P Orbital Drawing
P Orbital Drawing - For an f orbital, see below. Get the definition of a p orbital in electronic structure, learn its shape, and see its possible numerical values. When drawing orbital diagrams, we include empty boxes to depict any empty orbitals in the same subshell that we are filling. This type of hybridization is required whenever an atom is surrounded by three groups of electrons. Web a molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. The phosphorus orbital diagram contains 2 electrons in the 1s orbital, 2 electrons in the 2s orbital, the six electrons in the 2p orbital, the two electrons in the 3s orbital, and the remaining. There is a zero probability of finding the electron on that plane. Web a p orbital is shaped like 2 identical balloons tied together at the nucleus. Notice that the number of lines we draw for each orbital equals half the number of electrons each orbital can hold! Web the shapes of p, d and f orbitals are described verbally here and shown graphically in the orbitals table below. The orbital diagram for phosphorus is drawn with 5 orbitals. Web 21,441 according to the quantum atomic model, an atom can have many possible numbers of orbitals. Carbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons. This means that you can only put two electrons (with opposite spin) in the first shell. Those electrons can participate in resonance. H 2s (c) draw the electron dot structure for: Web what is the orbital diagram for phosphorus (p)? F 2 view solution q 2 Remember that l must always be less than n. Four of them fill the 1s and 2s orbitals. Web solution verified by toppr p orbital has 3 orientations: As the value of l increases, the number of orbitals in a given subshell increases, and the shapes of the orbitals become more complex. This means that you can only put two electrons (with opposite spin) in the first shell. Get the definition of a p orbital in electronic structure,. Web p orbitals (l=1) only s orbitals are spherically symmetrical. Web an orbital is a space where a specific pair of electrons can be found. How likely it is to form bonds, and with which other elements. Label the positions of the oxygen nuclei with the symbol o. There is a zero probability of finding the electron on that plane. Remember that l must always be less than n. Web p orbitals (l=1) only s orbitals are spherically symmetrical. Web this means that the s orbital can contain up to two electrons, the p orbital can contain up to six electrons, the d orbital can contain up to 10 electrons, and the f orbital can contain up to 14 electrons.. So a p orbital is just that dumbbell shape. Web an orbital is a space where a specific pair of electrons can be found. The three p orbitals are at right angles to each other and have a lobed shape. Those electrons can participate in resonance. How likely it is to form bonds, and with which other elements. Get the definition of a p orbital in electronic structure, learn its shape, and see its possible numerical values. A p orbital consists of two lobes of electron density on either side of the nucleus. As the value of l increases, the number of orbitals in a given subshell increases, and the shapes of the orbitals become more complex. For. This means that you can only put two electrons (with opposite spin) in the first shell. Web as we will see below, the periodic table organizes elements in a way that reflects their number and pattern of electrons, which makes it useful for predicting the reactivity of an element: So let's say that that's the nucleus and i'll just draw. Remember that l must always be less than n. Those electrons can participate in resonance. Label the positions of the oxygen nuclei with the symbol o. This is also due to the history when they were discovered. Web if that nitrogen is sp two hybridized, that nitrogen has a p orbital, so we can go ahead and draw in a. Imagine shells around the nucleus, that get bigger and bigger. There is a zero probability of finding the electron on that plane. An s orbital is a sphere. Web solution verified by toppr p orbital has 3 orientations: H 2s (c) draw the electron dot structure for: Imagine a horizontal plane through the nucleus, with one lobe of the orbital above the plane and the other beneath it; As the value of l increases, the number of orbitals in a given subshell increases, and the shapes of the orbitals become more complex. The orbital shows where there is a 95% chance of finding a particular electron. Let me draw them a little bit closer together. The size of the p orbitals also increases as the energy level or. As such, the first shell has no p orbitals; Web p orbitals (l=1) only s orbitals are spherically symmetrical. This type of hybridization is required whenever an atom is surrounded by three groups of electrons. 22 similar questions q 1 (a) draw the electron dot structure for: So let me draw the nucleus of two atoms, and i'll just draw one of each of their p orbitals. P x, p y & p z was this answer helpful? Web p orbitals (l=1) only s orbitals are spherically symmetrical. So let's say that that's the nucleus and i'll just draw their p orbitals. How likely it is to form bonds, and with which other elements. These orbitals can be categorized on the basis of their size, shape or orientation. Because the 2 p subshell has l = 1, with three values of ml (−1, 0, and +1), there are three 2 p orbitals.
quantum chemistry How do 1s and 2p orbitals overlap? Chemistry
[Solved] sketch sigma and pi bond from p orbital Course Hero

How To Draw Orbitals Deepcontrol3

Shapes of Atomic Orbitals — Overview & Examples Expii
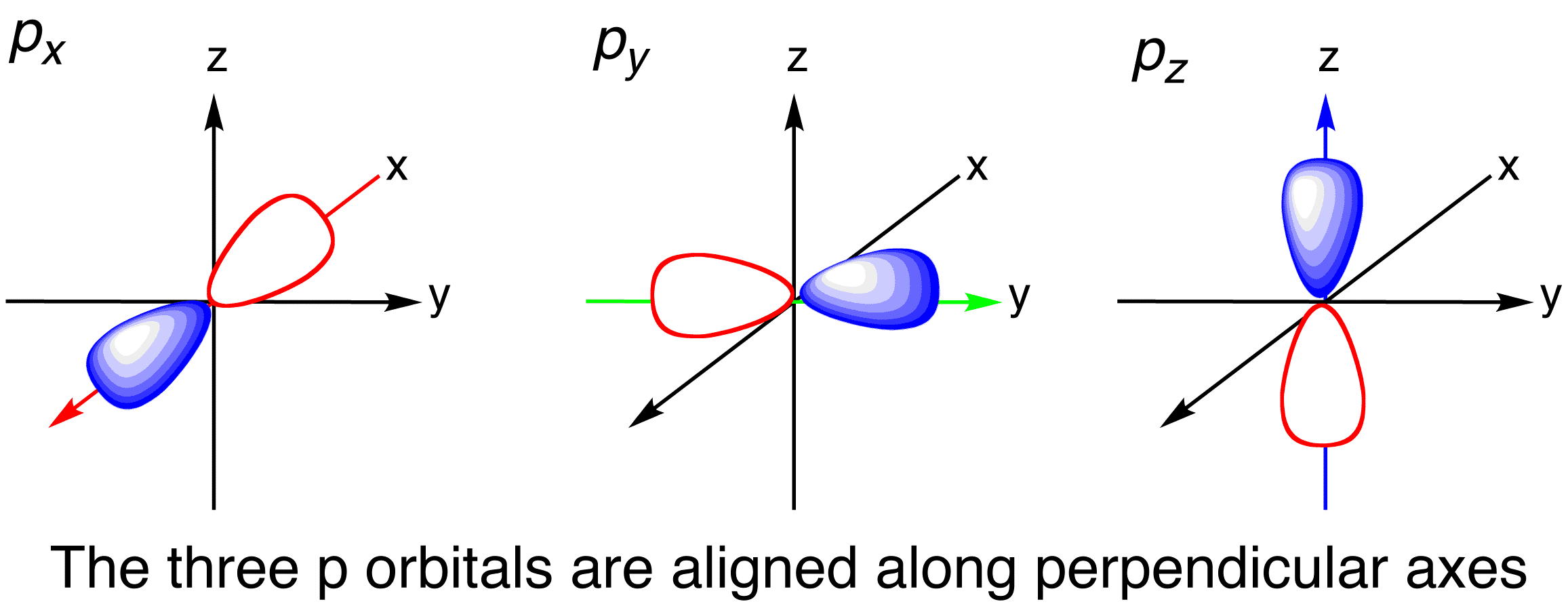
Shape of porbitals in 3D

Atomic orbitals explained polizhuge
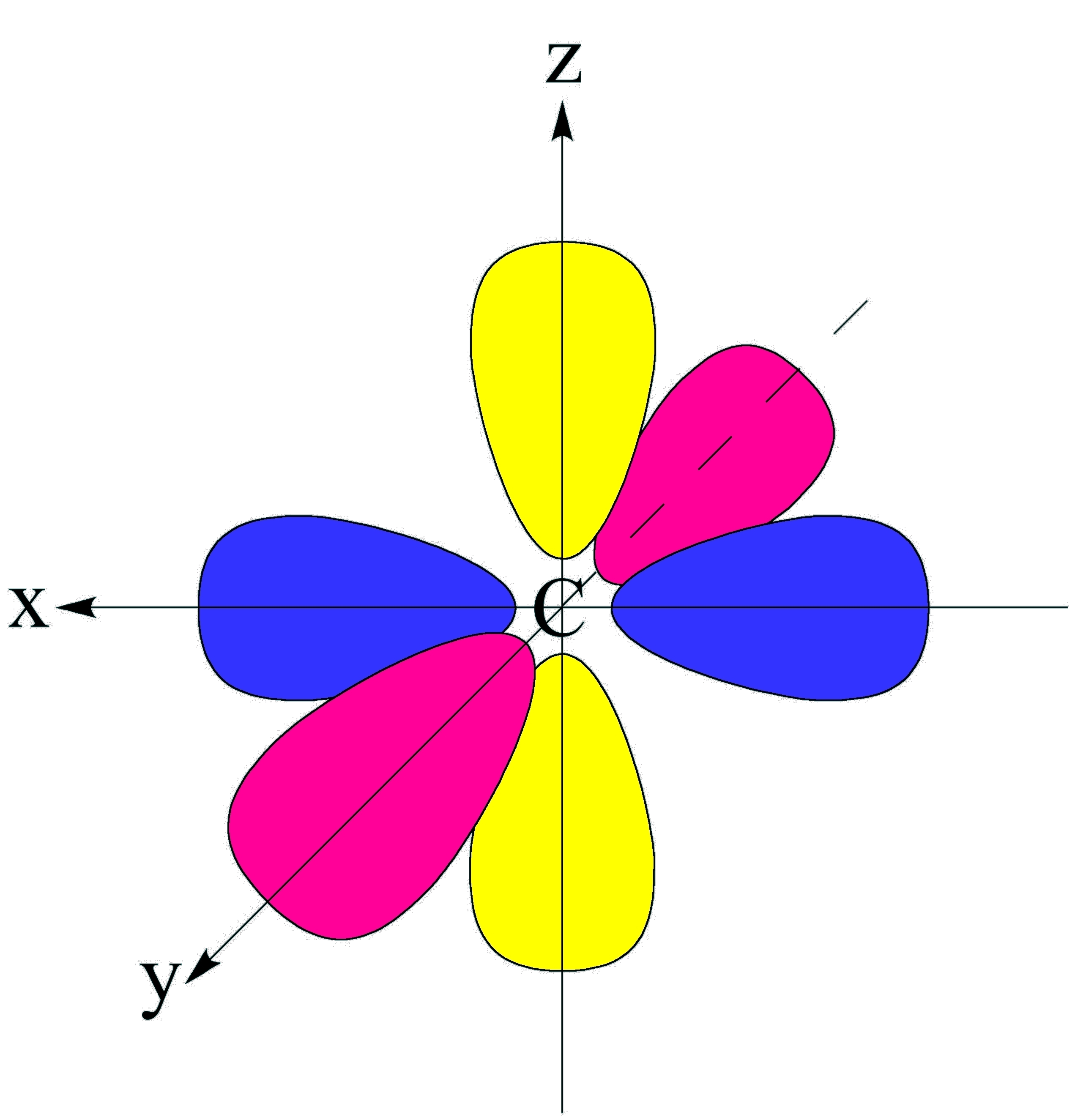
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Orbital

2. What is the shape of p orbital? Brainly.ph

Describe the shapes of s and p orbitals.

8.3 Development of Quantum Theory CHEM 1114 Introduction to Chemistry
A Smaller Sized Orbital Means There Is A Greater Chance.
Four Of Them Fill The 1S And 2S Orbitals.
A Fundamental Principle Of These Theories Is That As Atoms Bond To Form Molecules, A Certain Number Of Atomic Orbitals.
The P Sub Shell Can Hold A Maximum Of Six Electrons As There Are Three Orbitals Within This Sub Shell.
Related Post: