Frog Dissection Drawing
Frog Dissection Drawing - Web place the frog in the dissecting pan ventral side up. A frog, a pig, a sea star, and an earthworm. Observe that each forelimb is divided into an upper arm, forearm, and hand. Use scissors to lift the abdominal muscles away from the body cavity. The frog has three eyelids: Use this guide for complete instructions. As members of the class amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. In this lab, as we continue our dissection, we will take a close look at the frog’s. Web the frog body is divided into two sections: Life the flaps of the body wall and pin back. Place the frog in the dissecting pan ventral side up. A frog, a pig, a sea star, and an earthworm. It can also be a great way to prepare students for dissection, showing them structures they will see in 3d. Frogs and other small animals are typically dissected in biology labs to learn anatomy. Cut along the midline of the. Use scissors to lift the abdominal muscles away from the body cavity. Web the frog body is divided into two sections: Notice the appendages developed for a terrestrial life. The frog is a tetrapod, meaning that it possesses 4 limbs for locomotion. Cut along the midline of the body to the forelimbs. Cut along the midline of the body to the forelimbs. Make transverse (horizontal) cuts near the arms and legs. If your class is going to dissect a frog, your teacher should provide all the necessary tools for the job. Web the app features four dissectible animal models: Includes a list of terms to study for lab practical. Life the flaps of the body wall and pin back. During the dissection, students typically examine the organs, including the heart, lungs, liver, stomach, and intestines. Use scissors to lift the abdominal muscles away from the body cavity. Web if your classroom doesn’t have access to frog dissection specimens, visible biology ’s interactive 3d frog model can walk students through. Use scissors to lift the abdominal muscles away from the body cavity. Index life science and biology, resources for naturalists frog dissection diagram and labeling high resolution pdf for printing click here citing research references when you research information you must cite the reference. Along with toads, they make up the largest group of amphibians. Cut along the midline of. Why is the color and texture the way that it is? Products used in this video:frog specimen: Thank you for joining us for part two of our three frog dissection labs. The fleshy upper eyelid, the thinner lower eyelid, and the transparent nictitating membrane. Make transverse (horizontal) cuts near the arms and legs. Thank you for joining us for part two of our three frog dissection labs. Web 1 prepare the dissection tray and get your frog. Draw the internal anatomy of your frog. The frog has no neck so the trunk follows immediately behind the head. Index life science and biology, resources for naturalists frog dissection diagram and labeling high resolution pdf. On the outside of the frog’s head are two external nares, or nostrils; Web frog dissection is a process of examining the internal anatomy of a frog by making cuts through the skin and muscles. Web if your classroom doesn’t have access to frog dissection specimens, visible biology ’s interactive 3d frog model can walk students through frog anatomy without. Draw the external anatomy of your frog. Includes a list of terms to study for lab practical. The frog has three eyelids: Web the app features four dissectible animal models: Draw the internal anatomy of your frog. Web obtain a preserved frog and place it on your dissecting tray, dorsal surface up. Notice the appendages developed for a terrestrial life. Web the app features four dissectible animal models: One of the best ways to learn about adult amphibian anatomy is to dissect a preserved frog and see how all the organs fit together inside its body. The. Basic line drawings that students can practice labeling. Thank you for joining us for part two of our three frog dissection labs. Frogs are vertebrates in a class called amphibians. Web the app features four dissectible animal models: As members of the class amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Products used in this video:frog specimen: The frog has three eyelids: It can also be a great way to prepare students for dissection, showing them structures they will see in 3d. During the dissection, students typically examine the organs, including the heart, lungs, liver, stomach, and intestines. Web frog dissection diagram and labeling go back to: Place the frog in the dissecting pan ventral side up. Frogs have similar body systems (like the digestive and circulatory systems) to other vertebrates like humans, making them a nice specimen for comparative anatomy. 110k views 4 years ago. Web place the frog in the dissecting pan ventral side up. Draw the external anatomy of your frog. Use this guide for complete instructions.
Frog Dissection MRS. MERRITT'S BIOLOGY CLASS
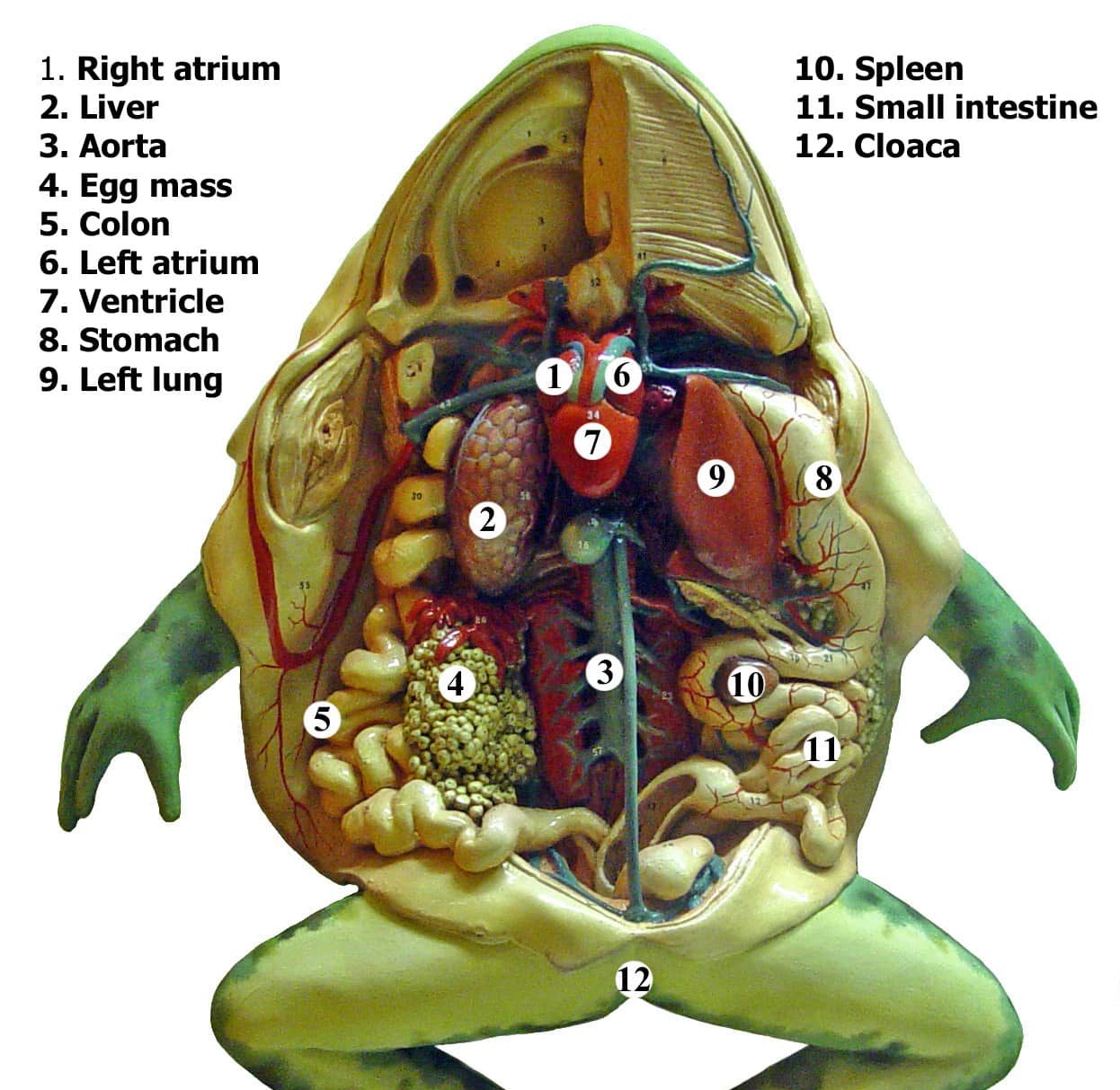
Frog dissection labeled diagram lomishelf

The Frog's Anatomy Illustration Poster Graphic poster
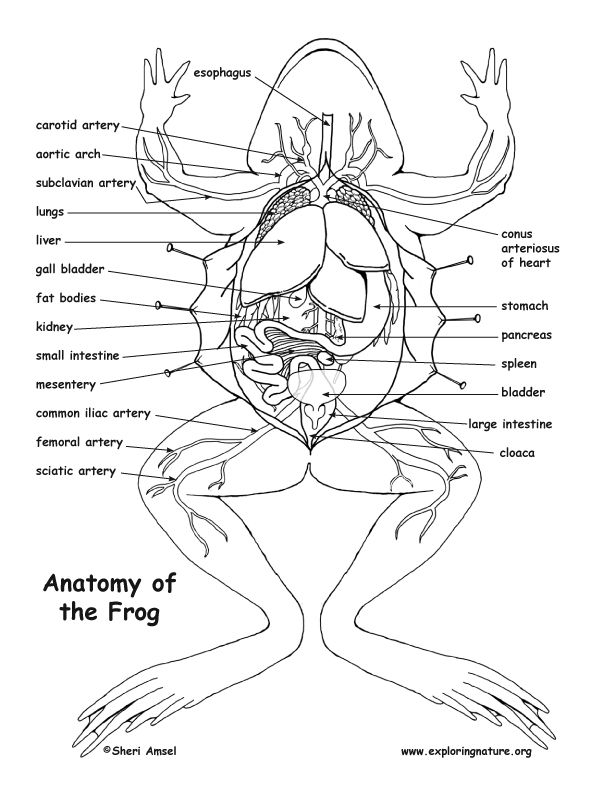
Frog Dissection Diagram and Labeling

Frog Dissection Art Print by turtletimehewitt XSmall in 2021 Frog

Frog Dissection Carolina Biological Supply

Frog Dissection Diagram and Labeling
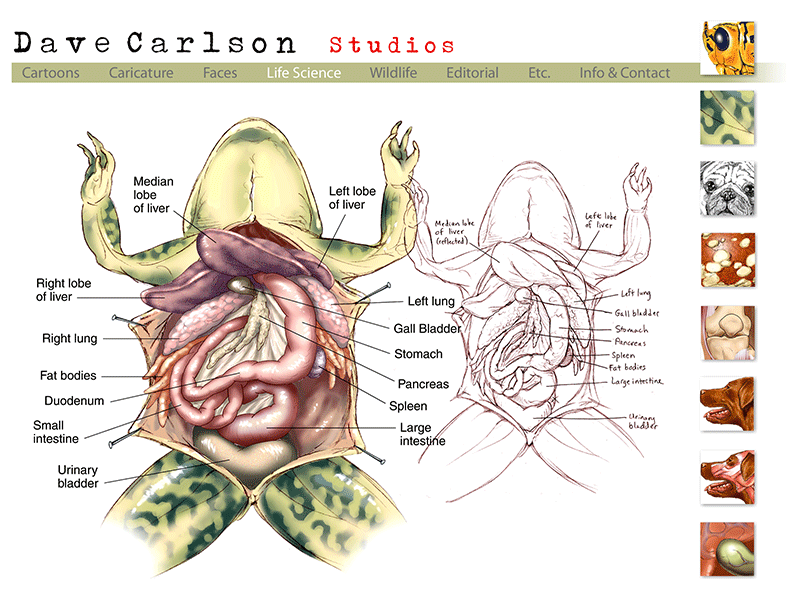
Anatomy Of A Frog

Frog Anatomy, Illustration Stock Image C030/7183 Science Photo
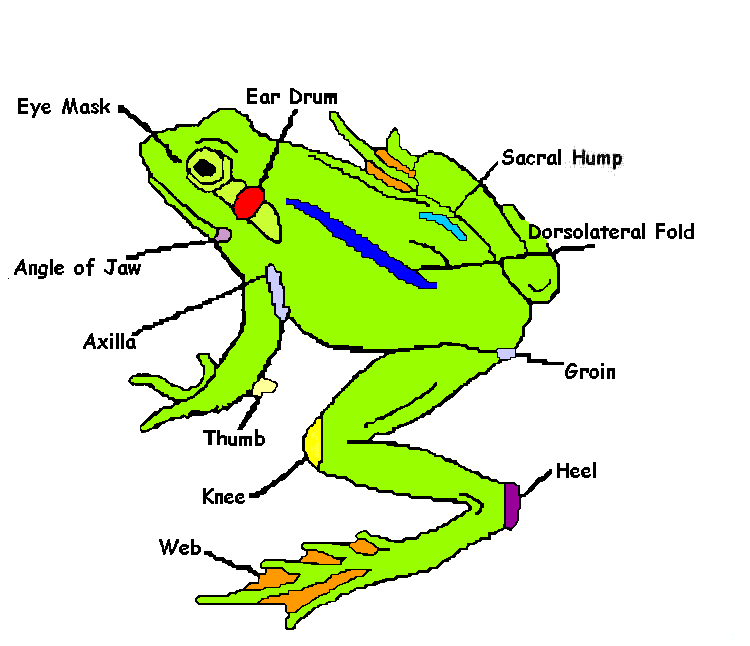
Frog Dissection External Anatomy
If Your Class Is Going To Dissect A Frog, Your Teacher Should Provide All The Necessary Tools For The Job.
Web If Your Classroom Doesn’t Have Access To Frog Dissection Specimens, Visible Biology ’S Interactive 3D Frog Model Can Walk Students Through Frog Anatomy Without Prep Or Cleanup.
Web The Frog Body Is Divided Into Two Sections:
Eggs Are Laid And Fertilized In Water.
Related Post: