Drawing Of Skeletal Muscle
Drawing Of Skeletal Muscle - Each skeletal muscle is an organ that consists of various integrated tissues. Web the striated appearance of skeletal muscle fibres is due to the organisation of two contractile proteins: Web how to draw human muscular system. Let's take a step back now and just understand how muscles look, at least structurally, or how they relate to things that we normally associate with muscles. These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. The skeletal muscle fibres are multinucleated. Learn step by step drawing tutorial. Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. Within muscles, there are layers of connective tissue called the epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium. Web anatomy of a skeletal muscle cell. Bundles of muscle fibers, called fascicles, are covered by the perimysium. Muscles work on a macro level, starting with tendons that attach muscles to bones. The skeletal muscle fibres are multinucleated. Within muscles, there are layers of connective tissue called the epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium. Let's take a step back now and just understand how muscles look, at least structurally, or how they relate to things that we normally associate with muscles. Each organ or muscle consists of skeletal muscle tissue, connective tissue, nerve tissue, and blood or vascular tissue. The three connective tissue layers. Web drawing muscles can be challenging like the hands and. Web zygote body is a free online 3d anatomy atlas. Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. Skeletal muscles do not work by themselves. Web the striated appearance of skeletal muscle fibres is due to the organisation of two contractile proteins: This type of muscle creates movement in the body. Actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament). Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. Anatomy is a huge subject and requires a blend of scientific information and artistic practicality. Learn step by step drawing tutorial. These muscle cells are slender and long and are termed as muscle fibres. There are more than 600 skeletal muscles, and they makes up about 40 percent of a person’s body weight. Skeletal muscles do not work by themselves. Web make better art by understanding the human skeleton and mastering muscle structure. Muscles fibres, actin, and myosin. Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. Web the lever system of muscle and bone interactions. The membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; Web blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. Web structure of skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscles act not only to produce movement but also to stop movement, such as resisting gravity to maintain posture. These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Web zygote body is a free online 3d anatomy atlas. The functional unit of contraction in a skeletal muscle fibre is the sarcomere ,. Web muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. Web i think we have a respectable sense of how muscles. Web each skeletal muscle is an organ that consists of various integrated tissues. Learn step by step drawing tutorial. Skeletal muscles do not work by themselves. Skeletal muscles act not only to produce movement but also to stop movement, such as resisting gravity to maintain posture. Muscles fibres, actin, and myosin. Excitable tissue responds to stimuli through electrical signals. Bundles of muscle fibers, called fascicles, are covered by the perimysium. The cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. The skeletal muscle fibres are multinucleated. Muscles fibres, actin, and myosin. These muscle cells are slender and long and are termed as muscle fibres. This type of muscle creates movement in the body. Muscles are arranged in pairs based on their functions. A whole skeletal muscle is considered an organ of the muscular system. Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilise bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. The cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. Skeletal muscles do not work by themselves. Download a free printable outline of this video and draw along with us. Web how to draw human muscular system. Contractile tissue is able to generate tension of force. Web make better art by understanding the human skeleton and mastering muscle structure. Each organ or muscle consists of skeletal muscle tissue, connective tissue, nerve tissue, and blood or vascular tissue. So let me draw a flexing bicep right here. If you don't have a printer just keep this open. Bundles of muscle fibers, called fascicles, are covered by the perimysium. Web in this video i have shown the simplest way of drawing muscle drawing. The functional unit of contraction in a skeletal muscle fibre is the sarcomere ,. Web blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. Web skeletal muscle is an excitable, contractile tissue responsible for maintaining posture and moving the orbits, together with the appendicular and axial skeletons. Web structure of skeletal muscle. Within muscles, there are layers of connective tissue called the epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium.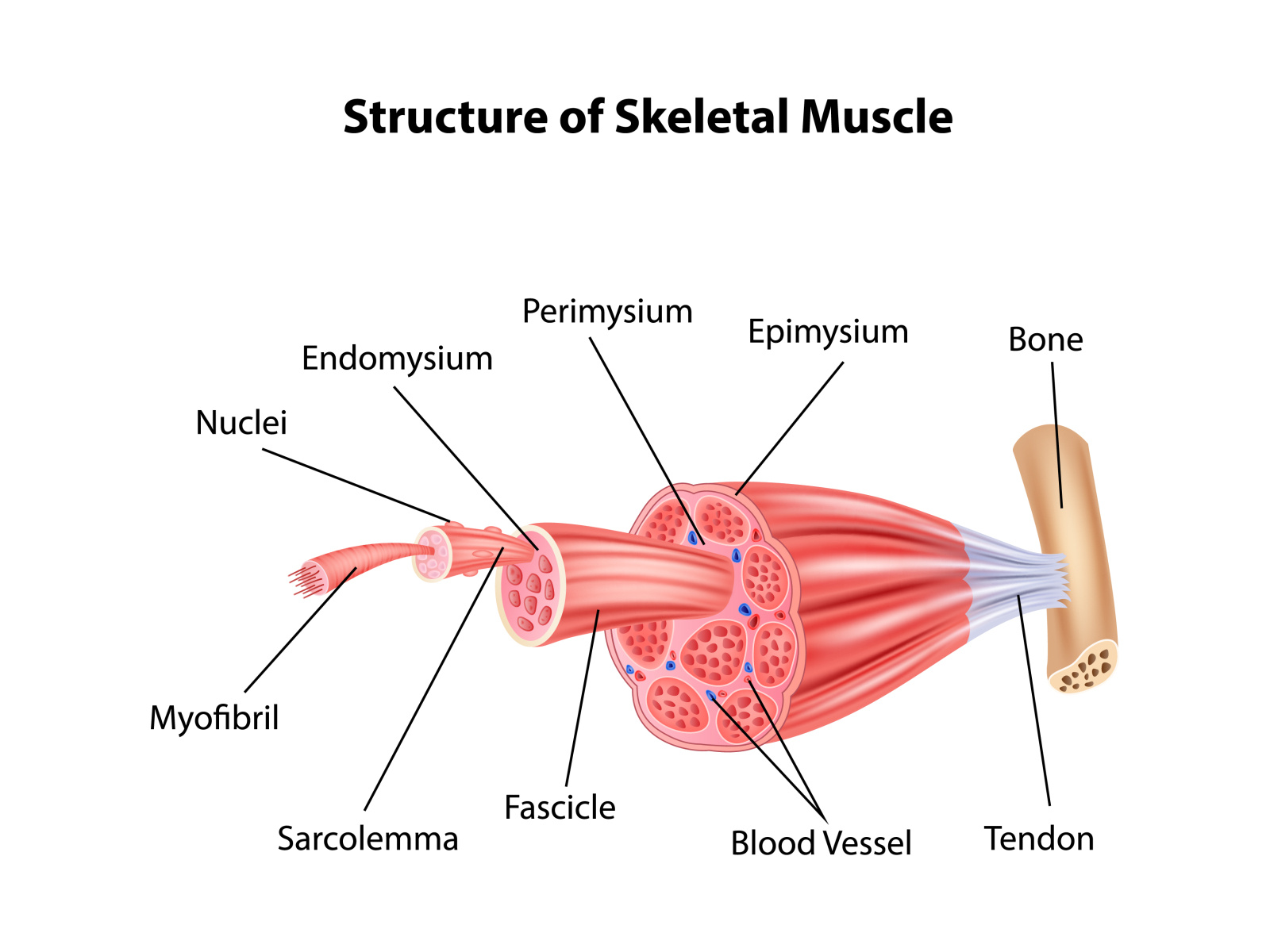
Structure Skeletal Muscle Anatomy by Tigatelu on Dribbble

Skeletal Muscle Diagram 101 Diagrams

How To Draw Structure Of Skeletal Muscle YouTube
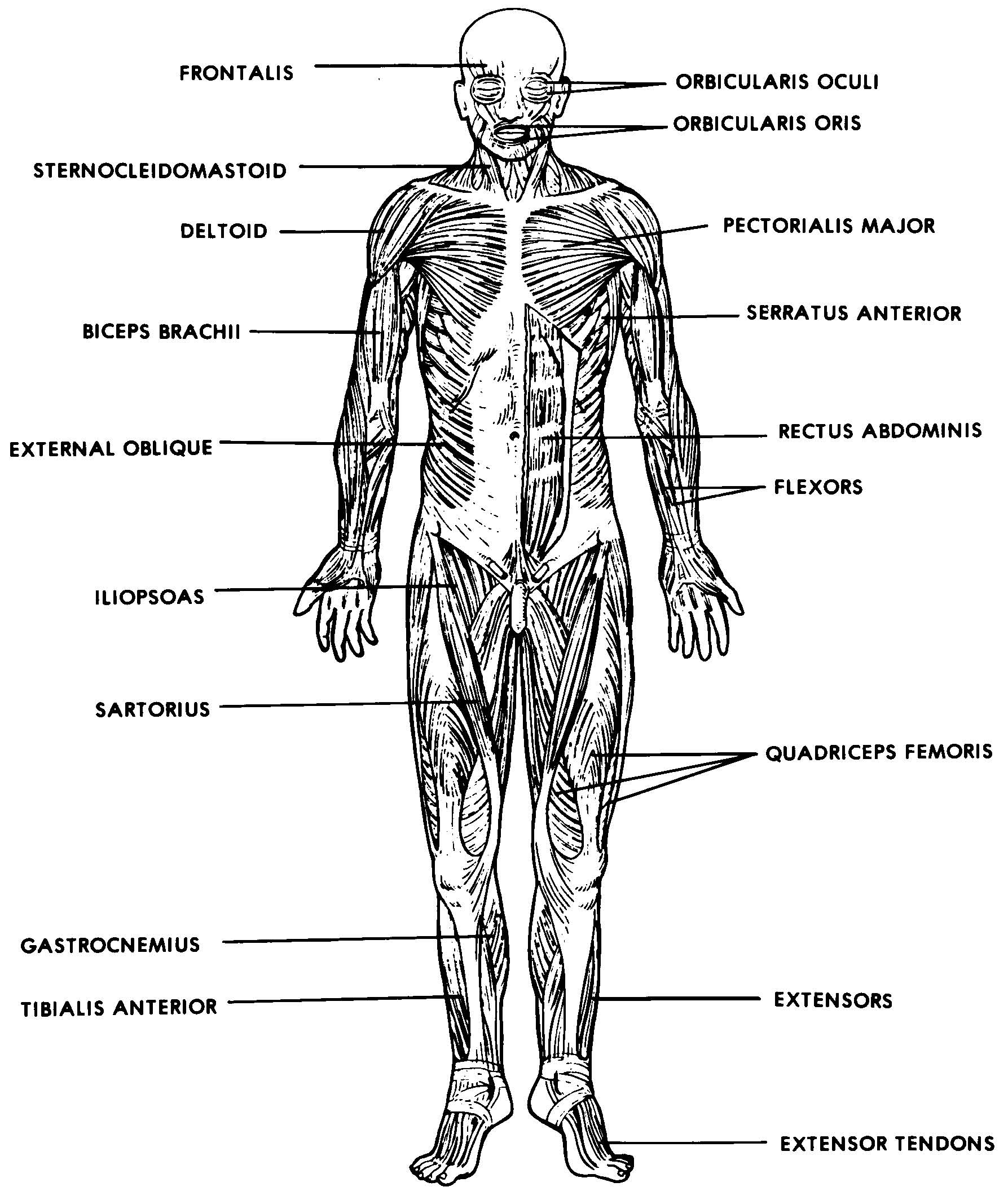
Images 05. Muscular System Basic Human Anatomy
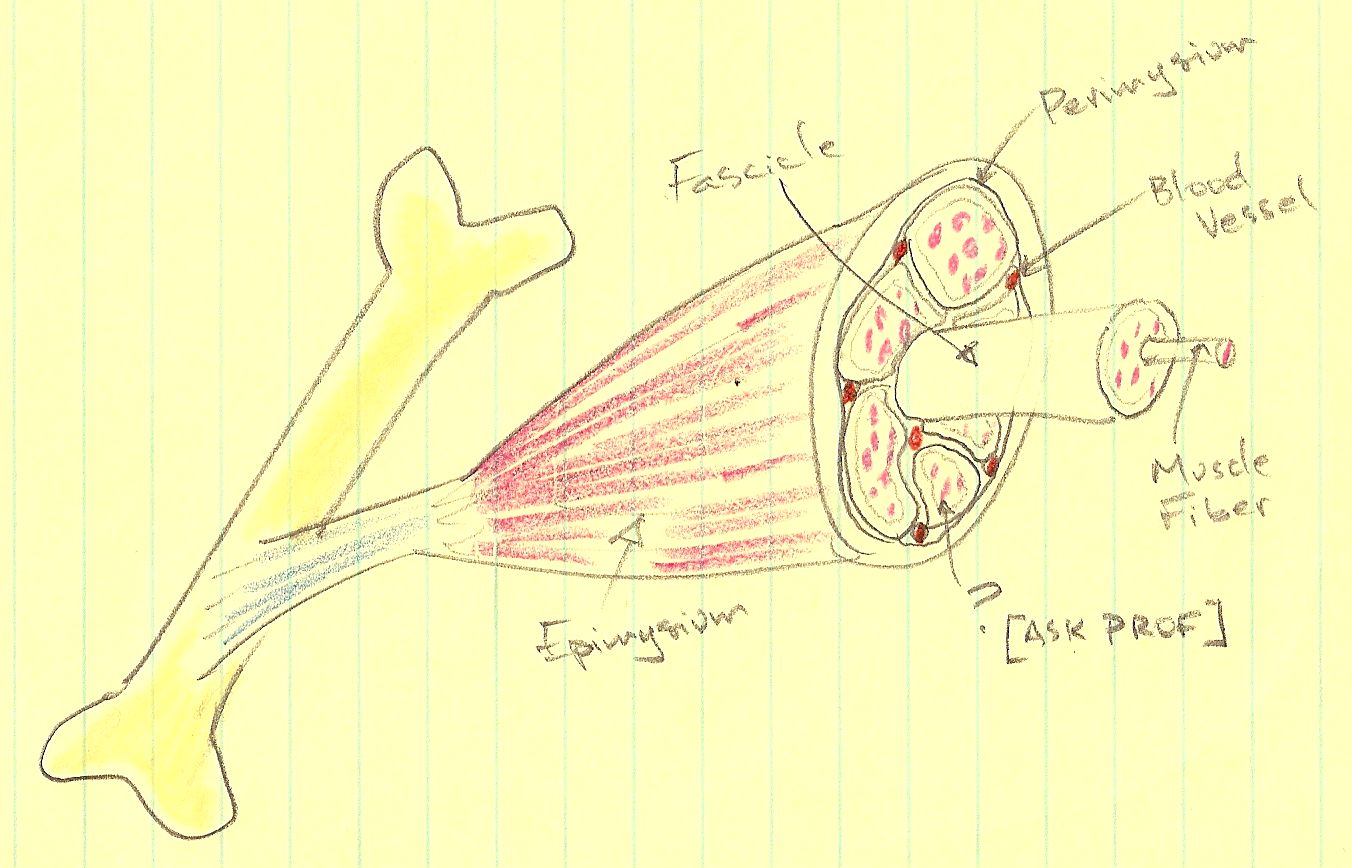
Skeletal Muscle Drawing at Explore collection of
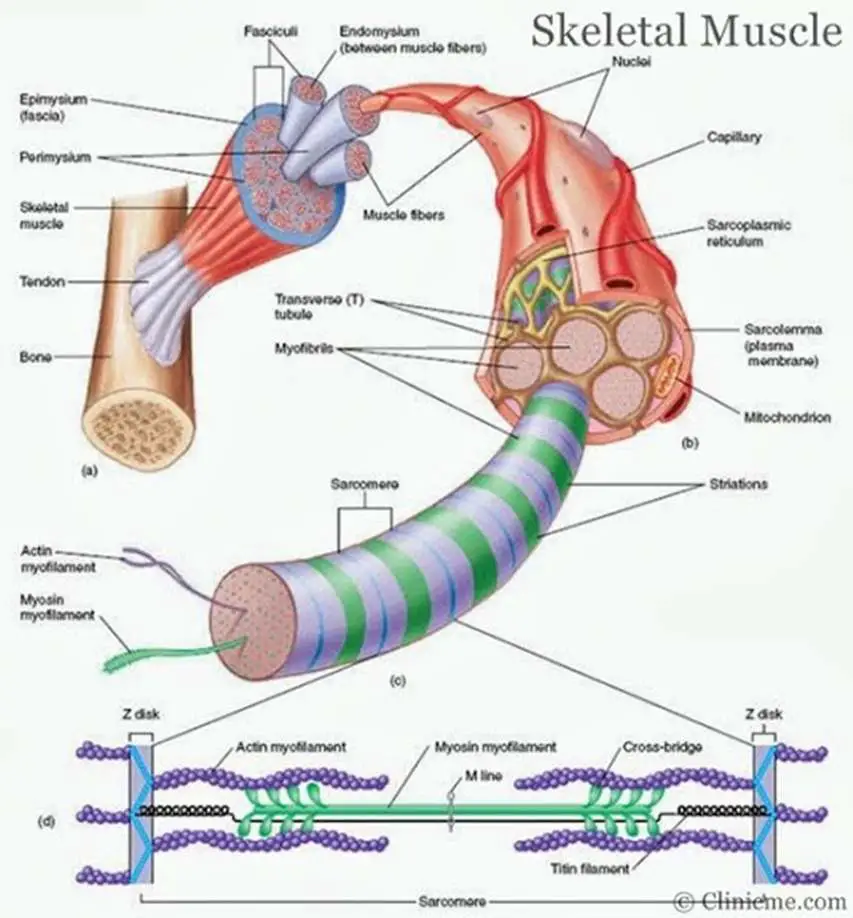
Skeletal muscle diagram Healthiack

Introduction to Skeletal Muscle Boundless Anatomy and Physiology

Schematic representation of the skeletal muscle structure. The

Skeletal muscle, illustration Stock Image C006/3938 Science Photo
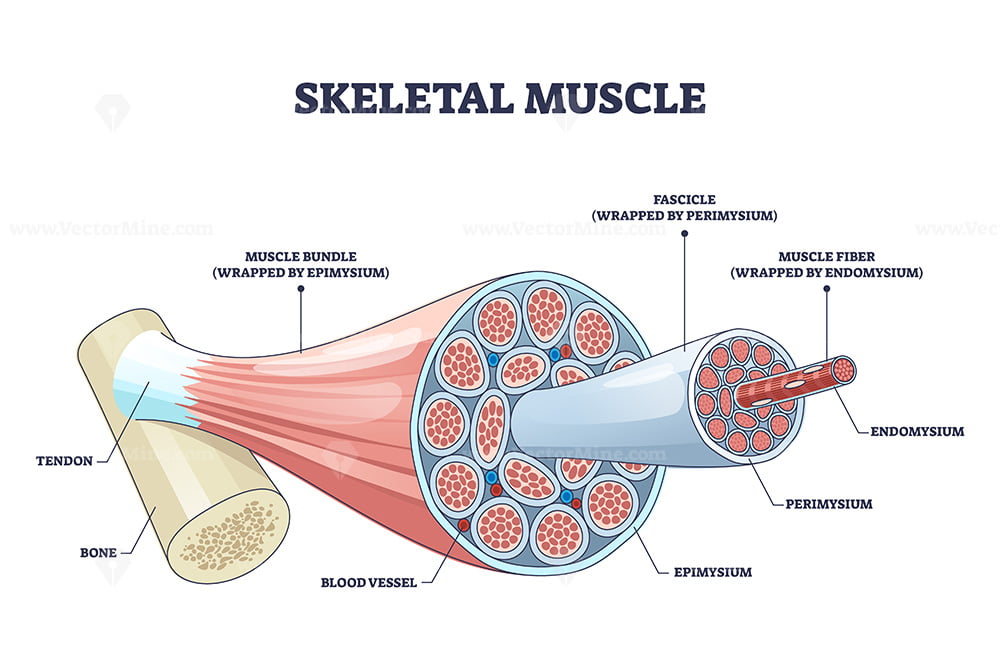
Skeletal muscle structure with anatomical inner layers outline diagram
Therefore, I’m Going To Teach You How To Draw The Body Structure And Muscles Of The Human Male Whether You’re A.
For Muscles Attached To The Bones Of The Skeleton, The Connection Determines The Force, Speed, And Range Of Movement.
Actin (Thin Filament) And Myosin (Thick Filament).
Muscles Are Arranged In Pairs Based On Their Functions.
Related Post: