Drawing Of The Cell Cycle
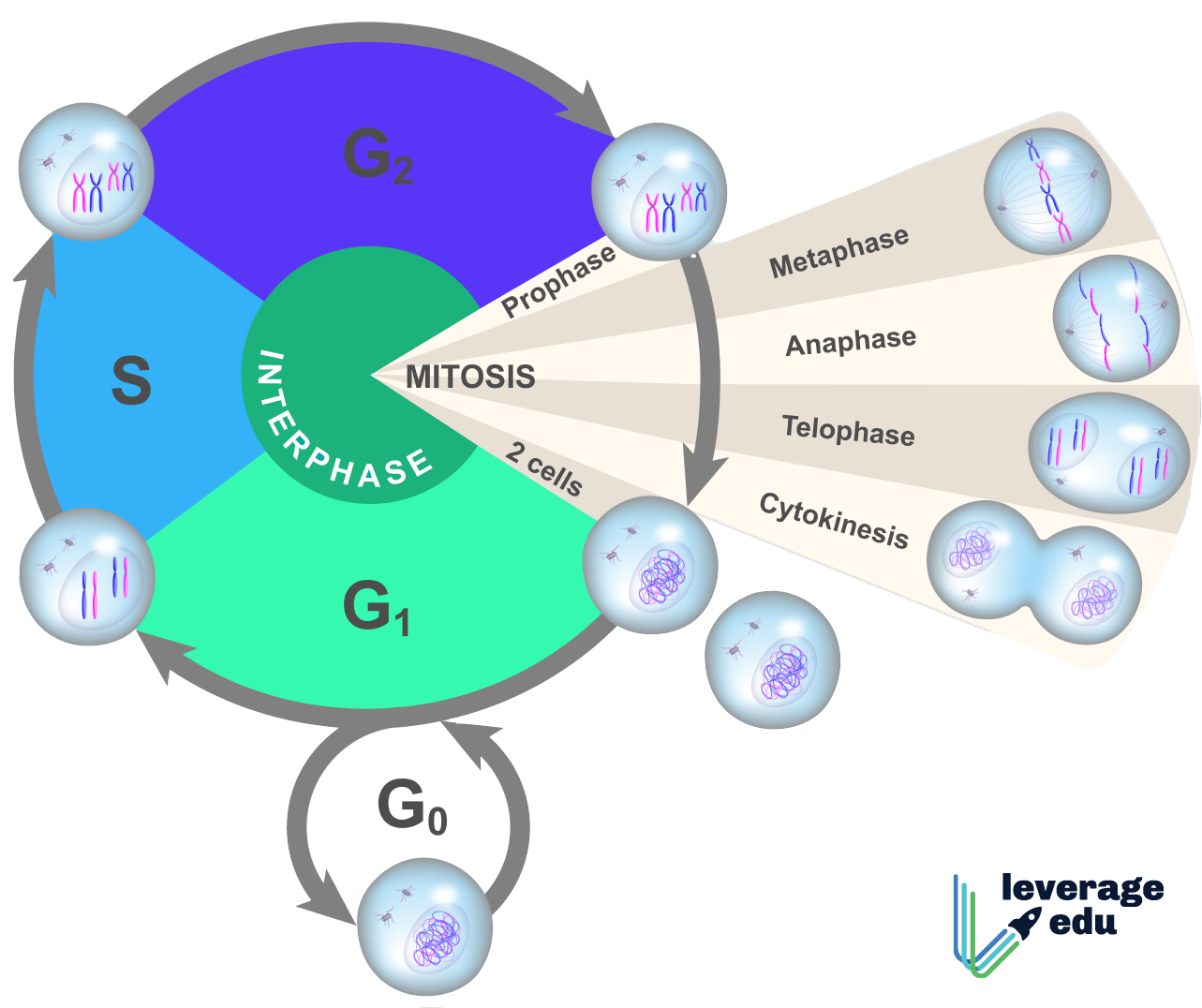
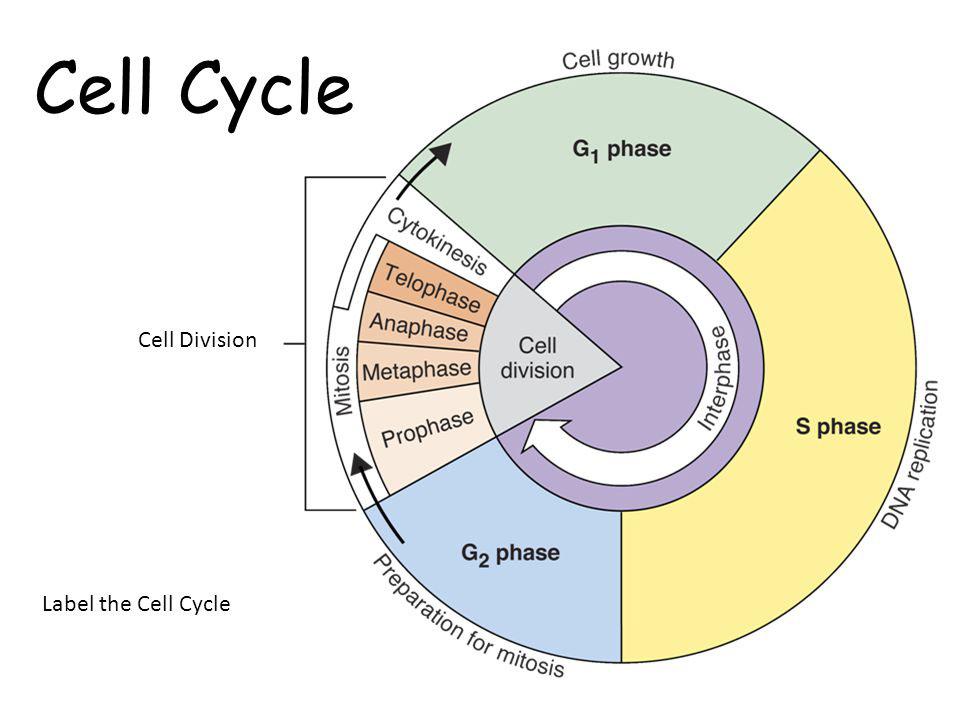
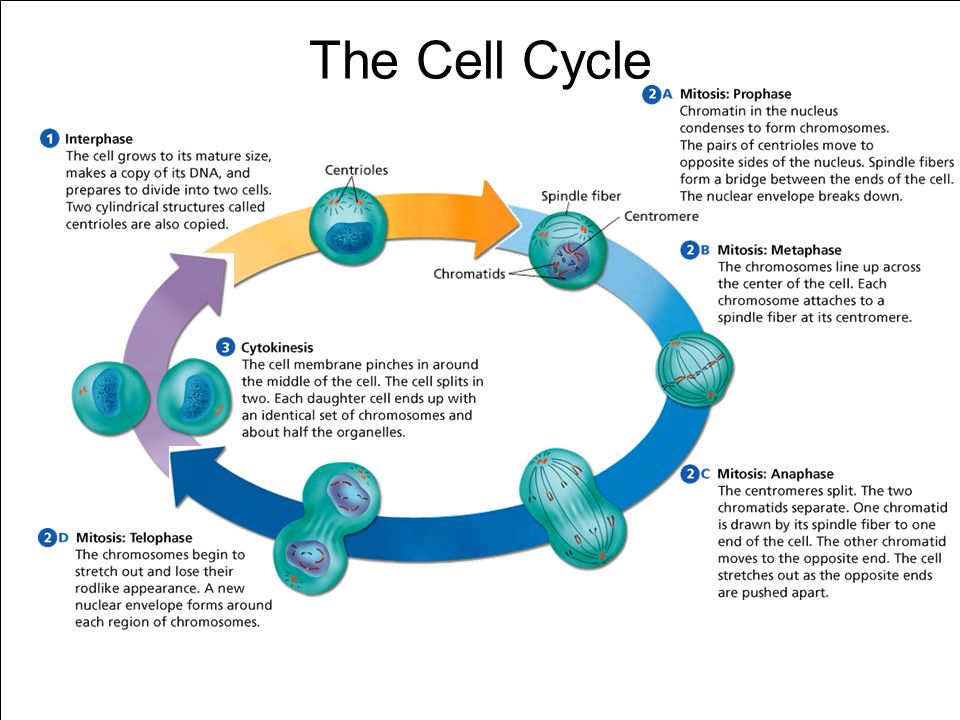
Drawing Of The Cell Cycle - Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. The interphase part of the life cycle of a cell. There are a number of checkpoints, but the three most important ones are: The g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Web cell cycle checkpoints a checkpoint is a stage in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the cell examines internal and external cues and decides whether or not to move forward with division. Interphase is the longest part of the cell cycle. Web cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produces two identical (clone) cells. And as we'll see, interphase is where a cell spends most of its life. The cell cycle has two major phases: Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Cell division is responsible for a newborn baby gradually growing into an adult. Web cell cycle or cell division refers to the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its maturity and subsequent division. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase. The g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Web cell cycle, the ordered sequence of events that occur in a cell in preparation for cell division. During mitosis, chromosomes will align, separate, and move into new daughter cells. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called. The g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Interphase is the longest part of the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle is a set of steps cells go through to grow, replicate, divide, and start the process again. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. The g 2 checkpoint, at the g 2 Web cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produces two identical (clone) cells. Therefore, it can be called the life cycle of a cell. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components: Web 0:00. Web cell cycle checkpoints a checkpoint is a stage in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the cell examines internal and external cues and decides whether or not to move forward with division. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. This is when the cell grows and. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. Web cell cycle checkpoints a checkpoint is a stage in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the cell examines internal and external cues and decides whether or not to move forward with division. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed. These processes define the two major phases of the cell cycle. The interphase part of the life cycle of a cell. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. There are a number of checkpoints, but the three most important ones are: Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division. In this article, we will look at the different stages of this and what happens in each stage. This cell cycle is used by all eukaryotic cells to produce new cells. The role of mitosis in the cell cycle is to replicate the genetic material in an existing cell—known as the “parent cell”—and distribute that genetic material to two new. Mitosis is a process that occurs during the cell cycle. And as we'll see, interphase is where a cell spends most of its life. In addition, the process of cell growth where the cell absorbs nutrients and prepares for its cell division is also a part of the cell cycle. The interphase part of the life cycle of a cell.. Web the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: This process is vital for the growth, development, repair, and maintenance of living organisms. Therefore, it can be called the life cycle of a cell. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. There are a number of checkpoints,. Web a cell cycle is thus a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides to produce new cells. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. This cell cycle is used by all eukaryotic cells to produce new cells. These processes define the two major phases of the cell cycle. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. Web cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produces two identical (clone) cells. Web the most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies precisely into two genetically identical daughter cells. The cell cycle is a series of events that cells go through to grow, replicate their dna, and divide. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Web cell cycle checkpoints a checkpoint is a stage in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the cell examines internal and external cues and decides whether or not to move forward with division. Interphase is the longest part of the cell cycle. The g 2 checkpoint, at the g 2 The great majority of the cell divisions that happen in your body involve mitosis. Cell division is responsible for a newborn baby gradually growing into an adult. Web the cell cycle is a continuous process that includes all significant events of the cell, ranging from duplication of dna and cell organelles to subsequent partitioning of the cytoplasm. Interphase and mitosis (or the mitotic (m) phase).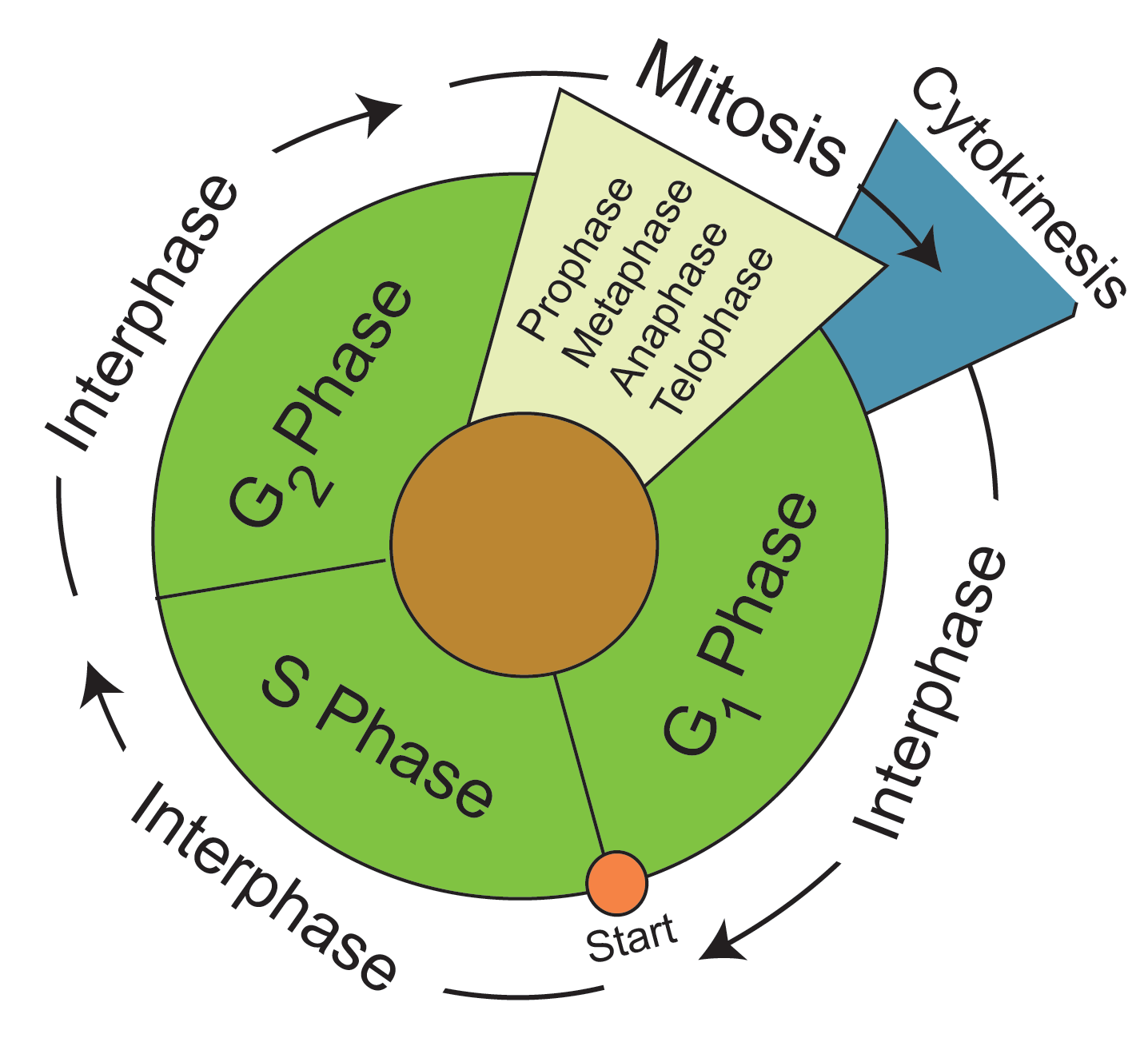
Cell Cycle Phases , Diagram , Types and Comparison
Phases of Cell Cycle01 Leverage Edu

The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology

Cell cycle labelling. Schematic representation of the cell cycle and

The Cell Cycle Interphase & Mitosis ALevel Biology Revision Notes
Phases of Cell cycle Online Biology Notes
Cell Cycle Drawing at GetDrawings Free download

Cell Division An Intro AmoebaMike
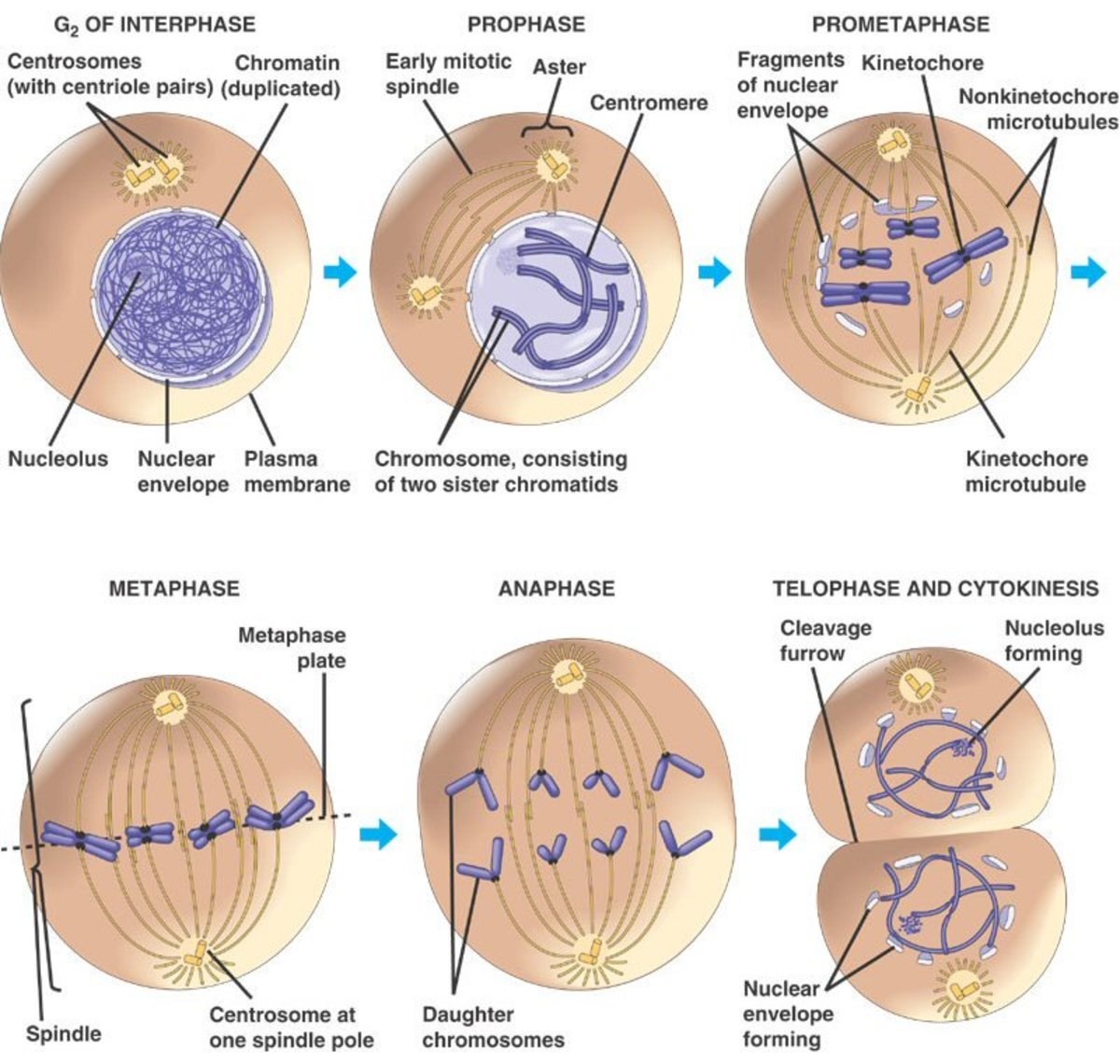
Stages of the Cell Cycle Mitosis (Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase
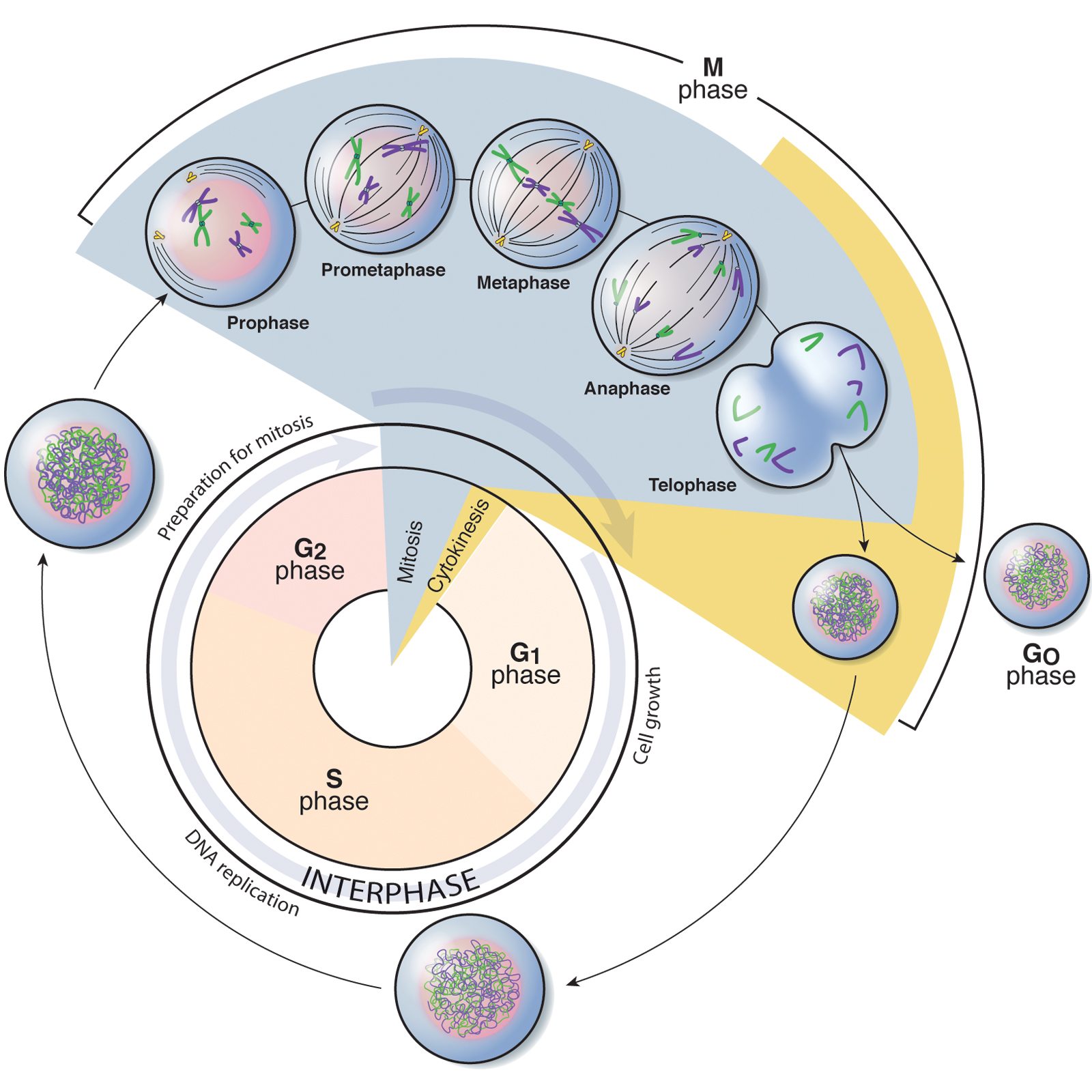
Phases of the cell cycle Battista Illustration
Cells On The Path To Cell Division Proceed Through A Series Of Precisely Timed And Carefully Regulated Stages.
These Events Include Duplication Of Its Genome And Synthesis Of The Cell Organelles Followed By Division Of The Cytoplasm.
Interphase And The Mitotic (M) Phase.
Cells On The Path To Cell Division Proceed Through A Series Of Precisely Timed And Carefully Regulated Stages.
Related Post: