun Science News
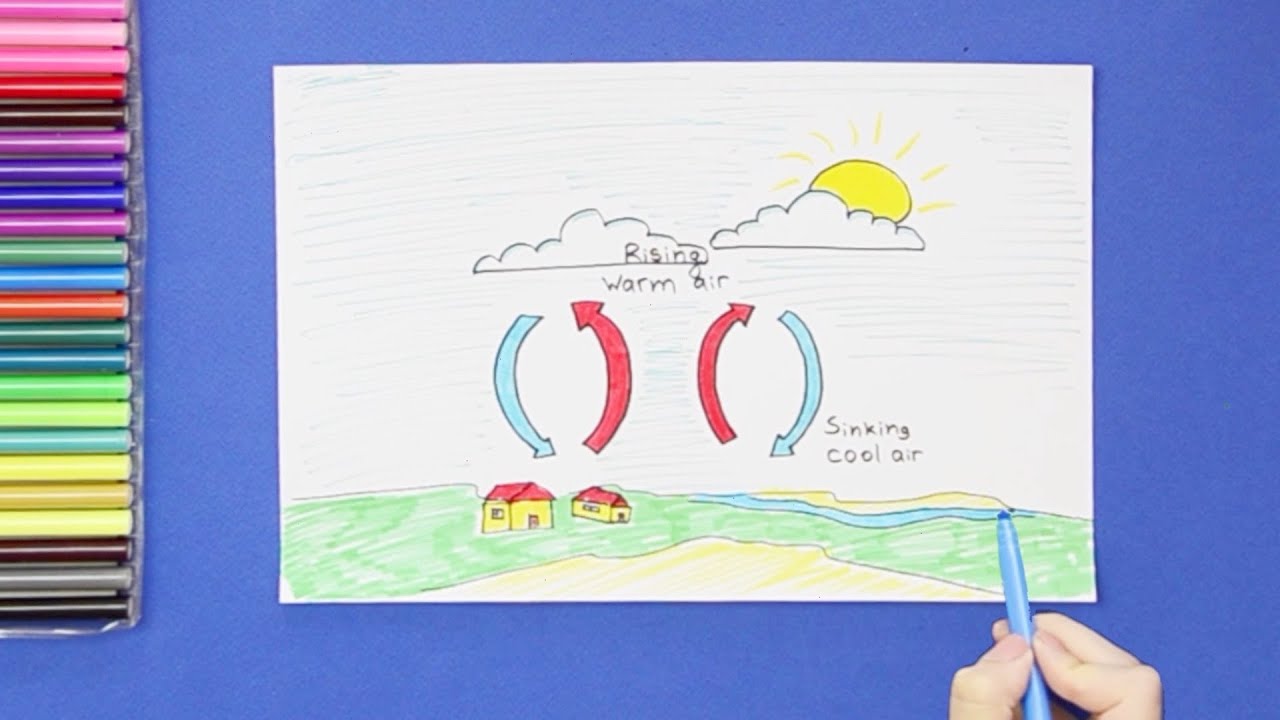
How to draw convection currents in atmosphere YouTube
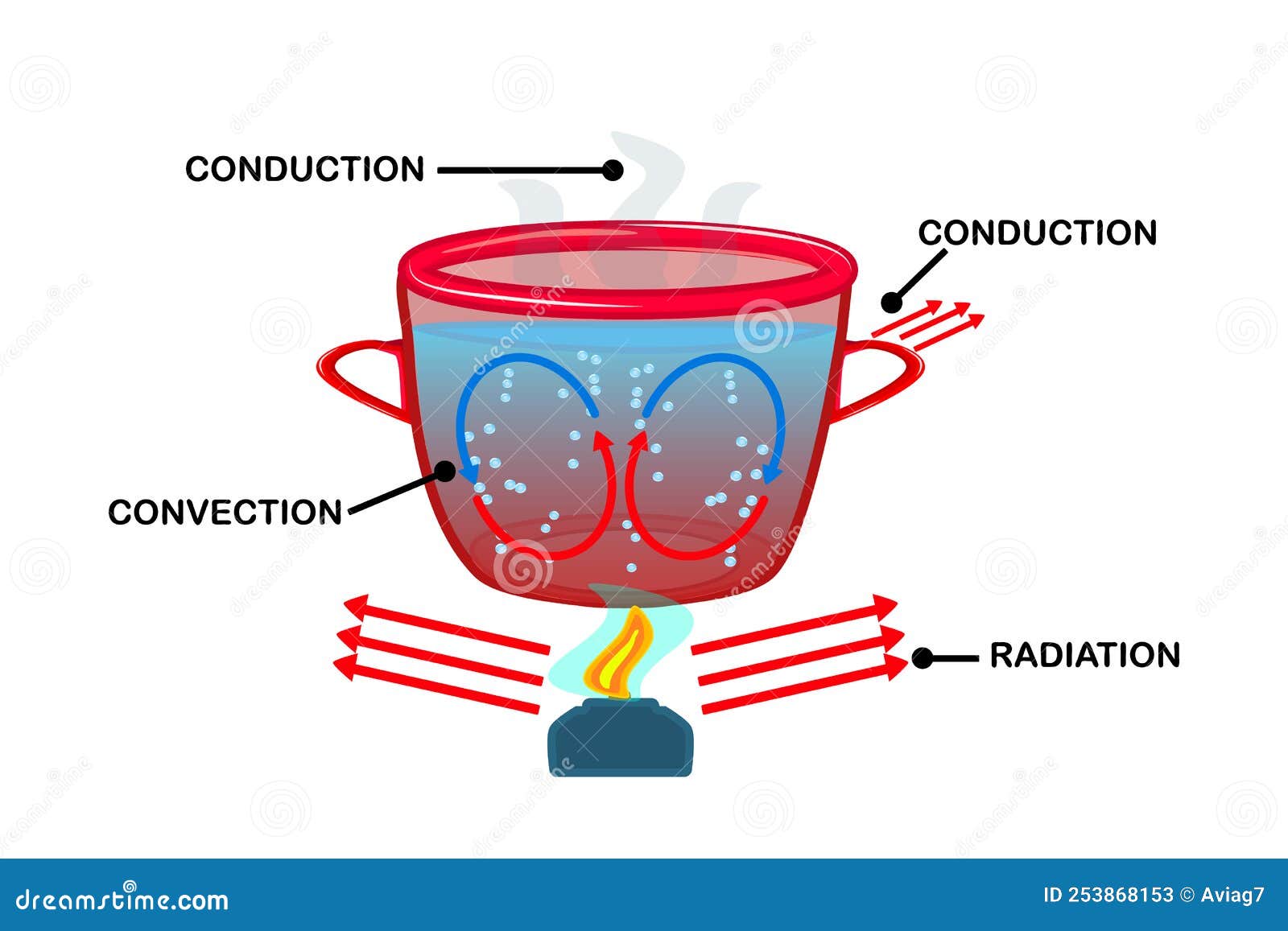
Heat Transfer. Convection Currents Labeled Diagram. Stock Vector
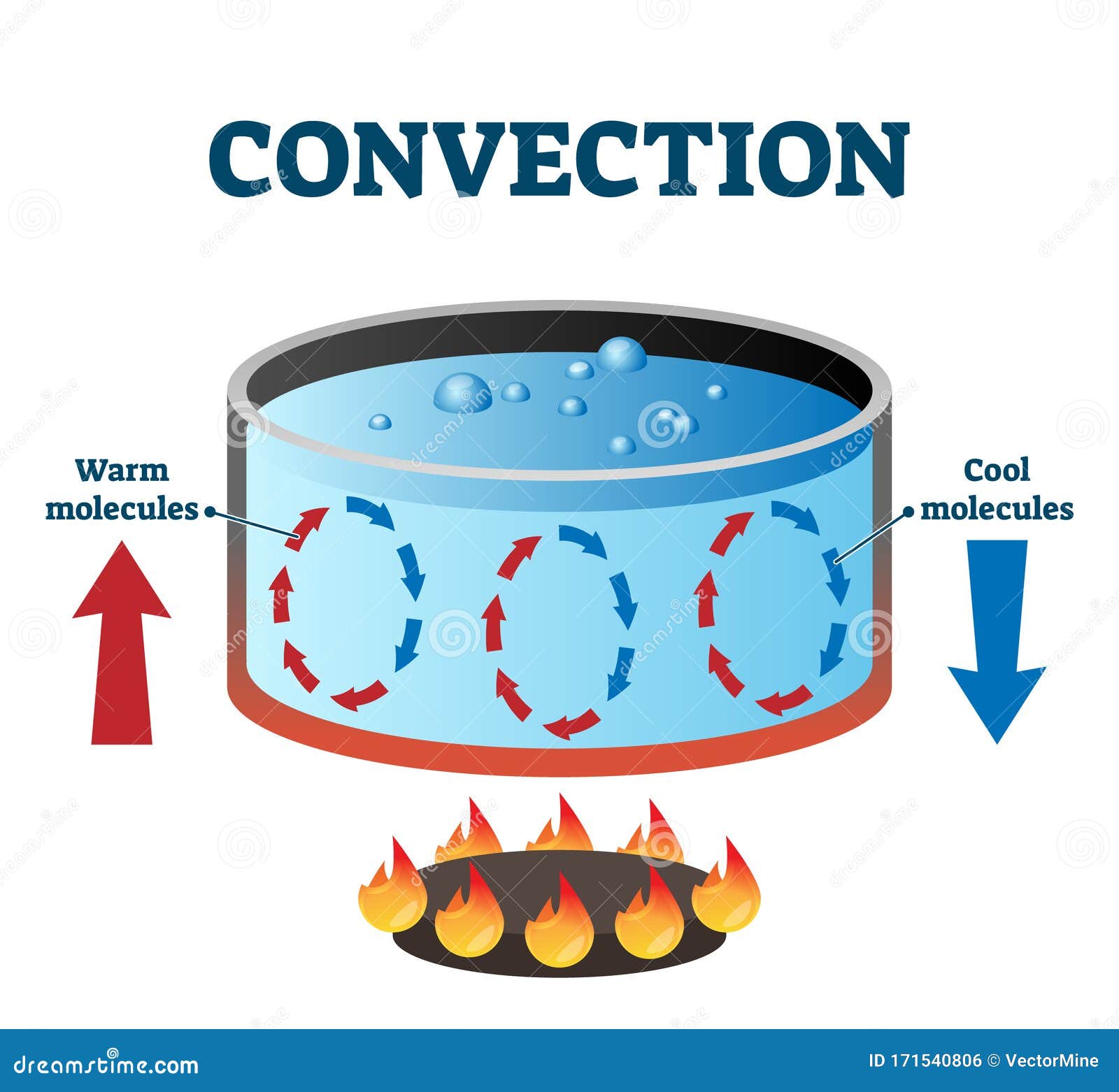
convection currents labeled diagram Coloso
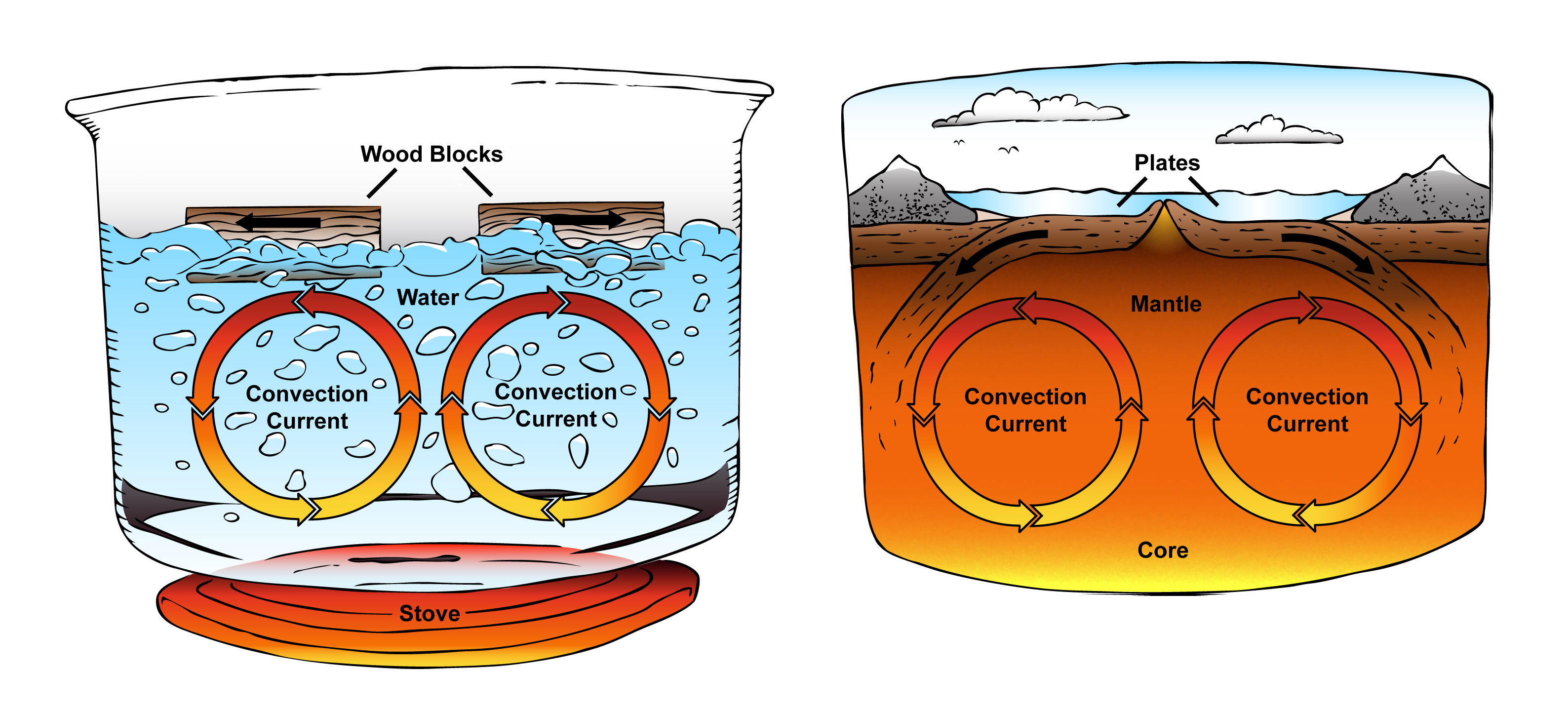
What are Convection Currents?
Web Convection Is Heat Transfer By The Macroscopic Movement Of Mass.
Convection Can Produce Horizontal Flow That Can Cause (Or Is Related To) Plate Motions.
Web Convection Is The Transfer Of Thermal Energy By Particles Moving Through A Fluid.
Web Energy That Is Transferred Between An Object And Another Object Or Its Surrounding Environment Due To A Difference In Temperature.
Related Post: