How To Draw A Position Graph From A Velocity Graph
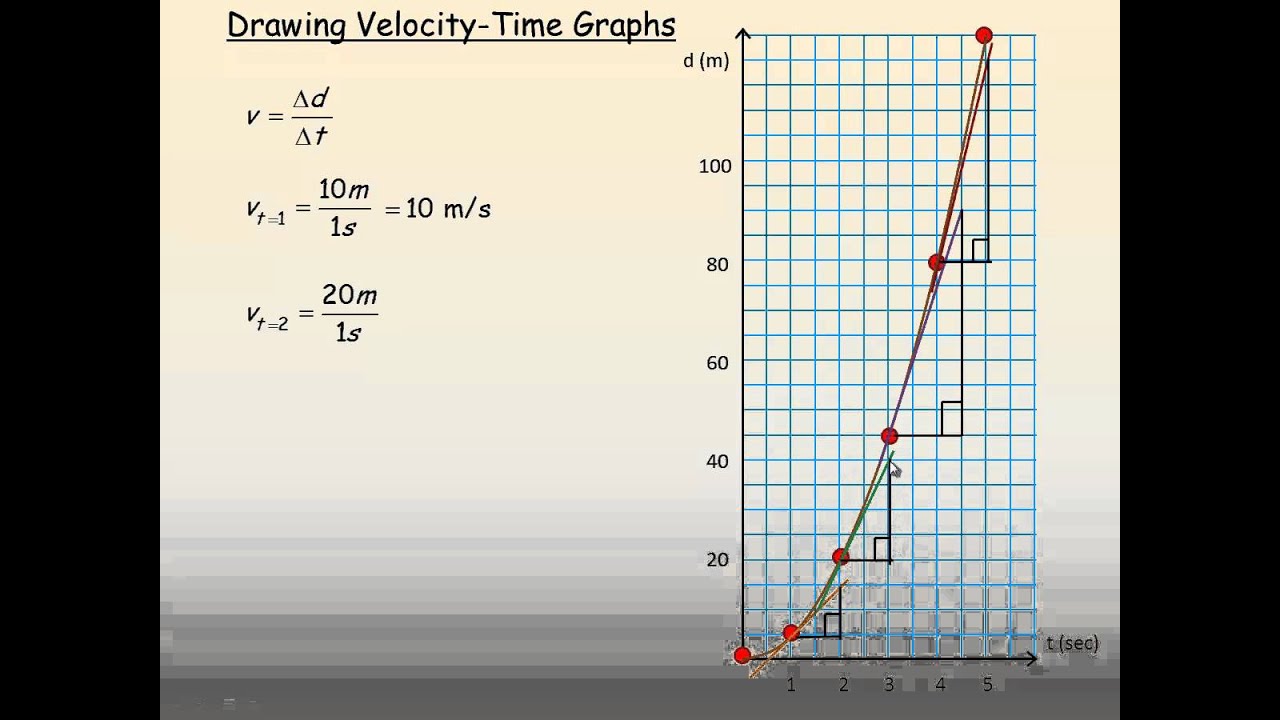
How To Draw A Position Graph From A Velocity Graph - Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. Other quantities, such as displacement, are said to depend upon it. Here, let's take an example and it'll make a lot of sense. Web given a position vs time graph, draw a velocity vs time graph (constant velocities only) Determine the direction by considering whether the slope is positive or negative. Web the equation for the straight line is y equals mx + b. Beth drives east at 30 m s , then slows to a stop at the red light. We know that v = d / t. Web drawing a position graph from a velocity graph. The slope of this line will be the average velocity of our object. New resources finding midpoint & endpoint: Thin slice tasks simplify square root flash cards Time graph by sliding the points up or down. And then you add them to the initial position. What is its average velocity. We know that v = d / t. Here, let's take an example and it'll make a lot of sense. Beth drives east at 30 m s , then slows to a stop at the red light. Web use the formula: A keyframe marks the point in time where you specify a value, such as spatial position, opacity, or audio. Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. Web as we will learn, the specific features of the motion of objects are demonstrated by the shape and the slope of the lines on a velocity vs. We will also get some intuition behind why slope or steepness of position time graphs represent velocity.. It accepts user inputs in creating prediction graphs, then generates an accurate comparison graph. To see why, consider the slope of the position vs. If we make a graph of position vs time and our object is moving at a constant velocity, the graph will form a straight line. Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to. Constant velocity versus changing velocity Web drawing a position graph from a velocity graph. Using the graph to determine displacement, distance, average velocity, average speed, instantaneous velocity, and instantaneous speed. Web adjust the initial position and the shape of the velocity vs. To create a change in a property over time, you set at least two keyframes—one keyframe for the. A keyframe marks the point in time where you specify a value, such as spatial position, opacity, or audio volume. We will also get some intuition behind why slope or steepness of position time graphs represent velocity. Time graph to determine position. We know that v = d / t. Web about transcript how to read a position vs. Web just as we could use a position vs. Web 124k views 13 years ago. A graph of position versus time, therefore, would have position on the vertical axis (dependent variable) and time on the horizontal axis (independent variable). Determine the direction by considering whether the slope is positive or negative. So the value of the slope at a particular. We will also get some intuition behind why slope or steepness of position time graphs represent velocity. Web as we will learn, the specific features of the motion of objects are demonstrated by the shape and the slope of the lines on a velocity vs. New resources finding midpoint & endpoint: Time graph to determine velocity, we can use a. The slope of this line will be the average velocity of our object. Time change as they adjust to match the motion shown on the velocity vs. The steeper the slope is, the faster the motion is changing. Velocity (v) = change in position (δx) / time interval (δt). The final position will be the initial position plus the area. Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. We call this a linear graph. And then you add them to the initial position. Web just as we could use a position vs. That is the area between y =0 and the velocity function. Time graph to determine position. To see why, consider the slope of the position vs. Web this video relates distance traveled and velocity through graphing. Top voted tue60845 8 years ago Web use the formula: Web given a position vs time graph, draw a velocity vs time graph (constant velocities only) The three motion graphs a high school physics student needs to know are: And then you add them to the initial position. A keyframe marks the point in time where you specify a value, such as spatial position, opacity, or audio volume. (c) between t = 0 and t = 5.0 s. Velocity is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. We know that v = d / t. Time change as they adjust to match the motion shown on the velocity vs. Web just as we could use a position vs. Web the slope of a position graph represents the velocity of the object.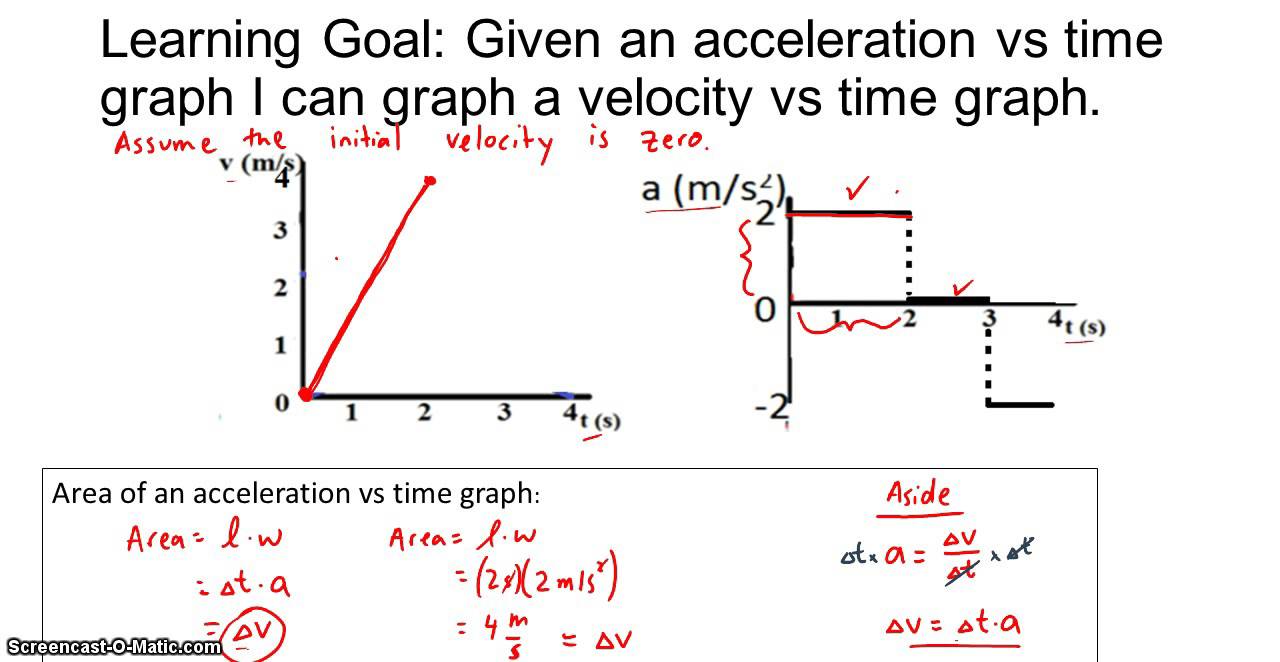
Drawing Velocity Graphs Given Acceleration Graphs YouTube
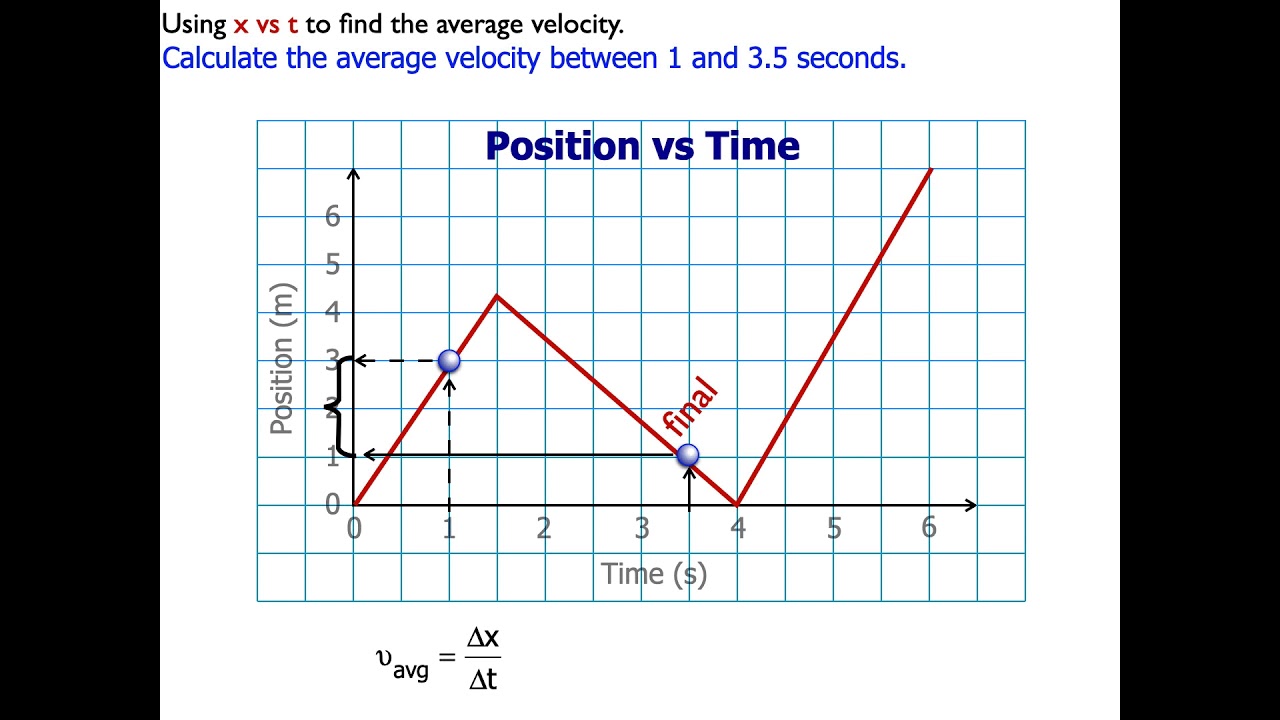
How to Calculate the average velocity from a position vs time graph
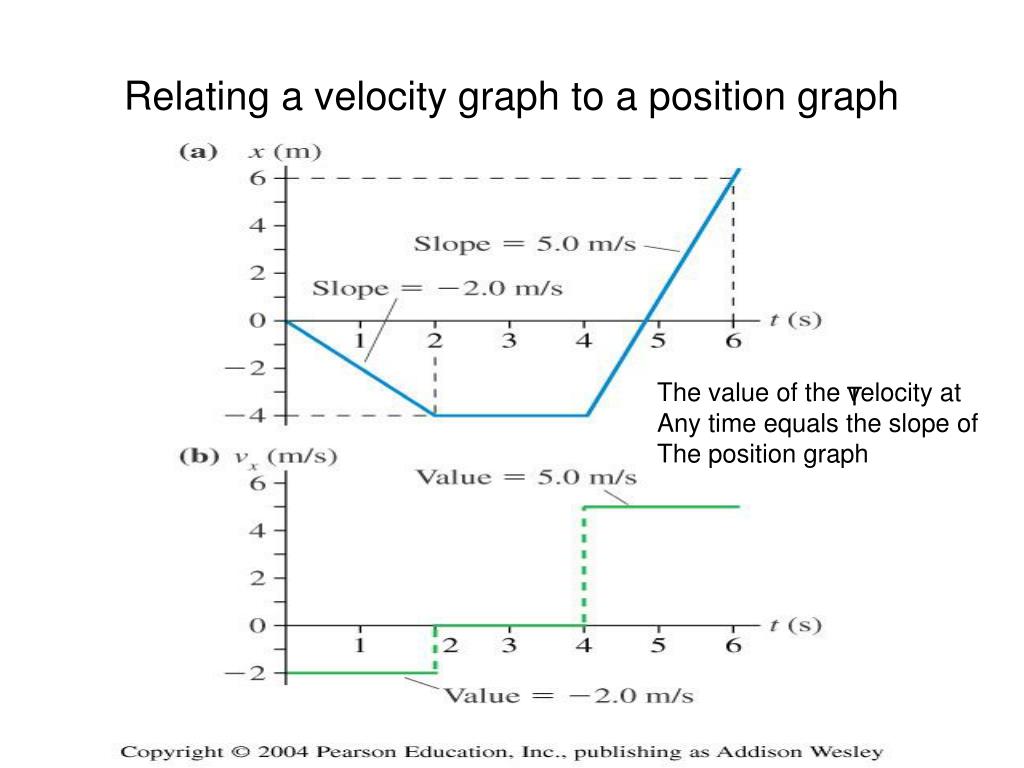
PPT Chapter 2 Kinematics PowerPoint Presentation ID762189
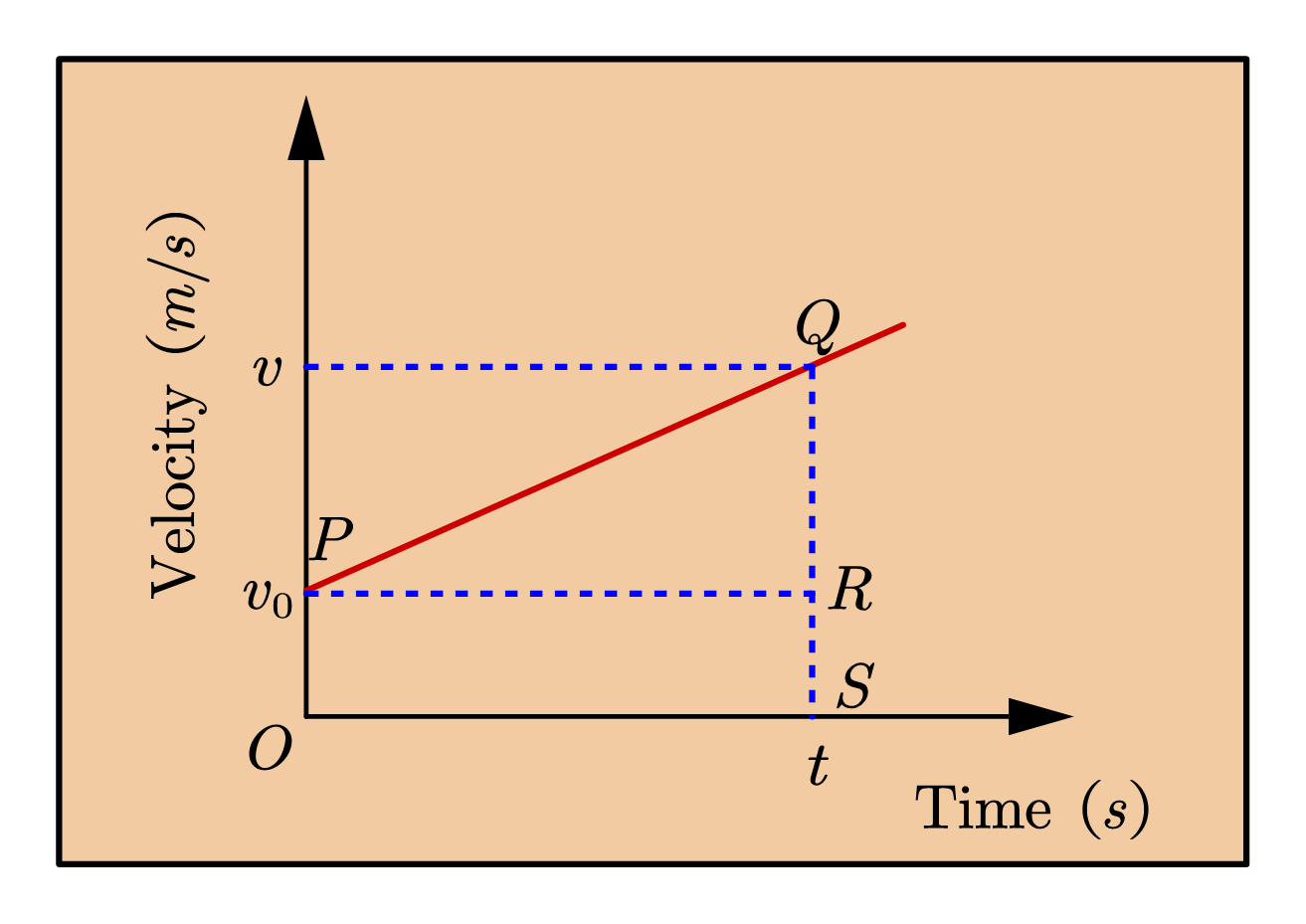
What is Velocity time graph? physicscatalyst's Blog

Constant Acceleration How to Make a Velocity Graph from a Position

position graphs from velocity graphs YouTube

Drawing a velocity graph from a position graph YouTube

Drawing a position graph from a velocity graph YouTube

How to calculate velocity from a position vs time graph YouTube
Drawing VelocityTime Graphs YouTube
Time Graph To Determine Velocity, We Can Use A Velocity Vs.
So You Have 2 Seconds At 4 M/S, And 1 Second At, On Average, 3 M/S.
Constant Velocity Versus Changing Velocity
So The Value Of The Slope At A Particular Time Represents The Velocity Of The Object At That Instant.
Related Post: